Abstract
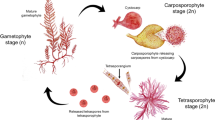
The green algal genus Ulva (Ulvophyceae) has been recently perceived as a model organism, due to its tractability for genetic analyses. This biomass is drawing considerable attention as a potential feedstock for energy security, including emerging applications in functional foods, bio-fuels and energy, pharmaceutical, biotechnological industries, etc. Nevertheless, unlike other commercially farmed seaweeds where clonal propagation is practiced, this genus solely relies on motile reproductive cells (zoospores or gametes) for seeding or seedling production. The culture practices encompass photobioreactor, land-based and open sea farming. The knowledge of reproduction is pivotal for efficient seeding technologies, selecting and domesticating fast growing varieties as well as genetic improvement. The successful induction of reproduction in Ulva spp. is being achieved through external environmental stimuli as well as by manipulating sporulation and swarming inhibitor concentration. However, comprehensive biochemical and molecular evidences are underdeveloped and further knowledge is imperative to improve aquaculture practice. This mini-review provides comprehensive insights into life cycle, spore formation, mechanisms for the induction of reproduction, biochemical and molecular aspects of sporulation besides advances in the farming of Ulva spp. with future prospective. The existing commercial trade of Japan about 1500 t dry annum−1 is poised to become the leading industry with focus on niche, high-value products in the coming decade.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alsufyani T, Engelen AH, Diekmann OE, Kuegler S, Wichard T (2014) Prevalence and mechanism of polyunsaturated aldehydes production in the green tide forming macroalgal genus Ulva (Ulvales, Chlorophyta). Chem Phys Lipids 183:100–109
Bliding C (1968) A critical survey of European taxa Ulvales II. Ulva, Ulvaria, Monostroma, Kornmannia. Bot Notiser 121:535–629
Bolton JJ, Robertson-Andersson DV, Shuuluka D, Kandjengo L (2009) Growing Ulva (Chlorophyta) in integrated systems as a commercial crop for abalone feed in South Africa: a SWOT analysis. J Appl Phycol 21:575–583
Bolton JJ, Cyrus MD, Brand MJ, Joubert M, Macey BM (2016) Why grow Ulva? Its potential role in the future of aquaculture. Perspect Phycol 3:113–120
Brawley SH, Johnson LE (1992) Gametogenesis, gametes and zygotes: an ecological perspective on sexual reproduction in the algae. Brit Phycol J 27:233–252
Carl C, de Nys R, Lawton RJ, Paul NA (2014a) Methods for the induction of reproduction in a tropical species of filamentous Ulva. PLoS One 9:e97396
Carl C, de Nys R, Paul NA (2014b) The seeding and cultivation of a tropical species of filamentous Ulva for algal biomass production. PLoS One 9:e98700
Castelar B, Reis RP, dos Santos Calheiros AC (2014) Ulva lactuca and U. flexuosa (Chlorophyta, Ulvophyceae) cultivation in Brazilian tropical waters: recruitment, growth, and ulvan yield. J Appl Phycol 26:1989–1999
Charrier B, Abreu MH, Araujo R, Bruhn A, Coates JC, De Clerck O, Katsaros C, Robaina RR, Wichard T (2017) Furthering knowledge of seaweed growth and development to facilitate sustainable aquaculture. New Phytol 216:967–975
Chemodanov A, Jinjikhashvily G, Habiby O, Liberzon A, Israel A, Yakhini Z, Golberg A (2017a) Net primary productivity, biofuel production and CO2 emissions reduction potential of Ulva sp. (Chlorophyta) biomass in a coastal area of the Eastern Mediterranean. Energ Convers Manage 148:497–1507
Chemodanov A, Robin A, Golberg A (2017b) Design of marine macroalgae photobioreactor integrated into building to support seagriculture for biorefinery and bioeconomy. Bioresour Technol 241:1084–1093
Chemodanov A, Robin A, Jinjikhashvily G, Yitzhak D, Liberzon A, Israel A, Golberg A (2019) Feasibility study of Ulva sp. (Chlorophyta) intensive cultivation in a coastal area of the Eastern Mediterranean Sea. Biofuels Bioprod Biorefin. https://doi.org/10.1002/bbb.1995
Chory J, Chatterjee M, Cook RK, Elich T, Fankhauser C, Li J, Reed J (1996) From seed germination to flowering, light controls plant development via the pigment phytochrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci 93:12066–12071
Clayton MN (1992) Propagules of marine macroalgae: structure and development. Brit Phycol J 27:219–232
Corradi MG, Gorbi G, Zanni C (2006) Hypoxia and sulphide influence gamete production in Ulva sp. Aquat Bot 84:44–150
Dan A, Hiraoka M, Ohno M, Critchley AT (2002) Observations on the effect of salinity and photon fluence rate on the induction of sporulation and rhizoid formation in the green alga Enteromorpha prolifera (Müller) J. Agardh (Chlorophyta, Ulvales). Fish Sci 68:1182–1188
De Clerck O, Kao SM, Bogaert KA, Blomme J, Foflonker F, Kwantes M, Califano et al. (2018) Insights into the evolution of multicellularity from the sea lettuce genome. Curr Biol 28(18):2921-2933.
