Abstract
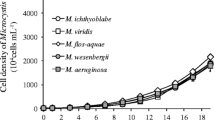
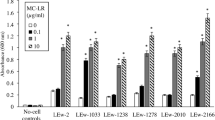
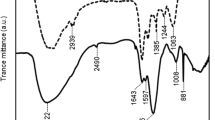
Microcystis, a genus of cyanobacteria that is dominant in eutrophic lakes, occurs mainly as colonial morphs under natural conditions but as single cells in laboratory cultures. Recent studies have suggested that Microcystis–bacteria interactions significantly influence Microcystis morphology, but the underlying mechanism remains unclear. In this study, a total of 48 strains of heterotrophic bacteria were purified from Microcystis mucilage. Five bacteria, Aeromonas veronii, Enterobacter aerogenes, Exiguobacterium acetylicum, Bacillus cereus and Shewanella putrefaciens, can induce unicellular Microcystis to form colonies. Heterotrophic bacteria stimulated Microcystis growth and induced the production of extracellular polymeric substances in coculture treatments. Extracellular polymeric substances, such as extracellular polysaccharides (EPS), were responsible for the mucilage formation in colonial Microcystis. We analysed extracellular metabolic compounds produced by Microcystis aeruginosa and Microcystis wesenbergii using gas chromatography mass spectrometry. Filtrate extracts from coculture treatments indicated that some compounds, such as 2-dodecen-1-yl(-) succinic anhydride and benzoic acid, 2,3-bis[(trimethylsilyl)oxy]-, trimethylsilyl ester, might play a significant role in colonial M. aeruginosa or M. wesenbergii formation. Our data suggested that the interaction of Microcystis and heterotrophic bacteria was crucial for the formation of Microcystis colony and outbreak of Microcystis blooms.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams JH (1978) Synergistic combinations of hydrated potassium borate, antiwear agents, and organic sulfide antioxidants. US Patent 4089790A
Armstrong E, Yan L, Boyd KG, Wright PC, Burgess JG (2001) The symbiotic role of marine microbes on living surfaces. Hydrobiologia 461:37–40
Bell WH (1984) Bacterial adaptation to low-nutrient conditions as studied with algal extracellular products. Microb Ecol 10:217–230
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Bratbak G, Thingstad TF (1985) Phytoplankton-bacteria interactions: an apparent paradox? Analysis of a model system with both competition and commensalism. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 25:23–30
Brunberg AK (1999) Contribution of bacteria in the mucilage of Microcystis spp. (Cyanobacteria) to benthic and pelagic bacterial production in a hypereutrophic lake. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 29:13–22
Burkert PH, Drakare S, Blomqvist P (2001) Effects of the mixotrophic flagellate Ochromonas sp. on colony formation in Microcystis aeruginosa. Aquat Ecol 35:11–17
Burton K (1956) A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J 62:315
Chen W, Peng L, Wan N, Song L (2009) Mechanism study on the frequent variations of cell-bound microcystins in cyanobacterial blooms in Lake Taihu: implications for water quality monitoring and assessments. Chemosphere 77:1585–1593
Doucette GJ (1995) Interactions between bacteria and harmful algae: a review. Nat Toxins 3:65–74
Dubois M, Gilles KA, Hamilton JK, Rebers P, Smith F (1956) Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal Chem 28:350–356
Dziallas C, Grossart HP (2011) Temperature and biotic factors influence bacterial communities associated with the cyanobacterium Microcystis sp. Environ Microbiol 13:1632–1641
Forni C, Telo' FR, Caiola MG (1997) Comparative analysis of the polysaccharides produced by different species of Microcystis (Chroococcales, Cyanophyta). Phycologia 36:181–185
Giroldo D, Ortolano PI, Vieira AA (2007) Bacteria–algae association in batch cultures of phytoplankton from a tropical reservoir: the significance of algal carbohydrates. Freshw Biol 52:1281–1289
Imai A, Fukushima T, Matsushige K (1999) Effects of iron limitation and aquatic humic substances on the growth of Microcystis aeruginosa. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 56:1929–1937
Ishikawa K, Walker R, Tsujimura S, Nakahara H, Kumagai M (2004) Estimation of Microcystis colony size in developing water blooms via image analysis. J Jpn Soc Water Environ 4:69–72
Ivanovic J, Misic D, Zizovic I, Ristic M (2012) In vitro control of multiplication of some food-associated bacteria by thyme, rosemary and sage isolates. Food Control 25:110–116
