Abstract
Group social skills interventions (GSSIs) are a commonly offered treatment for children with high functioning ASD. We critically evaluated GSSI randomised controlled trials for those aged 6–25 years. Our meta-analysis of outcomes emphasised internal validity, thus was restricted to trials that used the parent-report social responsiveness scale (SRS) or the social skills rating system (SSRS). Large positive effect sizes were found for the SRS total score, plus the social communication and restricted interests and repetitive behaviours subscales. The SSRS social skills subscale improved with moderate effect size. Moderator analysis of the SRS showed that GSSIs that include parent-groups, and are of greater duration or intensity, obtained larger effect sizes. We recommend future trials distinguish gains in children’s social knowledge from social performance.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
The social difficulties in autism spectrum disorders (ASD) are characterized by deficits in social cognition, interaction and communication (American Psychiatric Association 2013). These deficits are often referred to collectively as social skills difficulties. The term social skills is a complex and multi-facetted construct.
Definitional Issues
Many competing definitions and theoretical models of social skills exist (Elliott and Gresham 1987; Gresham 1986; Merrell and Gimpel 2014; Nangle et al. 2010), but the core features invariably include behaviours that are performed in a social context (McFall 1982) and entail person to person engagement (Cordier et al. 2015).
Social skills deficits are an important target for intervention because they have a significant impact on academic, adaptive and psychological functioning (Coie et al. 1995; Elliott et al. 2001; Spence 1995). Group social skills interventions (GSSIs) are often recommended for children with high functioning ASD. As their name indicates they aim to improve social skills, suggesting that well-designed programmes aim to improve both social performance and social knowledge. Their use has increased substantially in the last 15 years (Volkmar et al. 2004; Reichow and Volkmar 2010; Reichow et al. 2012; Kasari et al. 2012; Matson et al. 2007).
The content, teaching strategy, mode of delivery and intensity of therapy provided by GSSIs is variable. Manualised group GSSIs typically include behavioural modelling of a specific social skill, practising the skill through role-play and individualised feedback on performance. Some teaching strategies are ‘didactic’, with structured lessons. Others elicit social skills through play; these are called ‘performance’ interventions (Kaat and Lecavalier 2014). The mode of delivery differs between GSSIs, and can require a combination of parent, peer or teacher involvement. Some programmes are intense, requiring 12 or more 90 min sessions, delivered weekly. Others require attendance at summer camps.
Effectiveness of GSSIs
Despite the popularity of GSSIs, evidence for their effectiveness is limited (Schneider 1992; Beelmann et al. 1994), in part because of weak study methodology (White et al. 2007; Cappadocia and Weiss 2011; Ferraioli and Harris 2011; Rao et al. 2008; Reichow and Volkmar 2010; McMahon et al. 2013). Objective analysis has been hindered because outcomes are often measured by just one mode (e.g. questionnaire or observation) and by a limited range of informants (often parents, and/or teachers). Both the choice of outcome measures and the choice of informants can influence expectancy biases and mask or exaggerate treatment effects (McMahon et al. 2013). Parents are the most commonly used informants, but their reports are prone to expectancy bias (McMahon et al. 2013). They may also find it difficult to characterise their child’s social limitations in comparison to other (typical) children (Schneider and Byrne 1989).
Besides parents, other potential sources of information about treatment effectiveness include ratings of outcomes by the participants themselves, the study’s own administrators, teachers, peers, study staff and blind observers. Teachers and blinded study administrative assessors can report on whether changes of performance generalise to other settings, outside the family (White et al. 2007; Gates et al. 2017). Self-report is particularly valuable to evaluate gains in social knowledge.
Outcome Measures
Whilst blind-rated observations of behavioural change are potentially the most objective measures of outcome, questionnaires are used more frequently (Kaat and Lecavalier 2014). Questionnaires can yield biased data, for instance if rated by parents who are subject to expectancy effects. For that reason, they are sometimes combined with cognitive measures, behavioural observations and sociometric tasks (McMahon et al. 2013; Kaat and Lecavalier 2014). Each mode of reporting has advantages and disadvantages. Observations invariably encompass only a brief period of data collection, in limited environments, so may lack external validity unless repeated observations are obtained in different settings. In contrast, self-report of increases in knowledge and parental-reports of behavioural change, whilst reflecting broader environmental contexts, are both subject to positive expectancy biases. Teacher reports, whilst less subject to expectancy bias, may in contrast reflect a lack of sensitivity to real change, due to limited opportunities to identify social behaviour and potential problems associated with their interpretation and scoring of measures.
