Abstract
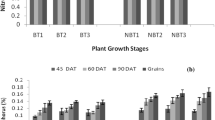
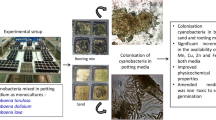
Cyanobacteria are essential in paddy fields, aiding soil fertility. Soil pollution, caused by excessive chemical fertilizers and pesticides, poses a global crisis. To use cyanobacterial biofertilizers effectively, strains need to tolerate and break down these agrochemicals, including herbicides. This study examined the ability of potential plant growth promoting cyanobacterial strains Nostoc commune MBDU 101 and Scytonema bohneri MBDU 104 to tolerate salinity - NaCl (100 mM) and chlorpyrifos (5 mg L-1) stress of Oryza sativa L. grown under hydroponic conditions, both individually and in combination with each other. These cyanobacterial strains have already been proven for their ability to produce phytohormones and are now assessed for their salinity and insecticide tolerance through growth parameters, including chlorophyll, carotenoids, and protein content, over 24 days under test conditions. Those treatments that demonstrated optimal cyanobacterial growth were subsequently tested for their impact on O. sativa L. under hydroponic conditions along with a control group. Notably, N. commune MBU101 under chlorpyrifos stress showed distinctive positive effects on plant growth, with a shoot length of 3.18 cm, seedling length of 6.68 cm, 13 lateral roots, and a leaf length of 6.73 cm. Scytonema bohneri MBDU 104 (SB104) exposed to NaCl stress exhibited the highest seedling weight among all treatments and the control. GC-MS analysis of N. commune revealed the presence of 3,5,6-trichloro-2-methoxypyridine (TMP) and 3,5,6-trichloro-2-pyridinol (TCP) as degradation products of chlorpyrifos. These findings emphasize the potential of these cyanobacterial strains in enhancing soil health and crop growth while mitigating the environmental impact of agrochemicals.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available upon reasonable request
References
Arora S (2017) Diagnostic properties and constraints of salt-affected soils. In: Arora S, Singh AK, Singh YP (eds) Bioremediation of salt affected soils: an Indian perspective. Springer, Cham, pp 41–52
Álvarez C, Navarro JA, Molina-Heredia FP, Mariscal V (2020) Endophytic colonization of rice ( Oryza sativa L.) by the symbiotic strain Nostoc punctiforme PCC 73102. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 33:1040–1045
Banerjee M, Modi P (2010) Micropropagation of Bacopa monnieri using cyanobacterial liquid medium. Plant Tissue Cult Biotech 20:225–231
Battah MG (2013) Beneficial effects of calcium chloride on two cyanobacterial species under sodium chloride stress. Egypt J Microbiol 48:71–85
Becze A, Cepoi L, Simedru D, Rudi L, Chiriac T, Rudic V (2017) Study regarding the influence of the salinity stress on the antioxidant capacity of Arthrospira platensis. Agricultura 103:12–16
Branch G (2007) Characterization of a soil cyanobacterium Fischerella sp. J Biol Sci 7:931–936
Cáceres T, Megharaj M, Venkateswarlu K, Sethunathan N, Naidu R (2010) Fenamiphos and related organophosphorus pesticides: Environmental fate toxicology. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 205:117–162
Chen S, Liu C, Peng C, Liu H, Hu M, Zhong G (2012) Biodegradation of chlorpyrifos and its hydrolysis product 3,5,6-trichloro-2-pyridinol by a new fungal strain Cladosporium cladosporioides Hu-01. PLoS One 7:e47205
Chen Z, Juneau P, Qiu B (2007) Effects of three pesticides on the growth, photosynthesis and photoinhibition of the edible cyanobacterium Ge-Xian-Mi (Nostoc). Aquat Toxicol 81:256–265
Chua M, Erickson TE, Merritt DJ, Chilton AM, Ooi MK, Muñoz-Rojas M (2020) Bio-priming seeds with cyanobacteria: effects on native plant growth and soil properties. Restor Ecol 28:S168–S176
Cuartero J, Fernández-Muñoz R (1999) Tomato and salinity. Sci Hortic 78:83–125
Debouba M, Gouia H, Suzuki A, Ghorbel MH (2006) NaCl stress effects on enzymes involved in nitrogen assimilation pathway in tomato Lycopersicon esculentum seedlings. J Plant Physiol 163:1247–1258