Jancula D, Marsalek B (2011) Critical review of actually available chemical compounds for prevention and management of cyanobacterial blooms. Chemosphere 85:1415–1422
Joung SH, Kim CJ, Ahn CY, Jang KY, Boo SM, Oh HM (2006) Simple method for a cell count of the colonial cyanobacterium, Microcystis sp. J Microbiol 44:562–565
Kessel M, Eloff JN (1975) The ultrastructure and development of the colonial sheath of Microcystis marginata. Arch Microbiol 106:209–214
Klock JH, Wieland A, Seifert R, Michaelis W (2007) Extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) from cyanobacterial mats: characterisation and isolation method optimisation. Mar Biol 152:1077–1085
Kolattukudy P (1968) Tests whether a head to head condensation mechanism occurs in the biosynthesis of n-hentriacontane, the paraffin of spinach and pea leaves. Plant Physiol 43:1466
Kurmayer R, Christiansen G, Chorus I (2003) The abundance of microcystin-producing genotypes correlates positively with colony size in Microcystis sp. and determines its microcystin net production in Lake Wannsee. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:787–795
Lee JA, Kontopoulou M, Parent JS (2005) Synthesis and characterization of polyethylene-based ionomer nanocomposites. Polymer 46:5040–5049
Lin LH, Chen KM (2006) Preparation and surface activity of gelatin derivative surfactants. Colloids Surf A 272:8–14
Liu X, Dong M, Chen X, Jiang M, Lv X, Yan G (2007) Antioxidant activity and phenolics of an endophytic Xylaria sp. from Ginkgo biloba. Food Chem 105:548–554
Liu YM, Chen MJ, Wang MH, Jia RB, Li L (2013) Inhibition of Microcystis aeruginosa by the extracellular substances from an Aeromonas sp. J Microbiol Biotechnol 23:1304–1307
Ma J, Brookes JD, Qin B, Paerl HW, Gao G, Wu P, Zhang W, Deng J, Zhu G, Zhang Y, Xu H, Niu H (2014) Environmental factors controlling colony formation in blooms of the cyanobacteria Microcystis spp. in Lake Taihu, China. Harmful Algae 31:136–142
Ma QZ, Wu FJ, Zhang DQ, Peng WX (2011) Py-GC-MS analysis on benzene-alcohol extractives of Phyllostachys pubescens for biomedical engineering. Key Eng Mater 480:211–214
Malloy KL, Suyama TL, Engene N, Debonsi H, Cao Z, Matainaho T, Spadafora C, Murray TF, Gerwick WH (2011) Credneramides A and B: neuromodulatory phenethylamine and isopentylamine derivatives of a vinyl chloride-containing fatty acid from cf. Trichodesmium sp. nov. J Nat Prod 75:60–66
Manage PM, Kawabata Z, Nakano S-i (2001) Dynamics of cyanophage-like particles and algicidal bacteria causing Microcystis aeruginosa mortality. Limnology 2:73–78
Middelboe M, Søndergaard M, Letarte Y, Borch N (1995) Attached and free-living bacteria: production and polymer hydrolysis during a diatom bloom. Microb Ecol 29:231–248
Mohamed H, Ons M, Yosra ET, Rayda S, Neji G, Moncef N (2009) Chemical composition and antioxidant and radical‐scavenging activities of Periploca laevigata root bark extracts. J Sci Food Agric 89:897–905
Nakamura N, Nakano K, Sugiura N, Matsumura M (2003) A novel cyanobacteriolytic bacterium, Bacillus cereus, isolated from a eutrophic lake. J Biosci Bioeng 95:179–184
Ngang JEJ et al (2014) Characterization of Mexican coriander (Eryngium foetidum) essential oil and its inactivation of Listeria monocytogenes In vitro and during mild thermal pasteurization of pineapple juice. J Food Protect 77:435–443
Parker DL (1982) Improved procedures for the cloning and purification of Microcystis cultures (Cyanophyta) 1. J Phycol 18:471–477
Parveen B, Ravet V, Djediat C, Mary I, Quiblier C, Debroas D, Humbert JF (2013) Bacterial communities associated with Microcystis colonies differ from free living communities living in the same ecosystem. Environ Microbiol Rep 5:716–724
Pereira S, Zille A, Micheletti E, Moradas‐Ferreira P, De Philippis R, Tamagnini P (2009) Complexity of cyanobacterial exopolysaccharides: composition, structures, inducing factors and putative genes involved in their biosynthesis and assembly. FEMS Microbiol Rev 33:917–941
Plude JL, Parker DL, Schommer OJ, Timmerman RJ, Hagstrom SA, Joers JM, Hnasko R (1991) Chemical characterization of polysaccharide from the slime layer of the cyanobacterium Microcystis flos-aquae C3-40. Appl Environ Microbiol 57:1696–1700
Porter KG (1980) The use of DAPI for identifying and counting aquatic microflora. Limnol Oceanogr 25:943–948
Reynolds CS, Jaworski G, Cmiech H, Leedale G (1981) The formation of colonies or aggregates might be phenotypic response of individuals to current environmental conditions. Phil Trans R Soc B 4:419–477