de Góes HG, Reis RP (2011) An initial comparison of tubular netting versus tie–tie methods of cultivation for Kappaphycus alvarezii (Rhodophyta, Solieriaceae) on the south coast of Rio de Janeiro State, Brazil. J Appl Phycol 23:607–613
Dittmann KK, Rasmussen BB, Castex M, Gram L, Bentzon-Tilia M (2017) The aquaculture microbiome at the centre of business creation. Microb Biotechnol 10:1279–1282
Fernand F, Israel A, Skjermo J, Wichard T, Timmermans KR, Golberg A (2017) Offshore macroalgae biomass for bioenergy production: Environmental aspects, technological achievements and challenges. Renew Sust Energ Rev 75:35–45
Fjeld A (1972) Genetic control of cellular differentiation in Ulva mutabilis. Gene effects in early development. Dev Biol 28:326–343
Friedlander M (2008) Israeli R & D activities in seaweed cultivation. Isr J Plant Sci 56:15–28
Gao S, Chen X, Yi Q, Wang G, Pan G, Lin A, Peng G (2010) A strategy for the proliferation of Ulva prolifera, main causative species of green tides, with formation of sporangia by fragmentation. PLoS One 5:e8571
Gao G, Clare AS, Rose C, Caldwell GS (2017) Intrinsic and extrinsic control of reproduction in the green tide-forming alga, Ulva rigida. Environ Exp Bot 139:14–22
Ghaderiardakani F, Coates JC, Wichard T (2017) Bacteria-induced morphogenesis of Ulva intestinalis and Ulva mutabilis (Chlorophyta): a contribution to the lottery theory. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 93
Ghaderiardakani F, Califano G, Mohr JF, Abreu MH, Coates JC, Wichard T (2019) Analysis of algal growth- and morphogenesis-promoting bacterial factors in an integrated multi-trophic aquaculture system for farming the green seaweed Ulva spp. Aquacult Env Interact 11:375–391
Grueneberg J, Engelen AH, Costa R, Wichard T (2016) Macroalgal morphogenesis induced by waterborne compounds and bacteria in coastal seawater. PLoS One 11:e0146307
Gupta V, Trivedi N, Simoni S, Reddy CRK (2018) Marine macroalgal nursery: a model for sustainable production of seedlings for large scale farming. Algal Res 31:463–468
Hafting JT, Critchley AT, Cornish ML, Hubley SA, Archibald AF (2012) On-land cultivation of functional seaweed products for human usage. J Appl Phycol 24:385–392
Hagström Å, Pinhassi J, Zweifel UL (2000) Biogeographical diversity among marine bacterioplankton. Aquat Microb Ecol 21:231–244
Han T, Choi GW (2005) A novel marine algal toxicity bioassay based on sporulation inhibition in the green macroalga Ulva pertusa (Chlorophyta). Aquat Toxicol 75:202–212
Han T, Han YS, Park CY, Jun YS, Kwon MJ, Kang SH, Brown MT (2008) Spore release by the green alga Ulva: a quantitative assay to evaluate aquatic toxicants. Environ Pollut 153:699–705
Hatfield JL, Prueger JH (2015) Temperature extremes: effect on plant growth and development. Weather Clim Extrem 10:4–10
Hayden HS, Blomster J, Maggs CA, Silva PC, Stanhope MJ, Waaland JR (2003) Linnaeus was right all along: Ulva and Enteromorpha are not distinct genera. Eur J Phycol 38:277–294
He Y, Wang Y, Hu C, Sun X, Li Y, Xu N (2019) Dynamic metabolic profiles of the marine macroalga Ulva prolifera during fragmentation-induced proliferation. PLoS One 14:e0214491
Hiraoka M, Enomoto S (1998) The induction of reproductive cell formation of Ulva pertusa Kjellman (Ulvales, Ulvophyceae). Phycol Res 46:199–203
Hiraoka M, Oka N (2008) Tank cultivation of Ulva prolifera in deep seawater using a new “germling cluster” method. J Appl Phycol 20:97–102
Hiraoka M, Shimada S (2004) Biology of a special green laver, Ulva prolifera from the Shimanto River. Aquabiology 26:508–515
