Abstract
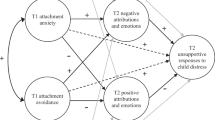
Previous research has demonstrated the importance of maternal attachment style to children’s well-being, but the mediators of this relationship are understudied. Parental affect is one potential mediator. Previous research has documented the relationship between parental attachment and parental affect, and between parental affect and parental behaviors, but maternal affect has not yet been established as a mechanism through which attachment influences parenting behaviors. We hypothesized that parental affect would mediate the relationship between parental attachment and parental behaviors in mothers. A community-based sample of 132 mothers of at least one child between the ages of 2 and 12 completed questionnaires on maternal attachment, maternal affect, and parenting behaviors. Confirming previous research, significant relationships were found between maternal attachment and affect, maternal attachment and parenting behaviors, and maternal affect and parenting behaviors. As predicted, maternal affect mediated the relationship between maternal attachment style and parenting behavior. Specifically, positive affect mediated the relationship between maternal attachment and nurturance, secure base, safe haven, and companionship parenting behaviors. Negative affect mediated the relationship between maternal attachment and nurturance. Implications include acknowledging differential roles of positive and negative affect in their influence on parental behaviors.
Highlights
-
Maternal affect may mediate the relation between parental attachment and parenting behaviors.
-
Positive affect and negative affect differ in terms of how they influence the relation between parental attachment and parenting behaviors.
-
Established relations between negative affect and parental behaviors in clinical populations are similar to those in community samples.
-
The indirect relation between parental attachment and parenting behaviors via maternal affect is significant.
-
Positive affect is also related to parental behaviors in a community sample.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adam, E. K., Gunnar, M. R., & Tanaka, A. (2004). Adult attachment, parent emotion, and observed parenting behavior: Mediator and moderator models. Child Development, 75(1), 110–122. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8624.2004.00657.
Alford, D. J., Lyddon, W. J., & Schreiber, R. (2006). Adult attachment and working models of emotion. Counselling Psychology Quarterly, 19(1), 45–56. https://doi.org/10.1080/09515070600673687.
Arellano, P. A. E., Harvey, E. A., & Thakar, D. A. (2012). A longitudinal study of the relation between depressive symptomatology and parenting practices. Family Relations: An Interdisciplinary Journal of Applied Family Studies, 61(2), 271–282. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1741-3729.2011.00694.
Ata, S., & Yağan Güder, S. (2020). Parents’ attachment to their children and their level of interest in them in predicting children’s self-concepts. Early Child Development and Care, 190(2), 161–174. https://doi.org/10.1080/03004430.2018.1461092.
Aviezer, O., Sagi, A., Joels, T., & Ziv, Y. (1999). Emotional availability and attachment representations in kibbutz infants and their mothers. Developmental Psychology, 35(3), 811–821. https://doi.org/10.1037/0012-1649.35.3.811.
Baron, R. M., & Kenny, D. A. (1986). The moderator–mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 51(6), 1173–1182. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.51.6.1173.
Baumrind, D. (1971). Current patterns of parental authority. Developmental Psychology, 4(1, Pt.2), 1–103. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0030372.
Bowlby, J. (1982). Attachment and loss. Basic Books.
Brennan, K. A., Clark, C. L., & Shaver, P. R. (1998). Self-report measurement of adult attachment: An integrative overview. In J. A. Simpson & W. S. Rholes (Eds.), Attachment theory and close relationships (pp. 46–76). The Guilford Press.
Cameron, J. J., Finnegan, H., & Morry, M. M. (2012). Orthogonal dreams in an oblique world: A meta-analysis of the association between attachment anxiety and avoidance. Journal of Research in Personality, 46(5), 472–476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrp.2012.05.001.
Cohn, D. A., Cowan, P. A., Cowan, C. P., & Pearson, J. (1992). Mothers’ and fathers’ working models of childhood attachment relationships, parenting styles, and child behavior. Development and Psychopathology, 4(3), 417–431. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0954579400000870.
Cooke, J. E., Kochendorfer, L. B., Stuart-Parrigon, K. L., Koehn, A. J., & Kerns, K. A. (2019). Parent–child attachment and children’s experience and regulation of emotion: A meta-analytic review. Emotion, 19(6), 1103–1126. https://doi.org/10.1037/emo0000504.
Crowell, J. A., & Feldman, S. S. (1988). Mothers’ internal models of relationships and children’s behavioral and developmental status: A study of mother-child interaction. Child Development, 59(5), 1273–1285. https://doi.org/10.2307/1130490.
Crowell, J. A., & Feldman, S. S. (1991). Mothers’ working models of attachment relationships and mother and child behavior during separation and reunion. Developmental Psychology, 27(4), 597–605. https://doi.org/10.1037/0012-1649.27.4.597.