Rippka R (1988) Isolation and purification of cyanobacteria. Method Enzymol 167:3
Romo S, Soria J, Fernandez F, Ouahid Y, Barón-Solá Á (2013) Water residence time and the dynamics of toxic cyanobacteria. Freshw Biol 58:513–522
Scott JH, Nealson KH (1994) A biochemical study of the intermediary carbon metabolism of Shewanella putrefaciens. J Bacteriol 176:3408–3411
Sedmak B, Eleršek T (2006) Microcystins induce morphological and physiological changes in selected representative phytoplanktons. Microb Ecol 51:508–515
Sharman M, Read WA, Castle L, Gilbert J (1994) Levels of di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate and total phthalate esters in milk, cream, butter and cheese. Food Addit Contam 11:375–385
Shen H, Niu Y, Xie P, Tao M, Yang X (2011) Morphological and physiological changes in Microcystis aeruginosa as a result of interactions with heterotrophic bacteria. Freshw Biol 56:1065–1080
Shi L, Cai Y, Kong F, Yu Y (2012) Specific association between bacteria and buoyant Microcystis colonies compared with other bulk bacterial communities in the eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Environ Microbiol Rep 4:669–678
Shi L, Cai Y, Wang X, Li P, Yu Y, Kong F (2010) Community structure of bacteria associated with Microcystis colonies from cyanobacterial blooms. J Freshw Ecol 25:193–203
Shirai M, Matumaru K, Ohotake A, Takamura Y, Aida T, Nakano M (1989) Development of a solid medium for growth and isolation of axenic Microcystis strains (cyanobacteria). Appl Environ Microbiol 55:2569–2571
Sundh I (1992) Biochemical composition of dissolved organic carbon derived from phytoplankton and used by heterotrophic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:2938–2947
Tajima I, Yamamoto M (1987) Characterization of plasma polymers from tetramethylsilane, octamethylcyclotetrasiloxane, and methyltrimethoxysilane. J Polym Sci Polym Chem 25:1737–1744
Tian C, Liu X, Tan J, Lin S, Li D, Yang H (2012) Isolation, identification and characterization of an algicidal bacterium from Lake Taihu and preliminary studies on its algicidal compounds. J Environ Sci 24:1823–1831
Valdor R, Aboal M (2007) Effects of living cyanobacteria, cyanobacterial extracts and pure microcystins on growth and ultrastructure of microalgae and bacteria. Toxicon 49:769–779
Walker HL, Higginbotham LR (2000) An Aquatic bacterium that lyses cyanobacteria associated with off-flavor of channel catfish Ictalurus punctatus. Biol Control 18:71–78
Wang X, Cotter E, Iyer KN, Fang J, Williams BJ, Biswas P (2015) Relationship between pyrolysis products and organic aerosols formed during coal combustion. Proc Combust Inst 35:2347–2354
Worm J, Sondergaard M (1998) Dynamics of heterotrophic bacteria attached to Microcystis spp. (Cyanobacteria). Aquat Microb Ecol 14:19–28
Wu ZX, Song LR (2008) Physiological comparison between colonial and unicellular forms of Microcystis aeruginosa Kütz. (Cyanobacteria). Phycologia 47:98–104
Xu H, Yu G, Jiang H (2013) Investigation on extracellular polymeric substances from mucilaginous cyanobacterial blooms in eutrophic freshwater lakes. Chemosphere 93:75–81
Zhang M, Kong FX, Tan X, Yang Z, Cao HS, Xing P (2007) Biochemical, morphological, and genetic variations in Microcystis aeruginosa due to colony disaggregation. World J Microb Biotechnol 23:663–670
Zhang P, Zhai C, Wang X, Liu C, Jiang J, Xue Y (2013) Growth competition between Microcystis aeruginosa and Quadrigula chodatii under controlled conditions. J Appl Phycol 25:555–565
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. J. S. Owen for his constructive suggestions and professional editing, Mr Liang Chen for his help in revising the manuscript, and Dr. Yuan Niu and Juan Lin for their help in sample preparation. This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31400407), the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (Grant no. 2012ZX07105-004) and State Key Laboratory of freshwater ecology and biotechnology (2014FB15 and 2014FBZ02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, W., Shen, H., Shi, P. et al. Experimental evidence for the role of heterotrophic bacteria in the formation of Microcystis colonies. J Appl Phycol 28, 1111–1123 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-015-0659-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-015-0659-5