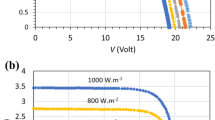
This paper presents the dynamic characteristic of a tandem silicon/amorphous silicon (a-Si:H/a-Si:H) photovoltaic (PV) module measured in the nonstationary regime. The current-voltage (I–V) characteristics of the PV module are generally measured by using a pulsed solar simulator. Distortions of the I–V curves can often be observed when measurements are done under the solar simulator with different pulse durations or different sweeping rates of the curve tracing, a direction of the curve tracing from short circuit to open circuit (SCOC), or from open circuit to short circuit (OCSC). In this paper, the measurements were made on the a-Si:H/a-Si:H tandem PV module consisting of 40 cells in series connection. The PV module area is 0.78 m2. Dissimilarities of the I–V curves of the PV modules can be observed by the deviation of power at maximum point (Pm) and fill factor (FF). From the experimental results, it is found that the largest deviation of Pm is 6.12% for 1 ms sweeping duration with OCSC direction of the curve tracing. Dissimilarities of the I–V curves can be explained by charging and discharging capacitive currents due to a voltage dependence of solar cell parameters. Moreover, the capacitance effects can be described by a dynamic impedance measurement of the PV module in the dark with forward and reverse biasing. The voltage and time-dependent parameters are the diffusion capacitance (CD), transient or junction capacitance (CT), series resistance (Rs), and shunt resistance (Rsh),which can be revealed by an impedance plot.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
X. Deng and E. A. Schiff, Amorphous Silicon-Based Solar Cells, J. Wiley, West Sussex, (2003).
Y. Hamakawa, Amorphous Semiconductor Technologies and Devices, North-Holland Publishing comp. (1982).
R. F. Pierret, Semiconductor Device Fundamentals, Addison-Wesley (1996).
I. Mora-Sero, Y. Luo, G. Garcia-Belmonte, J. Bisquert, D. Munoz, C. Voz, J. Puigdollers, and R. Alcubilla, Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells, 92, 505–509 (2008).
M. Cwil, M. Igalson, P. Zabierowski, C. A. Kaufmann, and A. Neisser, Thin Solid Films, 515, 6229–6232 (2007).
R. Ani Kumar, M. S. Suresh, and J. Nagaraju, IEEE Trans. Power Electrics, 21, No. 2, 543–548 (2006).
D. Chenvidhya, K. Kirtikara, and C. Jivacate, Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells, 86, 243–251 (2005).
J. Johnson, D. Schoenwald, S. Kuszmaul, and J. Strauch, Sandia Report, SAND2011-4247, Printed June (2011).
J. Johnson, B Gudgel, A. Meares, and A. Fresquez, Sandia Report, SAND2013-5916, Printed July (2013).
N. Silsirivanich, M. Seapan, C. Limsakul, D. Chenvidhaya, and K. Kirtikara, 23th Int. PVSEC Conf., October 30–November 1, Taipei, Taiwan, 21–22 (2013).
M. Seapan, C. Limsakul, N. Chayavanich, D. Chenvidhya, and K. Kirtikara, The 33rd IEEE Photovoltaic Specialists Conf., San Diego, CA, USA, May 11–16, 2008, 52–54 (2008).
International Standard, IEC61646, 2nd ed., 21–22 (2008)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in Zhurnal Prikladnoi Spektroskopii, Vol. 82, No. 2, pp. 292–298, March–April, 2015.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Silsirivanich, N., Chenvidhya, D., Kirtikara, K. et al. Nonstationary Effects at Photovoltaic Module Characterization Using Pulsed Solar Simulator. J Appl Spectrosc 82, 286–292 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10812-015-0099-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10812-015-0099-7