El-Helow ER, Badawy ME, Mabrouk ME, Mohamed EA, El-Beshlawy YM (2013) Biodegradation of chlorpyrifos by a newly isolated Bacillus subtilis strain, Y242. Bioremed J 17:113–123
Escalante FM, Cortés-Jiménez D, Tapia-Reyes G, Suárez R (2015) Immobilized microalgae and bacteria improve salt tolerance of tomato seedlings grown hydroponically. J Appl Phycol 27:1923–1933
Fadl-Allah EM, El-Komy HM, Al-Harbi NA, Sholkamy EN (2011) In vitro creation of artificial nitrogen fixing cyanobacterium (Nostoc muscorum) association with wheat. Afr J Microbiol Res 5:302–310
Farhan M, Ahmad M, Kanwal A, Butt ZA, Khan QF, Raza SA, Qayyum H, Wahid A (2021) Biodegradation of chlorpyrifos using isolates from contaminated agricultural soil, its kinetic studies. Sci Rep 11:10320
Fernandes TA, Iyer V, Apte SK (1993) Differential responses of nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria to salinity and osmotic stresses. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:899–904
Galhano V, Peixoto F, Gomes-Laranjo J, Fernández-Valiente E (2009) Differential effects of bentazon and molinate on Anabaena cylindrica, an autochthonous cyanobacterium of Portuguese rice field agro-ecosystems. Water Air Soil Poll 197:211-222
Gayathri M, Shunmugam S, Mugasundari AV, Rahman PK, Muralitharan G (2018) Growth kinetic and fuel quality parameters as selective criterion for screening biodiesel producing cyanobacterial strains. Bioresour Technol 247:453–462
Gayathri M, Shunmugam S, Thajuddin N, Muralitharan G (2017) Phytohormones and free volatile fatty acids from cyanobacterial biomass wet extract (BWE) elicit plant growth promotion. Algal Res 26:56–64
Bano S, Nadir M, Ahmed A, Rasool SG, Siddiqui PJA, Rasheed M (2021) Removal efficiency of marine filamentous cyanobacteria for pyrethroids and their effects on the biochemical parameters and growth. Algal Res 60:102546
Hu J, Jin L, Wang X, Cai W, Liu Y, Wang G (2014) Response of photosynthetic systems to salinity stress in the desert cyanobacterium Scytonema javanicum. Adv Space Res 53:30–36
Huang Y, Zhang W, Pang S, Chen J, Bhatt P, Mishra S, Chen S (2021) Insights into the microbial degradation and catalytic mechanisms of chlorpyrifos. Env Res 194:110660
Hussein KA, Joo JH (2018) Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria improved salinity tolerance of Lactuca sativa and Raphanus sativus. J Microbiol Biotechnol 28:938–945
Jaiswal TP, Chakraborty S, Sharma S, Mishra A, Mishra AK, Singh SS (2023) Prospects of a hot spring–originated novel cyanobacterium, Scytonema ambikapurensis, for wastewater treatment and exopolysaccharide-enriched biomass production. Env Sci Pollut Res 30:53424–53444
Jamil A, Riaz S, Ashraf M, Foolad MR (2011) Gene expression profiling of plants under salt stress. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 30:435–458
Jochum M, Moncayo LP, Jo YK (2018) Microalgal cultivation for biofertilization in rice plants using a vertical semi-closed airlift photobioreactor. PloS ONE 13:e0203456
Karthikeyan N, Prasanna R, Nain L, Kaushik BD (2007) Evaluating the potential of plant growth promoting cyanobacteria as inoculants for wheat. Eur J Soil Biol 43:23–30
Kumar MS, Praveenkumar R, Jeon BH, Thajuddin N (2014) Chlorpyrifos-induced changes in the antioxidants and fatty acid compositions of Chroococcus turgidus NTMS 12. Lett Appl Microbiol 59:535–541
Lal S, Lal R, Saxena DM (1987) Bioconcentration and metabolism of DDT, fenitrothion and chlorpyrifos by the blue-green algae Anabaena sp. and Aulosira fertilissima. Environ Pollut 46:187–96
Liu C, Zhao C, Wang L, Du X, Zhu L, Wang J, Kim YM, Wang J (2023) Biodegradation mechanism of chlorpyrifos by Bacillus sp. H27: Degradation enzymes, products, pathways and whole genome sequencing analysis. Env Res 239:117315
Long XH, Chi JH, Liu L, Li Q, Liu ZP (2009) Effect of seawater stress on physiological and biochemical responses of five Jerusalem Artichoke ecotypes. Pedosphere 19:208–216