Crowell, J. A., O’Connor, E., Wollmers, G., Sprafkin, J., & Rao, U. (1991). Mothers’ conceptualizations of parent-child relationships: Relation to mother-child interaction and child behavior problems. Development and Psychopathology, 3(4), 431–444. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0954579400007616.
Cummings, E. M., Keller, P. S., & Davies, P. T. (2005). Towards a family process model of maternal and paternal depressive symptoms: Exploring multiple relations with child and family functioning. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 46(5), 479–489. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7610.2004.00368.
Downey, G., & Coyne, J. C. (1990). Children of depressed parents: An integrative review. Psychological Bulletin, 108(1), 50–76. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.108.1.50.
Edelstein, R. S., Alexander, K. W., Shaver, P. R., Schaaf, J. M., Quas, J. A., Lovas, G. S., & Goodman, G. S. (2004). Adult attachment style and parental responsiveness during a stressful event. Attachment & Human Development, 6(1), 31–52. https://doi.org/10.1080/146167303100001659584.
Elgar, F. J., Mills, R. S. L., McGrath, P. J., Waschbusch, D. A., & Brownridge, D. A. (2007). Maternal and paternal depressive symptoms and child maladjustment: The mediating role of parental behavior. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 35(6), 943–955. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-007-9145-0.
Fairchild, A. J., & Finney, S. J. (2006). Investigating validity evidence for the Experiences in Close Relationships-Revised Questionnaire. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 66(1), 116–135. https://doi.org/10.1177/0013164405278564.
Feng, X., Shaw, D. S., Kovacs, M., Lane, T., O’Rourke, E. F., & Alarcon, J. H. (2008). Emotion regulation in preschoolers: The roles of behavioral inhibition, maternal affective behavior, and maternal depression. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 49, 132–141. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7610.2007.01828.x.
Fiedler, K., Schott, M., & Meiser, T. (2011). What mediation analysis can (not) do. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 47, 1231–1236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jesp.2011.05.007.
Fraley, R. C., & Waller, N. G. (1998). Adult attachment patterns: A test of the typological model. In J. A. Simpson & W. S. Rholes (Eds.), Attachment theory and close relationships (pp. 77–114). Guilford Press.
Fraley, R. C., Waller, N. G., & Brennan, K. A. (2000). An item response theory analysis of self-report measures of adult attachment. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 78(2), 350–365. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.78.2.350.
Fredrickson, B. L. (2001). The role of positive emotions in positive psychology: The broaden-and-build theory of positive emotions. American Psychologist, 56(3), 218–226.
Gentzler, A. L., Ramsey, M. A., & Black, K. R. (2015). Mothers’ attachment styles and their children’s self-reported security, as related to maternal socialization of children’s positive affect regulation. Attachment & Human Development, 17(4), 376–398. https://doi.org/10.1080/14616734.2015.1055507.
Green, B. L., Furrer, C., & McAllister, C. (2007). How do relationships support parenting? Effects of attachment style and social support on parenting behavior in an at-risk population. American Journal of Community Psychology, 40(1–2), 96–108. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10464-007-9127-y.
Hayes, A. F. (2009). Beyond Baron and Kenny: Statistical mediation analysis in the new millennium. Communication Monographs, 76(4), 408–420. https://doi.org/10.1080/03637750903310360.
Jones, J. D., & Cassidy, J. (2014). Parental attachment style: Examination of links with parent secure base provision and adolescent secure base use. Attachment & Human Development, 16(5), 437–461. https://doi.org/10.1080/14616734.2014.921718.
Jones, J. D., Cassidy, J., & Shaver, P. R. (2015). Parents’ self-reported attachment styles: A review of links with parenting behaviors, emotions, and cognitions. Personality and Social Psychology Review, 19(1), 44–76. https://doi.org/10.1177/1088868314541858.
Jouriles, E. N., Murphy, C. M., & O’Leary, K. D. (1989). Effects of maternal mood on mother-son interaction patterns. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 17(5), 513–525. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00916510.
Kline, R. B. (1998). Principles and practice of structural equation modeling. Guilford Press.
Koehn, A. J., & Kerns, K. A. (2018). Parent-child attachment: Meta-analysis of associations with parenting behaviors in middle childhood and adolescence. Attachment & Human Development, 20(4), 378–405. https://doi.org/10.1080/14616734.2017.1408131.
Lovejoy, M. C., Graczyk, P. A., O’Hare, E., & Neuman, G. (2000). Maternal depression and parenting behavior: A meta-analytic review. Clinical Psychology Review, 20(5), 561–592. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0272-7358(98)00100-7.
Main, M., Kaplan, N., & Cassidy, J. (1985). Security in infancy childhood, and adulthood: A move to the representational level. In I. Bretherton & E. Waters (Eds.), Growing points of attachment theory and research (pp. 66–104). Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
Mikulincer, M. (1998). Adult attachment style and individual differences in functional versus dysfunctional experiences of anger. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 74(2), 513–524. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.74.2.513.
