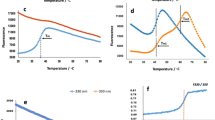
The reaction mechanism of cefonicid sodium with bovine serum albumin was investigated by traditional fluorescence spectroscopy and synchronous fluorescence spectroscopy. The results demonstrated that cefonicid sodium caused a strong fluorescence quenching of bovine serum albumin through a static quenching mechanism, during which the electrostatic force played the dominant role in this system, and the number of binding sites in the system was close to 1. It also showed that the primary binding site for cefonicid sodium was closer to tryptophan residues located in sub-hydrophobic domain IIA. Moreover, circular dichroism spectroscopy showed that the secondary structure of bovine serum albumin changed. The donor-to-acceptor distance r < 8 nm indicated that the static fluorescence quenching of bovine serum albumin was a nonradiation energy transfer process. The data obtained from Δλ = 60 nm and λex = 295 nm indicated that synchronous fluorescence spectroscopy had higher sensitivity and accuracy compared to traditional fluorescence spectroscopy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. D. Bani-Yaseen, J. Lumin., 131, No. 5, 1042–1047 (2011).
X. R. Li and Y. B. Hao, J. Mol. Struct., 1091, 109–117 (2015).
Y. F. Wei, X. H. Li, and D. M. Ma, Spect. Anal., 25, No. 4, 588–590 (2005).
H. M. Zhang, Y. Y. Wang, and Q. H. Zhou, J. Mol. Struct., 921, 156–162 (2009).
Q. Wang, S. R. Zhang, and X. H. Ji, Spectrochim. Acta A, 124, 84–90 (2014).
Y. P. Wang, G. W. Zhang, and L. H. Wang, Pestici. Biochem. Phys., 108, 66–73 (2014).
L. Z. Zhao, Y. S. Zhao, H. H. Teng, S. Y. Shi, and B. X. Ren, J. Appl. Spectrosc., 81, No. 4, 719–724 (2014).
L. Tang, S. Li, H. N. Bi, and X. Gao, Food Chem., 196, 550–559 (2016).
H. B. Shen, Z. Q. Gu, and K. Jian, J. Pharm. Biomed., 75, 86–93 (2013).
L. H. Zhang, B. S. Liu, and Z. Y. Li, Spectrosc. Lett., 48, 441–446 (2014).
S. Roy and T. K. Das, J. Appl. Spectrosc., 82, No. 4, 598–606 (2015).
Y. M. Yang, D. J. Li, and C. Xu, J. Mol. Struct., 1084, 229–235 (2015).
T. H. Wang, Z. M. Zhao, L. Zhang, and L. Ji, J. Mol .Struct., 937, Nos. 1–3, 65–69 (2009).
A. Naseri, S. Hosseini, and F. Rasoulzadeh, J. Lumin., 157, 104–112 (2015).
A. Sułkowska, M. Maciążek-Jurczyk, B. Bojko, J. Rownicka, I. Zubik-Skupien, E. Temba, D. Pentak, and W. W. Sulkowski, J. Mol. Struct., 881, Nos. 1–3, 97–106 (2008).
Z. X. Liao, X. Y. Yu, Q. Yao, and P. G. Yi, Spectrochim. Acta. A, 129, 314–319 (2014).
Y. Y. Hu, S. Q. Xu, and X. S. Zhu, Spectrochim. Acta. A, 74, No. 2, 526–531 (2009).
N. Ji, C. Qiu, X. J. Li, L. Xiong, and Q. J. Sun, Colloid Surf. B, 128, 594–599 (2015).
D. D. Chen, Q. Wu, J. Wang, Qi. Wang, and H. Qiao, Spectrochim. Acta A, 135, 511–520 (2015).
A. Iovescu, A. Băran, and G. Stîngă, J. Photochem. Photobiol. B, 1, No. 4, 198–205 (2015).
Y. Fan, Y. Li, H. Cai, J. Li, J. Miao, D. Fu, and Q. Yang, J. Appl. Spectrosc., 81, No. 5, 795–800 (2014).
H. X. Bai, C. Yang, and X. R. Yang, Front. Chem. China, 3, No. 1, 105–111 (2008).
N. Wang, L. Ye, F. F. Yan, and R. Xu, Int. J. Pharm., 351, Nos. 1–2, 55–60 (2008).
G. Siligardi, R. Hussain, and S. G. Patching, BBA Biomembranes, 1838, 34–42 (2014).
S. Tabassum, W. M. Al-Asbahy, M. Afzal, and F. Arjmand, J. Photochem. Photobiol. B, 114, 132–139 (2012).
N. Keswani and N. Kishore, J. Chem. Thermodyn., 43, 1406–1413 (2011).
X.Y. Yu, B. F. Jiang, Z. X. Liao, Y. Jiao, and P. G. Yi, Spectrochim. Acta. A, 149, 116–121 (2015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in Zhurnal Prikladnoi Spektroskopii, Vol. 84, No. 3, pp. 410–418, May–June, 2017.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duan, ST., Liu, BS., Li, TT. et al. Study of the Interaction of Cefonicid Sodium with Bovine Serum Albumin by Fluorescence Spectroscopy. J Appl Spectrosc 84, 431–438 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10812-017-0488-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10812-017-0488-1