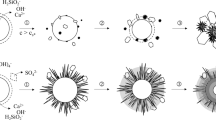
Cement-based materials sometimes encounter sulfate attack and ammonium salt environments during service, which can severely affect the long-term durability of these materials. In cement-based materials, the formation of thaumasite usually requires five conditions: sulfate, silicate, carbonate, and sufficient water and low temperature (<15°C). However, under other conditions, thaumasite can also form. To study the changing trend of thaumasite in an ammonium salt solution at ambient temperature (25°C), the formation process of thaumasite was studied by laser Raman spectroscopy and thermodynamic analysis. The reaction was accelerated in the presence of \( {\mathrm{NH}}_4^{+} \) ions at ambient temperature, and the presence of \( {\mathrm{SO}}_4^{2-} \) anions enhanced this trend; this enhancement was even greater than that at low temperature. The change in the Gibbs free energy of formation of thaumasite in the presence versus the absence of \( {\mathrm{NH}}_4^{+} \) ions was studied using thermodynamic methods, and the acceleration mechanism of the formation of thaumasite in the presence of \( {\mathrm{NH}}_4^{+} \) ions was explained.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Tang, X. Zuo, S. He, O. Ayinde, and G. Yin, Construct. Build. Mater., 129, 61–69 (2016).
X. Wang, Z. Pan, X. Shen, et al., Construct. Build. Mater., 124, 786–793 (2016).
X. Wang and Z. Pan, Construct. Build. Mater., 152, 434–443 (2017).
B. Zhang, F. Chen, X. Tian, et al., Research on Water Quality Variation of Seven Major Water Systems in China from 2005 to 2017, Yangtze River 2020, 51, No. 7, 33–39 (2020).
S. Miletic, M. Djuric, A. Mihajlov, et al., J. Serbian Chem. Soc., 74, No. 3, 331–347 (2009).
R. A. Edge and H. F. W. Taylor, Nature, 224 (5217), 363–364 (1969).
S. V. Goryainov, J. Raman Spectrosc., 47, No. 8, 984–992 (2016).
G. D. Gatta, G. J. McIntyre, J. G. Swanson, et al., Am. Mineral., 97, No. 7, 1060–1069 (2012).
M. Ardit, G. Cruciani, M. Dondi, et al., Mineralog. Mag., 78, No. 5, 1193–1208 (2014).
D. Deng, J. Xiao, Q. Yuan, et al., J. Build. Mater., 5, 532–541 (2005).
H. F. W. Taylor, Cement Chemistry, Lightning Source Inc. (1997).
W. Shen, Cement Technology, Hubei, Wuhan University of Technology Press (1991).
S. Mileti, M. Ili, S. Otovi, R. Foli, and Y. Ivanov, Construct. Build. Mater., 13, No. 3, 117–127 (1999).
S. Sahu, D. L. Exline, and M. P. Nelson, Cem. Concr. Compos., 24, No. 3, 347–350 (2002).
D. Deng, J. Xiao, Q. Yuan, et al., J. Build. Mater., 4, 400–409 (2005).
J. Xiao, Q. Meng, B. Ma, et al., J. Build. Mater., 18, No. 2, 263–268 (2015).
Y. Luo, S. Zhou, C. Wang, et al., Construct. Build. Mater., 229, Article ID 116865 (2019).
C. Li, S. Li, and Y. Bai, J. Build. Mater., 17, No. 3, 501–506 (2014).
K. Sotiriadis, E. Nikolopoulou, S. Tsivilis, et al., Construct. Build. Mater., 43, 156–164 (2013).
J. Xiao, Q. Meng, B. Ma, et al., J. Build. Mater., 18, No. 3, 369–374 (2015).
P. Atkins and J. de Paula, Physical Chemistry, New York, W. H. Freeman and Co. (2010).
T. Schmidt, B. Lothenbach, M. Romer, et al., Cem. Concr. Res., 38, No. 3, 337–349 (2008).
B. Lothenbach, T. Matschei, G. Möschner, and F. P. Glasser, Cem. Concr. Res., 38, No. 1, 1–18 (2008).
J. G. Speight, Lange's Handbook of Chemistry, McGraw-Hill Professional Publishing (2004).
A. Solonenko and V. V. Boksgorn, Russ. Chem. Bull., 66, No. 3, 439–446 (2017).
E. Thilo, Chin. Sci. Bull., 14, 429–431 (1957).
A. K. Katz, J. P. Glusker, S. A. Beebe, et al., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 118, No. 24, 5752–5763 (1996).
M. Kanzaki, Mineralog. J., 18, No. 1, 1–8 (1996).
T. An-Pang and K. Long, Acta Chim. Sin., 23, No. 2, 90–98 (1957).
Y. Xi, Chemical Structure, Bonding and Classification of Silicates, China Construction Industry Press (1989)
R. Chen, J. Wang, H. Liu, et al., Acta Chim. Sin., 11, 1084–1086 (1982).
R. K. Iler, The Chemistry of Silica-Solubility, Polymerization, Colloid and Surface Properties, and Biochemistry, New York, Wiley-Interscience Publication (1979).
F. Xiyi, Inorganic Chemistry Series, III, Beijing, Science Press (1988).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in Zhurnal Prikladnoi Spektroskopii, Vol. 89, No. 4, pp. 491–497, July–August, 2022.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Guo, S. & Li, Y. Formation of Thaumasite in Ammonium Salt Solution Based on Raman Spectroscopy and Thermodynamic Analysis. J Appl Spectrosc 89, 658–664 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10812-022-01407-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10812-022-01407-4