Gresham (1997) made a useful distinction between social skills acquisition deficits (an individual lacks the knowledge to perform a social behaviour) and social skills performance deficits (the individual has relevant skills knowledge but fails to apply that knowledge in real-life situations). There is evidence to support a theoretical distinction between social performance and social knowledge (Lerner and Mikami 2012; Lerner et al. 2012; Lerner and White 2015).
Several recent reports have conducted meta-analyses on the effectiveness of GSSIs (Gates et al. 2017; Reichow et al. 2012). Reichow et al. (2012) found evidence for modest improvements in social competence on both parent-report measures and self-report measures of friendships. Gates et al. (2017) found self-reports of knowledge acquisition were associated with large effect sizes in contrast to small effect sizes for parent and observer reports of performance (both blinded and non-blinded). Non-significant effects were observed for teacher reports. The self-report effect sizes appeared to be driven by increases in social knowledge rather than improvements in social performance (Gates et al. 2017). As indicated, a risk with participants rating themselves is that they tend to overestimate perceived improvements in their social skills (Gates et al. 2017; Kaat and Lecavalier 2014).
In this review, the assessment of social skills acquisition is focused on changes in social performance as measured by parental report, because the GSSIs meeting our criteria for inclusion had in common parent-rated outcomes. We acknowledge that a more complete account would include social knowledge acquisition (Gresham 1997) but the relevant data were lacking. Parents are the most frequently used informants. Among parent-rated measures employed by studies of GSSI effectivness, the social responsiveness scale (SRS) (Constantino and Gruber 2012) and the social skills rating system (SSRS) (Gresham and Elliott 1990) predominate (Crowe et al. 2011; Kaat and Lecavalier 2014; Matson and Wilkins 2009).
To date, GSSI reviews have assumed that diverse social skills outcome measures reflect the same underlying constructs, hence they have assumed that it is legitimate to combine the scores of a wide range of different tools for the purpose of outcome analysis (Reichow et al. 2012; Gates et al. 2017). As discussed, because social skills encompass distinct dimensions of, at least, social knowledge and social performance, this approach is not ideal (Kaat and Lecavalier 2014). We have taken advantage of the fact there are recently published well-designed studies on performance change using the same outcome measures (SRS and/or the SSRS), hence an opportunity to conduct a new meta-analysis with higher internal validity.
Aims
In this review, we conducted a meta-analysis focussed on individual parent-report measures of outcome, with a focus on the degree to which change in SRS and/or SSRS scores is mediated by a GSSI.
There has been no systematic review of the GSSI teaching syllabus content (Koenig et al. 2009). Few manualised intervention programmes have been published, but it is thought that intervention-specific factors such as treatment duration, intensity, teaching strategy (e.g. didactic or performance) and parental involvement may moderate program success (Reichow et al. 2012; McMahon et al. 2013). We thus also aimed to evaluate whether intervention-specific factors such as type of parent group, method of delivery, or duration have a moderating impact on specific aspects of social knowledge or performance improvement, by means of moderation analysis.
We hypothesised that specific dimensions of social skills are responsive to specific aspects of GSSI, providing support for the relative strengths (and weaknesses) of different GSSI programmes.
Methods
Literature Search
Online electronic searches were conducted on the EMBASE, Medline (Ovid), PsycINFO and CINAHL databases in December 2016. Eligibility criteria included medical subject heading (MeSH) key terms including ‘social skills’ and ‘group interventions’, as well as filters for the age of participants (filters overlapping with a 6–25 years age range) and the language of publication (English language). The complete search strategy can be found in the supplementary materials. The reference lists of studies included in the electronic search were screened to identify additional studies.
Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
Systematic Review
Two independent reviewers (JW and EK) rated the abstracts against the eligibility criteria. Disagreements between reviewers were resolved through discussion. A third independent reviewer was available for further consultation if consensus could not be reached, but was not required. Published studies were eligible if they met the following criteria: (1) randomised control trials (RCT) using a delayed treatment control group (2) multi-modal group social skills intervention including two or more children delivered by professionals (3) participants aged 6–25 years (4) assessment of social skills using the SRS and/or SSRS (Box 1). Only RCTs employing a delayed treatment control group were retained to reduce heterogeneity and increase internal validity.
The exclusion criteria were: (1) interventions conducted or assessed in a language other than English (2) studies including children with intellectual disabilities (Verbal IQ < 70) (3) reviews, conference proceedings, abstracts, theses, or protocols. Studies that were not conducted and assessed in English were excluded in order to reduce the possibility of changes occurring due to translations or the cultural context. Studies including children with ID were also excluded to reduce sample heterogeneity.
Meta-analysis
The authors of studies using the SRS and/or SSRS were contacted for missing total and subscale scores.