Hiraoka M, Shimada S, Ohno M, Serisawa Y (2003) Asexual life history by quadriflagellate swarmers of Ulva spinulosa (Ulvales, Ulvophyceae). Phycol Res 51:29–34
Kakinuma M, Coury DA, Kuno Y, Itoh S, Kozawa Y, Inagaki E, Amano H (2006) Physiological and biochemical responses to thermal and salinity stresses in a sterile mutant of Ulva pertusa (Ulvales, Chlorophyta). Mar Biol 149:97
Kalita TL, Tytlianov EA (2003) Effect of temperature and illumination on growth and reproduction of the green alga Ulva fenestrata. Russ J Mar Biol 29:316–322
Katsaros C, Weiss A, Llangos I, Theodorou I, Wichard T (2017) Cell structure and microtubule organisation during gametogenesis of Ulva mutabilis Føyn (Chlorophyta). Bot Mar 60:123–135
Kessler RW, Crecelius AC, Schubert US, Wichard T (2017) In situ monitoring of molecular changes during cell differentiation processes in marine macroalgae through mass spectrometric imaging. Anal Bioanal Chem 409:4893–4903
Kessler RW, Alsufyani T, Wichard T (2018) Purification of sporulation and swarming inhibitors from Ulva: application in algal life cycle controlling. In Protocols for Macroalgae Research, eds. Charrier B, Wichard T, Reddy CRK, 139-157. Boca Raton: CRC Press, Francis & Taylor Group.
Lawton RJ, Mata L, de Nys R, Paul NA (2013) Algal bioremediation of waste waters from land-based aquaculture using Ulva: selecting target species and strains. PLoS One 8:e77344
Li Y, Zhang X, Xu D, Zhuang Z, Ye N (2012) Differential gene expression in Ulva prolifera under low light and low temperature conditions. Curr Genet 58:235–244
Løvlie A, Bryhni E (1978) On the relation between sexual and parthenogenetic reproduction in haplo-diplontic algae. Bot Mar 21:155–164
Lüning K, Kadel P, Pang S (2008) Control of reproduction rhythmicity by environmental and endogenous signals in Ulva pseudocurvata (Chlorophyta). J Phycol 44:866–873
Mairh OP, Pandey RS, Tewari A, (1986) Culture of Enteromorpha flexuosa (Wulf.) J. Ag. (Chlorophyceae) in outdoor pool. Indian J Mar Res 15:212–218
Mantri VA, Singh RP, Bijo AJ, Kumari P, Reddy CRK, Jha B (2011) Differential response of varying salinity and temperature on zoospore induction, regeneration and daily growth rate in Ulva fasciata (Chlorophyta, Ulvales). J Appl Phycol 23:243–250
Marshall K, Joint I, Callow ME, Callow JA (2006) Effect of marine bacterial isolates on the growth and morphology of axenic plantlets of the green alga Ulva linza. Microb Ecol 52:302–310
Mata L, Schuenhoff A, Santos R (2010) A direct comparison of the performance of the seaweed biofilters, Asparagopsis armata and Ulva rigida. J Appl Phycol 22:639–644
Mata L, Magnusson M, Paul NA, de Nys R (2015) The intensive land-based production of the green seaweeds Derbesia tenuissima and Ulva ohnoi: biomass and bioproducts. J Appl Phycol 28:365–375
Matsuo Y, Suzuki M, Kasai H, Shizuri Y, Harayama S (2003) Isolation and phylogenetic characterization of bacteria capable of inducing differentiation in the green alga Monostroma oxyspermum. Environ Microbiol 5:25–35
Matsuo Y, Imagawa H, Nishizawa M, Shizuri Y (2005) Isolation of an algal morphogenesis inducer from a marine bacterium. Science 307:1598
Mhatre A, Navale M, Trivedi N, Pandit R, Lali AM (2018) Pilot scale flat panel photobioreactor system for mass production of Ulva lactuca (Chlorophyta). Bioresour Technol 249:582–591
Miyamura S (2010) Cytoplasmic inheritance in green algae: patterns, mechanisms and relation to sex type. J Plant Res 123:171–184
Moll B (2004) Aquatic surface barriers and methods for culturing seaweed. PCT Patent WO 2004/093525.
