Abstract
Purpose
Ablation index (AI) is a radiofrequency lesion quality marker. The AI value that allows effective and safe pulmonary vein isolation (PVI) is still debated. We evaluated the incidence of acute and late PV reconnection (PVR) with different AI settings and its predictors.
Methods
The Ablation Index Registry is a multicenter study that included patients with paroxysmal/persistent atrial fibrillation (AF) who underwent first-time ablation. Each operator performed the ablation using his preferred ablation catheter (ThermoCool® SmartTouch or Surround Flow) and AI setting (380 posterior-500 anterior and 330 posterior-450 anterior). We divided the study population into two groups according to the AI setting used: group 1 (330–450) and group 2 (380–500). Incidence of acute PVR was validated within 30 min after PVI, whereas the incidence of late PVR was evaluated at repeat procedure.
Results
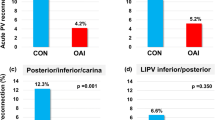
Overall, 490 patients were divided into groups 1 (258) and 2 (232). There was no significant difference in the procedural time, fluoroscopy time, and rate of the first-pass PVI between the two study groups. Acute PVR was observed in 5.6% PVs. The rate of acute PVR was slightly higher in group 2 (64/943, 6.8%, PVs) than in group 1 (48/1045, 4.6% PVs, p = 0.04). Thirty patients (6%) underwent a repeat procedure and late PVR was observed in 57/116 (49%) PVs (number of reconnected PV per patient of 1.9 ± 1.6). A similar rate of late PVR was found in the two study groups. No predictors of acute and late PVR were found.
Conclusion
Ablation with a lower range of AI is highly effective and is not associated with a higher rate of acute and late PVR. No predictors of PV reconnection were found.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Taghij P, El Haddad M, Philips T, Wolf M, Knecht S, Vandekerckhove Y, et al. Evaluation of a strategy aiming to enclose the pulmonary vein with contiguous and optimized radiofrequency lesion in paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. JACC Clin Electrophysiol. 2018;4:99–108.
Hussein A, Das M, Chaturvedi V, Asfour IK, Daryanani N, Morgan M, et al. Prospective use of ablation index targets improves clinical outcomes following ablation for atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2017;28:1037–47.
Solimene F, Schillaci V, Shopova G, Urraro F, Arestia A, Iuliano A, et al. Safety and efficacy of atrial fibrillation ablation guided by ablation index module. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2019;54:9–15.
Dhillon G, Ahsan S, Honarbakhsh S, Lim W, Baca M, Graham A, et al. A multicentered evaluation of ablation at higher power guided by ablation index: establishing ablation targets for pulmonary vein isolation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2019;30:357–65.
Stabile G, Lepillier A, De Ruvo E, Scaglione M, Anselmino M, Sebag F, et al. Reproducibility of pulmonary vein isolation guided by the ablation index: 1-year outcome of the AIR registry. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2020;31:1694–701.
Duytschaever M, Vijgen J, De Potter T, Scherr D, Van Herendael H, Knecht S, et al. Standardized pulmonary vein isolation workflow to enclose veins with contiguous lesions: the multicentre VISTAX trial. Europace. 2020;euaa157.
Solimene F, Lepillier A, De Ruvo E, Scaglione M, Anselmino M, Sebag FA, et al. Reproducibility of acute pulmonary vein isolation guided by the ablation index. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2019;42:874–81. https://doi.org/10.1111/pace.13710.
Das M, Loveday JJ, Wynn GJ, Gomes S, Saeed Y, Bonnett LJ, et al. Ablation index, a novel marker of ablation lesion quality: prediction of pulmonary vein reconnection at repeat electrophysiology study and regional differences in target values. Europace. 2017;19:775–83.
Stabile G, Di Donna P, Schillaci V, Di Monaco A, Iuliano A, Caponi D, et al. Safety and efficacy of pulmonary vein isolation using a surround flow catheter with contact force measurement capabilities: a multicenter registry. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2017;28:762–7.
Park CI, Lehrmann H, Keyl C, Schiebeling J, Allgeier J, Schurr P, et al. Mechanisms of Pulmonary Vein Reconnection After Radiofrequency Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation: The Deterministic Role of Contact Force and Interlesion Distance. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology. 2014;25(7):701–8.
Ullah W, Hunter RJ, Finlay MC, McLean A, Dhinoja MB, Sporton S, et al. Ablation index and surround flow catheter irrigation impedance-based appraisal in clinical ablation. J Am Coll Cardiol EP. 2017;3:1080–8.
El Haddad M, Taghji P, Phlips T, Wolf M, Demolder A, Choudhury R, et al. Determinants of acute and late pulmonary vein reconnection in contact force-guided pulmonary vein isolation: identifying the weakest link in the ablation chain. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2017;10(4):e004867. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCEP.116.004867.