López-Climent MF, Arbona V, Pérez-Clemente RM, Gómez-Cadenas A (2008) Relationship between salt tolerance and photosynthetic machinery performance in citrus. Environ Exp Bot 62:176–184
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Megharaj M, Kantachote D, Singleton I, Naidu R (2000) Effects of long-term contamination of DDT on soil microflora with special reference to soil algae and algal transformation of DDT. Environ Pollut 109:35–42
Megharaj M, Madhavi DR, Sreenivasulu C, Umamaheswari A, Venkateswarlu K (1994) Biodegradation of methyl parathion by soil isolates of microalgae and cyanobacteria. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 53:292–297
Megharaj M, Venkateswarlu K, Rao AS (1987) Metabolism of monocrotophos and quinalphos by algae isolated from soil. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 39:251–256
Möke F, Wasmund N, Bauwe H, Hagemann M (2013) Salt acclimation of Nodularia spumigena CCY9414 a cyanobacterium adapted to brackish water. Aquat Microb Ecol 70:207–214
Moore DJ, Reed RH, Stewart WD (1985) Responses of cyanobacteria to low level osmotic stress: implications for the use of buffers. J Gen Microbiol 131:1267–1272
Mutawie HH (2015) Growth and metabolic response of the filamentous cyanobacterium Spirulina platensis to salinity stress of sodium chloride. Life Sci J 12:71–78
Neti N, Zakkula V (2013) Analysis of chlorpyrifos degradation by Kocuria sp. using GC and FTIR. Curr Biotica 6:466–472
Nilsson M, Bhattacharya J, Rai AN, Bergman B (2002) Colonization of roots of rice (Oryza sativa) by symbiotic Nostoc strains. New Phytol 156:517–525
Padhi H, Rath B, Adhikary SP (1997) Tolerance of nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria to NaCl. Biol Plant 40:261–268
Panda BM, Balakrishna V, Pathy RN (2009) Estimating the toxicity and lethal dose concentration of five saline salts and two pesticides to cyanobacterium Anabaena 7120. Terrest Aquat Environ Toxicol 3:71–75
Parida AK, Das AB (2005) Salt tolerance and salinity effects on plants: a review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 60:324–349
Rady MM, Taha SS, Kusvuran S (2018) Integrative application of cyanobacteria and antioxidants improves common bean performance under saline conditions. Sci Hortic 233:61–69
Rai AK, Tiwari SP (1999) NO3–nutrition and salt tolerance in the cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. PCC 7120 and mutant strains. J Appl Microbiol 86:991–998
Rai S, Agrawal C, Shrivastava AK, Singh PK, Rai LC (2014) Comparative proteomics unveils cross species variations in Anabaena under salt stress. J Proteome 98:254–270
Ramakrishnan B, Megharaj M, Venkateswarlu K, Naidu R, Sethunathan N (2010) The impacts of environmental pollutants on microalgae and cyanobacteria. Crit Rev Env Sci Tech 40:699–821
Rippka R, Deruelles J, Waterbury JB, Herdman M, Stanier RY (1979) Generic assignments, strain histories and properties of pure cultures of cyanobacteria. J Gen Microbiol 111:1–61
Ritchie RJ (2006) Consistent sets of spectrophotometric chlorophyll equations for acetone, methanol and ethanol solvents. Photosynth Res 89:27–41
Singh BK, Walker A (2006) Microbial degradation of organophosphorus compounds. FEMS Microbiol Rev 30:428–471
Singh DP, Khattar JIS, Kaur M, Kaur G, Gupta M, Singh Y (2013) Anilofos tolerance and its mineralization by the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. strain PUPCCC 64. PLoS ONE 8:e53445
Singh DP, Prabha R, Yandigeri MS, Arora DK (2011a) Cyanobacteria-mediated phenylpropanoids and phytohormones in rice (Oryza sativa) enhance plant growth and stress tolerance. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 100:557–568
Singh DP, Khattar JIS, Nadda J, Singh Y, Garg A, Kaur N, Gulati A (2011b) Chlorpyrifos degradation by the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. strain PUPCCC 64. Environ Sci Pollut Res 18:1351–1359
Sheikh BA (2006) Hydroponics: key to sustain agriculture in water stressed and urban environment. Pak J Agric Agric Eng Vet Sci 22(2):53–57