Nardelli AE, Chiozzini VG, Braga ES, Chow F (2019) Integrated multi-trophic farming system between the green seaweed Ulva lactuca, mussel, and fish: a production and bioremediation solution. J Appl Phycol 31:847–856
Nielsen MM, Bruhn A, Rasmussen MB, Olesen B, Larsen MM, Møller HB (2012) Cultivation of Ulva lactuca with manure for simultaneous bioremediation and biomass production. J Appl Phycol 24:449–458
Nilsen G, Nordby Ø (1975) A sporulation-inhibiting substance from vegetative thalli of the green alga Ulva mutabilis, Føyn. Planta 125:127–139
Nordby Ø (1974) Light microscopy of meiotic zoosporogenesis and mitotic gametogenesis in Ulva mutabilis Føyn. J Cell Sci 15:443–455
Novaczek I, Bird CJ, McLachlan J (1986) The effect of temperature on development and reproduction in Chorda filum and C. tomentosa (Phaeophyta, Laminariales) from Nova Scotia. Can J Bot 64:2414–2420
Oertel W, Wichard T, Weissgerber A (2015) Transformation of Ulva mutabilis (Chlorophyta) by vector plasmids integrating into the genome. J Phycol 51:963–979
Ohno M (2006) Recent developments in the seaweed cultivation and industry in Japan. In Advances in seaweed cultivation and utilisation in Asia: proceedings of a workshop held in conjunction with the 7th Asiean Fisheries Forum, Penang. Kuala Lumpur: University of Malaya. 1-20 pp.
Oza RM, Rao PS (1977) Effect of different culture media on growth and sporulation of laboratory raised germlings of Ulva fasciata Delile. Bot Mar 20:427–432
Oza RM, Joshi HV, Mairh OP, Tewari A (1985) Swarmer production and cultivation of Ulva fasciata Delile in intertidal regions at Okha, west coast of India. Indian J Mar Sci 14:217–219
Oza RM, Krishna Kumar GR, Mairh OP, Zaidi SH (2001) Cultivation of Ulva fasciata Delile on the coast of Diu, West coast of India. Seaeed Res Utiln 23:5–12
Plettner INA, Steinke M, Malin G (2005) Ethene (ethylene) production in the marine macroalga Ulva (Enteromorpha) intestinalis L. (Chlorophyta, Ulvophyceae): effect of light-stress and co-production with dimethyl sulphide. Plant Cell Environ 28:1136–1145
Polne-Fuller M, Gibor A (1986) Algal cell, callus and tissue cultures and selection of algal strains. Beih Nova Hedwigia 83:30–36
Provasoli L, Pintner IJ (1980) Bacteria induced polymorphism in an axenic laboratory strain of Ulva lactuca (Chlorophyceae). J Phycol 32:479–482
Rao PS, Mantri VA (2006) Indian seaweed resources and sustainable utilization: scenario at the dawn of a new century. Curr Sci 164-174.
Robertson-Andersson D, Potgieter M, Hansen J, Bolton J, Troell M, Anderson R, Halling C, Probyn T (2008) Integrated seaweed cultivation on an abalone farm in South Africa. J Appl Phycol 20:579–595
Rybak AS, Gąbka M (2018) The influence of abiotic factors on the bloom-forming alga Ulva flexuosa (Ulvaceae, Chlorophyta): possibilities for the control of the green tides in freshwater ecosystems. J Appl Phycol 30:1405–1416
Sharrock RA (2008) The phytochrome red/far-red photoreceptor superfamily. Genome Biol 9:230
Singh RP, Reddy CRK (2014) Seaweed–microbial interactions: key functions of seaweed-associated bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 88:213–230
Singh RP, Mantri VA, Reddy CRK, Jha B (2011) Isolation of seaweed-associated bacteria and their morphogenesis-inducing capability in axenic cultures of the green alga Ulva fasciata. Aquat Biol 12:13–21
Smith GM (1947) On the reproduction of some Pacific coast species of Ulva. Am J Bot:80–87
Sousa AI, Martins I, Lillebø AI, Flindt MR, Pardal MA (2007) Influence of salinity, nutrients and light on the germination and growth of Enteromorpha sp. spores. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 341:142–150
Spoerner M, Wichard T, Bachhuber T, Stratmann J, Oertel W (2012) Growth and thallus morphogenesis of Ulva mutabilis (Chlorophyta) depends on a combination of two bacterial species excreting regulatory factors. J Phycol 48:1433–1447
Stanley MS, Perry RM, Callow JA (2005) Analysis of expressed sequence tags from the green alga Ulva linza (Chlorophyta). J Phycol 41:1219–1226
Steinhagen S, Barco A, Wichard T, Weinberger F (2019) Conspecificity of the model organism Ulva mutabilis and Ulva compressa (Ulvophyceae, Chlorophyta). J Phycol 55:25–36
Steyn PP (2000) A comparative study of the production and suitability of two Ulva species as abalone fodder in a commercial mariculture system. M. Sc. Dissertation. University of Port Elizabeth, South Africa.
