Abstract
Introduction
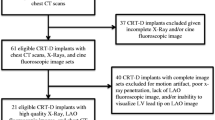
Lead insulation defects with externalization of the conductors exist in Riata defibrillator leads. Cinefluoroscopy is currently the gold standard to detect such defects. Prospective evaluation of alternative screening options such as chest radiography (CXR), which has been recommended by the FDA, is not well described.
Methods and results
Patients with Riata leads underwent cinefluoroscopy, CXR, and device interrogation. Leads were classified as abnormal (clear cable separation), borderline, or normal by independent evaluation of cinefluoroscopy and CXR. CXR evaluation was done in two ways as follows: (1) routine CXR read by daily staff radiologists for lead screening and (2) CXR evaluation by a radiologist educated about the lead defect. One hundred two patients were evaluated at our institution. Cinefluoroscopy showed externalized conductors in 33 patients (32 %). Twenty-five of 33 patients (76 %) who had abnormal cinefluoroscopic findings had abnormal CXR findings on blinded review by the educated radiologist. All 25 patients with abnormal CXR had abnormal findings on cinefluoroscopy. Daily staff radiologists without direct education other than prompts for lead screening detected CXR abnormalities in only 8 out of 102 (8 %) cases.
Conclusion
Cinefluoroscopy appears to be more sensitive than CXR for the detection of Riata cable extrusion. Interpretation of CXR by a radiologist with education in lead defects correlates highly with cinefluoroscopy with very high specificity. Depending on available resources for screening, CXR may be a reasonable alternative to cinefluoroscopy. Multidisciplinary collaboration across specialties (radiology and electrophysiology) can lead to improved diagnostic capability and thus the potential for enhanced quality of care.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Duray, G. Z., Israel, C. W., Schmitt, J., & Hohnloser, S. H. (2008). Implantable cardioverter–defibrillator lead disintegration at the level of the tricuspid valve. Heart Rhythm, 5(8), 1224–1225.
Jalal, Z., Derval, N., Ploux, S., & Bordachar, P. (2010). Unusual failure of a multilumen, small-diameter implantable cardioverter-defibrillator lead. Heart Rhythm, 7(8), 1166–1167.
Richards, M. W., Warren, C. E., & Anderson, M. H. (2010). Late failure of a single-coil transvenous implantable cardioverter–defibrillator lead associated with conductor separation. Europace, 12(8), 1191–1192.
Valk, S. D., Theuns, D. A., & Jordaens, L. (2013). Long-term performance of the St Jude Riata 1580–1582 ICD lead family. Neth Heart J, 21(3), 127–134.
Chan, C. W., & Chiang, C. S. (2012). An ICD lead with failure of outer insulation goes undetected by regular measurements. Pacing and Clinical Electrophysiology, 35(9), e261–262.
Erkapic, D., Duray, G. Z., Bauernfeind, T., De Rosa, S., & Hohnloser, S. H. (2011). Insulation defects of thin high-voltage ICD leads: an underestimated problem? Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 22(9), 1018–1022.
Krebsbach, A., Alhumaid, F., Henrikson, C. A., Calkins, H., Berger, R. D., & Cheng, A. (2011). Premature failure of a Riata defibrillator lead without impedance change or inappropriate sensing: a case report and review of the literature. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 22(9), 1070–1072.
Porterfield, J. G., Porterfield, L. M., Kuck, K. H., Corbisiero, R., Greenberg, S. M., Hindricks, G., et al. (2010). Clinical performance of the St. Jude Medical Riata defibrillation lead in a large patient population. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 21(5), 551–556.
Schmutz, M., Delacrétaz, E., Schwick, N., Roten, L., Fuhrer, J., Boesch, C., et al. (2012). Prevalence of asymptomatic and electrically undetectable intracardiac inside-out abrasion in silicon-coated Riata® and Riata® ST implantable cardioverter-defibrillator leads. International Journal of Cardiology.
Shen, S., Bhave, P., Giedrimas, E., Patel, T., Arora, R., Chicos, A. B., et al. (2012). Prevalence and predictors of cable extrusion and loss of electrical integrity with the Riata defibrillator lead. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 23(11), 1207–1212.
Liu, J., Rattan, R., Adelstein, E., Barrington, W., Bazaz, R., Brode, S., et al. (2012). Fluoroscopic screening of asymptomatic patients implanted with the recalled Riata lead family. Circulation. Arrhythmia and Electrophysiology, 5(4), 809–814.
Parvathaneni, S. V., Ellis, C. R., & Rottman, J. N. (2012). High prevalence of insulation failure with externalized cables in St. Jude Medical Riata family ICD leads: fluoroscopic grading scale and correlation to extracted leads. Heart Rhythm, 9(8), 1218–1224.
Larsen, J. M., Riahi, S., Nielsen, J. C., Videbaek, R., Haarbo, J., Due, K. M., et al. (2013). Nationwide fluoroscopic screening of recalled Riata defibrillator leads in Denmark. Heart Rhythm.
Cronin, E. M., Baranowski, B. J., & Martin, D. O. (2012). Failure of fluoroscopy to detect “inside-out” insulation failure and externalized conductors in a Riata ICD lead. Heart Rhythm.
Steinberg, C., Sarrazin, J. F., Philippon, F., Bouchard, M. A., O’Hara, G., Molin, F., et al. (2013). Detection of high incidence of Riata lead breaches by systematic posteroanterior and lateral chest X-ray in a large cohort. Europace, 15(3), 402–408.
Pachon, M., Arias, M. A., Nadal, R., & Jimenez-Lopez, J. (2013). Standard x-ray is inadequate for the identification of conductor cable externalization in Riata leads. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 24(4), 471.
The authors would like to thank the cardiac electrophysiology fellowship educational program support from Medtronic, Boston Scientific, and Biotronik.
Conflict of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lorvidhaya, P., Mendoza, I., Sehli, S. et al. Prospective evaluation of cinefluoroscopy and chest radiography for Riata lead defects: implications for future lead screening. J Interv Card Electrophysiol 38, 131–135 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-013-9822-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-013-9822-6