Slocombe SP, Ross M, Thomas N, McNeill S, Stanley MS (2013) A rapid and general method for measurement of protein in micro-algal biomass. Bioresour Technol 129:51–57
Steinbrenner J, Linden H (2001) Regulation of two carotenoid biosynthesis genes coding for phytoene synthase and carotenoid hydroxylase during stress-induced astaxanthin formation in the green alga Haematococcus pluvialis. Plant Physiol 125:810–817
Subashchandrabose SR, Ramakrishnan B, Megharaj M, Venkateswarlu K, Naidu R (2013) Mixotrophic cyanobacteria and microalgae as distinctive biological agents for organic pollutant degradation. Environ Internat 51:59–72
Supreeth M, Raju NS (2016) Bio-mineralization of organophosphorous insecticide-chlorpyrifos and its hydrolyzed product 3,5 6-trichloro-2-pyridinol by Staphylococcus sp. ES-2. Curr World Environ 11:486–491
Tiwari B, Chakraborty S, Srivastava AK, Mishra AK (2017) Biodegradation and rapid removal of methyl parathion by the paddy field cyanobacterium Fischerella sp. Algal Res 25:285–296
Tony AM, EL–Geuindi MSA, Hussein SM, Elwahab MZA (2016) Degradation of an organophosphorus insecticide (chlorpyrifos) in simulated wastewater using advanced oxidation processes and chemical oxidation. Appl Sci Rep 15:63–73
Vazquez-Duhalt R, Arredondo-Vega BO (1991) Haloadaptation of the green alga Botryococcus braunii (race A). Phytochemistry 30:2919–2925
Verma E, Chakraborty S., Tiwari B, Singh S, Mishra AK (2018) Alleviation of NaCl toxicity in the cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. PCC 7942 by exogenous calcium supplementation. J Appl Phycol 30:1465–1482
Wang H, Yang Y, Chen W, Ding L, Li P, Zhao X, Wang X, Li A, Bao Q (2013) Identification of differentially expressed proteins of Arthrospira (Spirulina) plantensis-YZ under salt-stress conditions by proteomics and qRT-PCR analysis. Proteome Sci 11:6
Wang J, Atolia E, Hua B, Savir Y, Escalante-Chong R, Springer M (2015) Natural variation in preparation for nutrient depletion reveals a cost–benefit tradeoff. PLoS Biol 13:e1002041
Wellburn AR (1994) The spectral determination of chlorophylls a and b, as well as total carotenoids, using various solvents with spectrophotometers of different resolution. J Plant Physiol 144:307–313
Wu Q, Li M, Gao X, Giesy JP, Cui Y, Yang L, Kong Z (2011) Genotoxicity of crude extracts of cyanobacteria from Taihu Lake on carp (Cyprinus carpio). Ecotoxicology 20:1010–1017
Wu Y, Wang F, Xiao X, Liu J, Wu C, Chen H, Kerr P, Shurin J (2017) Seasonal changes in phosphorus competition and allelopathy of a benthic microbial assembly facilitate prevention of cyanobacterial blooms. Env Microbiol 19:2483–2494
Zhang Y, Xu Q, Xi B (2013) Effect of NaCl salinity on the growth, metabolites, and antioxidant system of Microcystis aeruginosa. J Freshwat Ecol 28:477–487
Zribi L, Fatma G, Fatma R, Salwa R, Hassan R, Néjib RM (2009) Application of chlorophyll fluorescence for the diagnosis of salt stress in tomato Solanum lycopersicum (variety Rio Grande). Sci Hort 120:367–372
Funding
MG acknowledges National Post-doctoral Fellowship (PDF/2017 /002586). SS acknowledges DST- Women Scientist Scheme A (WOS-A), Govt. of India (SR/WOS-A/LS-79/2018 dt. 07.01.2019). Authors are thankful to DST-FIST programme (SR/FIST/LSI/-013/2012 dated 13.08.2012) for instrument facilities and Sophisticated Analytical instrumentation Facility, IIT-Bombay for GC/MS analysis. GM acknowledges the RUSA 2.0 Biological Sciences of Bharathidasan University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
G. M., M.G. and S. S. conceived the experiments and analysed the data; M.G and S, S, performed the experiments; G. M., S. S., J.S and M. G. wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gayathri, M., Shunmugam, S., Sridhar, J. et al. Evaluating the augmented effect of potential plant growth promoting cyanobacterial strains on salinity and insecticidal stress tolerance of Oryza sativa L. under hydroponic cultivation. J Appl Phycol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-024-03251-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-024-03251-9