Molero, F., Shaver, P. R., Fernández, I., & Recio, P. (2017). Attachment insecurities, life satisfaction, and relationship satisfaction from a dyadic perspective: The role of positive and negative affect. European Journal of Social Psychology, 47(3), 337–347. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejsp.2276.
Moreira, H., & Canavarro, M. C. (2015). Individual and gender differences in mindful parenting: The role of attachment and caregiving representations. Personality and Individual Differences, 87, 13–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2015.07.021.
Perry, M. A., & Fantuzzo, J. W. (2010). A multivariate investigation of maternal risks and their relationship to low-income, preschool children’s competencies. Applied Developmental Science, 14, 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1080/10888690903510281.
Power, T. G. (2002). Parenting dimensions inventory (PDI—S): A research manual. Unpublished manuscript. Pullman, WA: Washington State University.
Rholes, W. S., Simpson, J. A., & Blakely, B. S. (1995). Adult attachment styles and mothers’ relationships with their young children. Personal Relationships, 2(1), 35–54. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1475-6811.1995.tb00076.x.
Roisman, G. I., Holland, A., Fortuna, K., Fraley, R. C., Clausell, E., & Clarke, A. (2007). The Adult Attachment Interview and self-reports of attachment style: An empirical rapprochement. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 92(4), 678–697. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.92.4.678.
Safyer, P., Volling, B. L., Schultheiss, O. C., & Tolman, R. M. (2019). Adult attachment, implicit motives, and mothers’ and fathers’ parenting behaviors. Motivation Science, 5(3), 220–234. https://doi.org/10.1037/mot0000112.
Sagui-Henson, S. J., Armstrong, L. M., Mitchell, A. D., Basquin, C. A., & Levens, S. M. (2020). The effects of parental emotion regulation ability on parenting self-efficacy and child diet. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 29(8), 2290–2302. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-020-01745-x.
Sebire, S. J., Jago, R., Wood, L., Thompson, J. L., Zahra, J., & Lawlor, D. A. (2016). Examining a conceptual model of parental nurturance, parenting practices and physical activity among 5-6 year olds. Social Science & Medicine, 148, 18–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2015.11.022.
Selcuk, E., Günaydin, G., Sumer, N., Harma, M., Salman, S., Hazan, C., Dogruyol, B., & Ozturk, A. (2010). Self-reported romantic attachment style predicts everyday maternal caregiving behavior at home. Journal of Research in Personality, 44(4), 544–549. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrp.2010.05.007.
Sibley, C. G., Fischer, R., & Liu, J. H. (2005). Reliability and validity of the Revised Experiences in Close Relationships (ECR-R) self-report measure of adult romantic attachment. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 31(11), 1524–1536. https://doi.org/10.1177/0146167205276865.
Siegel, D. J. (1999). The developing mind. Guilford Press.
Tabachnick, B. G., & Fidell, L. S. (2001). Using multivariatesStatistics (Fourth Ed.). Allyn & Bacon.
Tellegen, A. (1982). A brief manual for the Multidimensional Personality Questionnaire. University of Minnesota, Departmentmof Psychology.
Teti, D. M., Gelfand, D. M., Messinger, D. S., & Isabella, R. (1995). Maternal depression and the quality of early attachment: An examination of infants, preschoolers, and their mothers. Developmental Psychology, 31(3), 364–376. https://doi.org/10.1037/0012-1649.31.3.364.
Verschueren, K., Dossche, D., Marcoen, A., Mahieu, S., & Bakermans-Kranenburg, M. (2006). Attachment representations and discipline in mothers of young school children: An observation study. Social Development, 15(4), 659–675. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9507.2006.00363.
Waters, E., & Cummings, M. (2000). A secure base from which to explore close relationships. Child Development, 71, 164–172. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8624.00130.
Watson, D., Clark, L. A., & Tellegen, A. (1988). Development and validation of brief measures of positive and negative affect: The PANAS scales. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 54(6), 1063–1070. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.54.6.1063.
Whipple, N., Bernier, A., & Mageau, G. A. (2011). A dimensional approach to maternal attachment state of mind: Relations to maternal sensitivity and maternal autonomy support. Developmental Psychology, 47(2), 396–403. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0021310.
Wolf, E. J., Harrington, K. M., Clark, S. L., & Miller, M. W. (2013). Sample size requirements for structural equation models: An evaluation of power, bias, and solution propriety. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 76(6), 913–934. https://doi.org/10.1177/0013164413495237.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lindh, J.A., Tey, J., Hall, M.E.L. et al. Maternal Attachment and Maternal Behavior: The Role of Maternal Affect. J Child Fam Stud 32, 2004–2014 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-022-02437-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-022-02437-4