Abstract
Background
Fibro-inflammatory processes in the extracellular matrix are closely associated with progressive structural remodeling in atrial fibrillation (AF). Serum concentrations of tenascin-C (TNC), an extracellular matrix glycoprotein, and of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (CRP) might serve as a marker of remodeling and progressive inflammation of the aorta and in myocardial diseases. This study aimed to clarify relationships between TNC and CRP in patients with AF.
Methods
This study included 38 patients with AF and five controls without left ventricular dysfunction who underwent catheter ablation. Blood was collected immediately before ablation from the left atrium (LA), right atrium (RA), and femoral artery (FA), and left and right atrial pressure was measured. Levels of TNC in the LA (TNC-LA), RA (TNC-RA), and FA (TNC-FA) and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (CRP) were measured. Atrial size was also determined by echocardiography.
Results
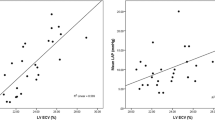
Levels of TNC corrected by atrial size were maximal in the LA, followed by the RA (3.69 ± 0.32 and 2.87 ± 0.38 ng/mL/cm, respectively). Mean transverse diameter corrected by body surface area was larger and mean atrial pressure was greater in the LA than the RA. A relationship was found between CRP from the femoral vein and TNC-LA and TNC-RA, but not TNC-FA. None of TNC-LA, TNC-RA, or TNC-FA correlated with ANP or BNP in the femoral vein.
Conclusions
Intracardiac (atrial) TNC expression plays an important role in the development of remodeling processes in the atrium with AF. Tenascin-C from the LA and RA (but not TNC, ANP, and BNP from FA) might serve as novel markers of these processes.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kirchhof P, Benussi S, Kotecha D, Ahlsson A, Atar D, Casadei B, et al. ESC guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with EACTS. Eur Heart J. 2016;37:2893–962.
Kaireviciute D, Lip GY, Balakrishnan B, Uzdavinys G, Norkunas G, Kalinauskas G, et al. Intracardiac expression of markers of endothelial damage/dysfunction, inflammation, thrombosis, and tissue remodeling, and the development of postoperative atrial fibrillation. J Thromb Haemost. 2011;9:2345–52.
Kimura T, Yoshimura K, Aoki H, Imanaka-Yoshida K, Yoshida T, Ikeda Y, et al. Tenascin-C is expressed in abdominal aortic aneurysm tissue with an active degradation process. Pathol Int. 2011;61:559–64.
Franz M, Berndt A, Grün K, Kuethe F, Fritzenwanger M, Figulla HR, et al. Serum levels of tenascin-C variants in congestive heart failure patients: comparative analysis of ischemic, dilated, and hypertensive cardiomyopathy. Clin Lab. 2014;60:1007–13.
Sato A, Hiroe M, Akiyama D, Hikita H, Nozato T, Hoshi T, et al. Prognostic value of serum tenascin-C levels on long-term outcome after acute myocardial infarction. J Card Fail. 2012;18:480–6.
Sakamoto N, Hoshino Y, Misaka T, Mizukami H, Suzuki S, Sugimoto K, et al. Serum tenascin-C level is associated with coronary plaque rupture in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Heart Vessel. 2014;29:165–70.
Franz M, Berndt A, Neri D, Galler K, Grün K, Porrmann C, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-9, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1,B+ tenascin-C and ED-A+ fibronectin in dilated cardiomyopathy: Potential impact on disease progression and patients’ prognosis. Int J Cardiol. 2013;168:5344–51.
Imanaka-Yoshida K, Aoki H. Tenascin-C and mechanotransduction in the development and diseases of cardiovascular system. Front Physiol. 2014;5:283.
Imanaka-Yoshida K, Yoshida T, Miyagawa-Tomita S. Tenascin-C in development and disease of blood vessels. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2014;297:1747–57.
Segers VFM, Brutsaert DL, De Keulenaer GW. Cardiac remodeling: endothelial cells have more to say than just NO. Front Physiol. 2018;9:382.
Nattel S, Harada M. Atrial remodeling and atrial fibrillation: recent advances and translational perspectives. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;63:2335–45.
Andrade J, Khairy P, Dobrev D, Nattel S. The clinical profile and pathophysiology of atrial fibrillation: relationships among clinical features, epidemiology, and mechanisms. Circ Res. 2014;114:1453–68.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Ms. Hiromi Nishimura, Ms. Motoko Oku, Ms. Mari Kurata, and Ms. Yoshiko Kurose for providing excellent technical and secretarial assistance.
Funding
This study was partially supported by a Research Grant from the University of Fukui and a JSPS Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C) (Grant number JP16K09426).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shiomi, Y., Yokokawa, M., Uzui, H. et al. Serum tenascin-C levels in atrium predict atrial structural remodeling processes in patients with atrial fibrillation. J Interv Card Electrophysiol 59, 401–406 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-019-00670-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-019-00670-4