Lee SR, Choi EK, Lee EJ, Choe WS, Cha MJ, Oh S. Efficacy of the optimal ablation index-targeted strategy for pulmonary vein isolation in patients with atrial fibrillation: the OPTIMUM study results. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2019;55:171–81. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-019-00565-4.
Calkins H, Hindricks G, Cappato R, Kim YH, Saad EB, Aguinaga L, et al. 2017 HRS/EHRA/ECAS/APHRS/SOLAECE expert consensus statement on catheter and surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm. 2017;14:e275–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrthm.2017.05.012.
Hocini M, Sanders P, Jaïs P, Weerasoriya R, Scavée C, Takahashi Y, et al. Prevalence of pulmonary vein disconnection after anatomical ablation for atrial fibrillation: consequences of wide atrial encircling of the pulmonary veins. Eur Heart J. 2005;26:696–704.
Phlips T, Taghji P, El Haddad M, Wolf M, Knecht S, Vandekerckhove Y, et al. Improving procedural and one-year outcome after contact force-guided pulmonary vein isolation: the role of interlesion distance, ablation index, and contact force variability in the ‘CLOSE’-protocol. Europace. 2018;20(FI_3):f419–27. https://doi.org/10.1093/europace/eux376.
De Pooter J, Strisciuglio T, El Haddad M, Wolf M, Phlips T, Vandekerckhove Y, et al. Pulmonary vein reconnection no longer occurs in the majority of patients after a single pulmonary vein isolation procedure. JACC Clin Electrophysiol. 2019;5(3):295–305.
Arentz T, Macle L, Kalusche D, Hocini M, Jais P, Shah D, et al. Dormant pulmonary vein conduction revealed by adenosine after ostial radiofrequency catheter ablation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2004;15:1041–7.
Chen C, Li D, Ho J, Liu T, Li X, Wang Z, et al. Clinical implications of unmasking dormant conduction after circumferential pulmonary vein isolation in atrial fibrillation using adenosine: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Physiol. 2019;9:1861.
Rajappan K, Kistler PM, Earley MJ, Thomas G, Izquierdo M, Sporton SC, et al. Acute and chronic pulmonary vein reconnection after atrial fibrillation ablation: a prospective characterization of anatomical sites. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2008;31:1598–605.
Higashiya S, Yamaji H, Murakami T, Hina K, Kawamura H, Murakami M, et al. Adjunctive interpulmonary isthmus ablation has no added effects on atrial fibrillation recurrence. Open Heart. 2017;4:e000593.
Hoffmann P, Ramirez ID, Baldenhofer G, Stangl K, Mont L, Althoff TF. Randomized study defining the optimum target interlesion distance in ablation index-guided atrial fibrillation ablation. Europace. 2020;22:1480–6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Concept/design: Solimene F., Lepillier A., Anselmino M., Bertaglia E., Stabile G.
Data analysis/interpretation: Solimene F., Lepillier A., De Ruvo E., Scaglione M., Anselmino M., Sebag F.A., Pecora D., Gallagher M.M., Rillo M., Viola G., Pisanò E., Abbey S., Lamberti F., Pani A., Zucchelli G., Sgarito G., De Simone A., Bertaglia E., Strisciuglio T., Stabile G.
Drafting article: Solimene F., Lepillier A., Anselmino M., Gallagher M.M., Rillo M., Viola G., De Santis V., Landolina M., De Simone A., Bertaglia E., Strisciuglio T., Stabile G.
Critical revision of article: Solimene F., Lepillier A., De Ruvo E., Scaglione M., Anselmino M., Sebag F.A., Pecora D., Gallagher M.M., Rillo M., Viola G., Pisanò E., Abbey S., Lamberti F., Pani A., Zucchelli G., Sgarito G., De Simone A., Bertaglia E., Strisciuglio T., Stabile G.
Approval of article: Solimene F., Lepillier A., De Ruvo E., Scaglione M., Anselmino M., Sebag F.A., Pecora D., Gallagher M.M., Rillo M., Viola G., Pisanò E., Abbey S., Lamberti F., Pani A., Zucchelli G., Sgarito G., De Simone A., Bertaglia E., Strisciuglio T., Stabile G.
Statistics: Bertaglia E., Strisciuglio T., Stabile G.
Data collection: Solimene F., Lepillier A., De Ruvo E., Scaglione M., Anselmino M., Sebag F.A., Pecora D., Gallagher M.M., Rillo M., Viola G., Pisanò E., Abbey S., Lamberti F., Pani A., Zucchelli G., Sgarito G., De Simone A., Bertaglia E., Strisciuglio T., Stabile G.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare no competing interest.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
As this is a multicenter study, the ethical committee of each center approved the study. Before inclusion in the study, every patient signed the informed consent.
Consent for publication
All authors consent to the publication of the manuscript in JICE.
Code availability
NA.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lepillier, A., Strisciuglio, T., De Ruvo, E. et al. Impact of ablation index settings on pulmonary vein reconnection. J Interv Card Electrophysiol 63, 133–142 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-021-00944-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-021-00944-w