Strain LWS, Borowitzka MA, Daume S (2006) Growth and survival of juvenile greenlip abalone (Haliotis laevigata) feeding on germlings of the macroalgae Ulva sp. J Shellfish Res 25:239–247
Stratmann J, Paputsoglu G, Oertel W (1996) Differentiation of Ulva mutabilis (Chlorophyta) gametangia and gamete release are controlled by extracellular inhibitors. J Phycol 32:1009–1021
Subbaramaiah K (1970) Growth and reproduction of Ulva fasciata Delile in nature and in culture. Bot Mar 13:25–27
Togashi T, Cox PA (2001) Tidal-linked synchrony of gamete release in the marine green alga, Monostroma angicava Kjellman. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 264:117–131
Tujula NA, Crocetti GR, Burke C, Thomas T, Holmström C, Kjelleberg S (2010) Variability and abundance of the epiphytic bacterial community associated with a green marine ulvacean alga. ISME J 4:301
Vesty EF, Kessler RW, Wichard T, Coates JC (2015) Regulation of gametogenesis and zoosporogenesis in Ulva linza (Chlorophyta): comparison with Ulva mutabilis and potential for laboratory culture. Front Plant Sci 6:15
Wang Y, Liu F, Liu X, Shi S, Bi Y, Moejes FW (2019) Comparative transcriptome analysis of four co-occurring Ulva species for understanding the dominance of Ulva prolifera in the Yellow Sea green tides. J Appl Phycol 31:3303–3316
Wheeler GL, Tait K, Taylor A, Brownlee C, Joint I (2006) Acyl-homoserine lactones modulate the settlement rate of zoospores of the marine alga Ulva intestinalis via a novel chemokinetic mechanism. Plant Cell Environ 29:608–618
Wichard T, Oertel W (2010) Gametogenesis and gamete release of Ulva mutabilis and Ulva lactuca (Chlorophyta): regulatory effects and chemical characterization of the “swarming inhibitor”. J Phycol 46:248–259
Wichard T, Charrier B, Mineur F, Bothwell JH, De Clerck O, Coates JC (2015) The green seaweed Ulva: a model system to study morphogenesis. Front Plant Sci 6:72
Yamazaki T, Endo M, Ito K, Suzuki R, Ota S, Kuwano K, Miyamura S, Toyoda A, Kawano S (2014) HAP2/GCS1 is involved in the sexual reproduction system of the marine macroalga Ulva compressa (Ulvales, Chlorophyta). Cytologia 9:575–584
Yamazaki T, Ichihara K, Suzuki R, Oshima K, Miyamura S, Kuwano K, Toyoda A, Suzuki Y, Sugano S, Hattori M, Kawano S (2017) Genomic structure and evolution of the mating type locus in the green seaweed Ulva partita. Sci Rep 7:11679
Zhang X, Xu D, Mao Y, Li Y, Xue S, Zou J, Ye N (2011) Settlement of vegetative fragments of Ulva prolifera confirmed as an important seed source for succession of a large-scale green tide bloom. Limnol Oceanogr 56:233–242
Zhang J, Kim JK, Yarish C, He P (2016) The expansion of Ulva prolifera O.F. Müller macroalgal blooms in the Yellow Sea, PR China, through asexual reproduction. Mar Pollut Bull 104:101–106
Acknowledgement
We thank the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, New Delhi for funding. The authors would like to thank Dr. Michael Friedlander and Dr. Alan Critchley their critical reviews on the manuscript. Thanks are also due to anonymous reviewer and handling editor for constructive suggestions. We are thankful to Dr. Amitava Das, Director, CSMCRI, Bhavnagar for encouragement and Dr. Pradeep Agarwal for facilities. This has PRIS registration number CSIR-CSMCRI 197/2018.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 113 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Balar, N.B., Mantri, V.A. Insights into life cycle patterns, spore formation, induction of reproduction, biochemical and molecular aspects of sporulation in green algal genus Ulva: implications for commercial cultivation. J Appl Phycol 32, 473–484 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-019-01959-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-019-01959-7