Abstract
Background
Zhang’s phenomenon (originally His electrogram alternans) is a new index of atrioventricular node dual pathway electrophysiology. This index has been described and validated in isolated hearts in vitro, but has not been recorded in vivo.
Methods
This study explored the feasibility of in vivo recording of Zhang’s phenomenon (His electrogram alternans) in six dogs with a custom-built bipolar electrode.
Results
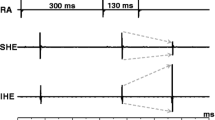
The His electrogram recorded from superior His bundle domain (superior His electrogram) was high in amplitude at basic beats and long coupling intervals (i.e., fast pathway conduction) and low amplitude at short prematurities (i.e., slow pathway conduction). In contrast, His electrogram recorded from the inferior His bundle domain (inferior His electrogram) was always from low amplitude during fast pathway conduction to high amplitude during slow pathway conduction. The characteristic His electrogram alternans had been recorded in vivo in all six animals.
Conclusions
This study provided the first data representing in vivo recording of Zhang’s phenomenon (His electrogram alternans) in large animals. Clinical studies are needed before this novel index can be applied in patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang, Y., Bharati, S., Mowrey, K. A., Zhuang, S., Tchou, P. J., & Mazgalev, T. N. (2001). His electrogram alternans reveal dual-wavefront inputs into and longitudinal dissociation within the bundle of His. Circulation, 104(7), 832–838.
Zhang, Y., Bharati, S., Mowrey, K. A., & Mazgalev, T. N. (2003). His electrogram alternans reveal dual atrioventricular nodal pathway conduction during atrial fibrillation: the role of slow-pathway modification. Circulation, 107(7), 1059–1065.
Zhang, Y., Bharati, S., Sulayman, R., Mowrey, K. A., Tchou, P. J., & Mazgalev, T. N. (2004). Atrioventricular nodal fast pathway modification: mechanism for lack of ventricular rate slowing in atrial fibrillation. Cardiovascular Research, 61(1), 45–55.
Zhang, Y., & Mazgalev, T. N. (2011). AV nodal dual pathway electrophysiology and Wenckebach periodicity. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 22(11), 1256–1262.
Zhang, Y., & Mazgalev, T. N. (2012). Atrioventricular node functional remodeling induced by atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm, 9(9), 1419–1425.
Zhang, Y. (2014). Transverse versus longitudinal electrical propagation within the atrioventricular node during dual pathway conduction: basis of dual pathway electrophysiology and His electrogram alternans (Zhang’s phenomenon). International Journal of Cardiology, 171(2), 259–264.
Hucker, W. J., Sharma, V., Nikolski, V. P., & Efimov, I. R. (2007). Atrioventricular conduction with and without AV nodal delay: two pathways to the bundle of His in the rabbit heart. American Journal of Physiology, 293(2), H1122–H1130.
Hucker, W. J., Fedorov, V. V., Foyil, K. V., Moazami, N., & Efimov, I. R. (2008). Images in cardiovascular medicine. Optical mapping of the human atrioventricular junction. Circulation, 117(11), 1474–1477.
Zhang, Y., Mowrey, K. A., Zhuang, S., Wallick, D. W., Popovic, Z. B., & Mazgalev, T. N. (2002). Optimal ventricular rate slowing during atrial fibrillation by feedback AV nodal-selective vagal stimulation. American Journal of Physiology, 282(3), H1102–H1110.
Mendez, C., & Moe, G. K. (1966). Demonstration of a dual A-V nodal conduction system in the isolated rabbit heart. Circulation Research, 19(2), 378–393.
Jackman, W. M., Beckman, K. J., McClelland, J. H., Wang, X., Friday, K. J., Roman, C. A., et al. (1992). Treatment of supraventricular tachycardia due to atrioventricular nodal reentry by radiofrequency catheter ablation of slow-pathway conduction. New England Journal of Medicine, 327(5), 313–318.
Mitrani, R. D., Klein, L. S., Hackett, F. K., Zipes, D. P., & Miles, W. M. (1993). Radiofrequency ablation for atrioventricular node reentrant tachycardia: comparison between fast (anterior) and slow (posterior) pathway ablation. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 21(2), 432–441.
Leitch, J., Klein, G. J., Yee, R., & Murdock, C. (1990). Invasive electrophysiologic evaluation of patients with supraventricular tachycardia. Cardiology Clinics, 8(3), 465–477.
Sheahan, R. G., Klein, G. J., Yee, R., Le Feuvre, C. A., & Krahn, A. D. (1996). Atrioventricular node reentry with ‘smooth’ AV node function curves: a different arrhythmia substrate? Circulation, 93(5), 969–972.
Kuo, C. T., Lin, K. H., Cheng, N. J., Chu, P. H., Hsu, T. S., Chiang, C. W., et al. (1999). Characterization of atrioventricular nodal reentry with continuous atrioventricular node conduction curve by double atrial extrastimulation. Circulation, 99(5), 659–665.
Maury, P., Raczka, F., Piot, C., & Davy, J. M. (2002). QRS and cycle length alternans during paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia: what is the mechanism? Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 13(1), 92–93.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y. In vivo recording of Zhang’s phenomenon (His electrogram alternans): a novel index of atrioventricular node dual pathway conduction. J Interv Card Electrophysiol 40, 99–103 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-014-9905-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-014-9905-z