Quality Assessment: Risk of Bias
Two reviewers (JW and EK) independently assessed the quality of eligible studies employing the Cochrane Collaboration Risk of Bias (RoB) v2 tool (Higgins 2016). The studies were assessed for bias in sequence generation, allocation concealment, baseline measurements, blinding or participants and personnel, blinding of outcome assessments, addressing incomplete outcomes, selective reporting and other potential biases (Higgins 2016) (Supplementary materials). Any disagreements between reviewers were resolved through discussion and consensus was reached on all ratings.
Data Extraction
Two reviewers independently extracted data (JW and EK) using a bespoke data extraction spreadsheet. The extraction spreadsheet is available from the authors upon request. Data were extracted on the intervention characteristics, patient characteristics, parental outcome measures used, and subsequent outcome scores. Authors were contacted for additional information when necessary.
Authors were contacted to provide total scores and subscale scores of the SRS and SSRS that were not published. The co-variates were the intervention type, duration (in hours), intensity (weekly vs summer camp), teaching strategy (didactic vs performance) and whether (yes/no) there was parental involvement in the intervention.
Data Analysis
Meta-analysis
Statistical analysis was conducted using STATA 14. The standardized mean difference (SMD) and 95% confidence interval for each outcome measure were used as a summary statistics. The post treatment measures of the treatment and delayed control groups were compared across studies. The SMD was interpreted as a small effect size for values of 0.20–0.50, moderate for values of 0.50–0.80, large for values of 0.80–1.30 and very large for values above 1.30 (Cohen 1988).
The random–effects model was used, as heterogeneity was suspected in the data. Heterogeneity was assessed using the Higgins heterogeneity I2 statistic. The degree of heterogeneity was considered low for values of 25–49%, moderate for values of 50–74% and high for values of 75% or more (Higgins et al. 2003). Statistically significant heterogeneity was assumed when p < 0.05.
Sensitivity Analyses
Publication bias was assessed using funnel plots with Egger’s test, and the trim and fill method (Egger et al. 1997).
Results
Study Selection
Systematic Review
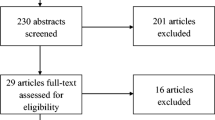
The electronic search returned 593 articles after duplicates were removed. Additional articles were identified through correspondence with authors and by screening reference lists of review articles picked up in the initial screening search. Studies were excluded if they did not fit the inclusion criteria or did not fit this review’s definition of group social skills interventions (Fig. 1). The screening process reduced the number of eligible articles to 123 that were fully assessed for eligibility. 10 studies that met criteria for eligibility were retained for qualitative synthesis.
Meta-analysis
The use of outcome measures was assessed in the 10 studies retained for qualitative synthesis. The authors were contacted for unpublished total and subscale scores. Following this correspondence there were sufficient data to conduct meta-analyses on 8 studies (5 used the SRS, 1 used the SSRS and 2 used both the SRS and SSRS).
Qualitative Synthesis
Intervention Characteristics
Five different types of intervention programmes were used, including established protocols such as PEERS, Children’s Friendship Training, summerMAX and SENSE Theatre; as well as an unnamed manualised Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT) social skills programme. The programmes varied by teaching strategy, parent assistance, duration and intensity (Table 1). All but one of the programmes (SENSE Theatre) took a didactic teaching approach. SENSE theatre was the only GSSI to employ a performance teaching strategy.
All GSSIs ran children groups, most interventions also ran parallel parent groups. Only the SENSE Theatre and the unnamed CBT social skills programme did not run parent groups (the CBT intervention did provide a handout for parents). The summerMAX and the SENSE Theatre programmes ran intense summer-camp style interventions where participants were required to attend 4–5 h of training 5 days a week for 2–5 weeks. The other programmes were less intensive and comprised 60–90 min sessions once a week for 10–16 weeks.
The syllabuses of GSSIs varied. Each GSSI emphasised different domains of social skills. These included social knowledge, social communication, social cognition and social emotions. Specifically, the interventions taught social rules and social cues, pragmatic language skills, cognitive social skills including problem solving, cognitive flexibility, social perception and/or perspective taking. All but PEERS taught non-verbal skills, such as social eye contact, facial expression, posture and social distance. Only the summerMAX programme focussed explicitly on self-perception (e.g. understanding one’s own emotions). Only SENSE theatre and PEERS addressed the issue of affect regulation (e.g. how to be a good sport, controlling emotional impulses or anxiety).
Assessment Characteristics
Although the programmes selected for this meta-analysis must have employed the SRS/SSRS, other parent-rated measures included the adapted skillstreaming checklist (ASC), the empathy (EQ) and the behavior assessment system for children–parent rating scales (BASC-PRS-2) (Table 2). We have not examined the psychometric properties of any of these assessment instruments in detail (see Cordier et al. 2015; Matson and Wilkins 2009 for comprehensive reviews).
All of the studies retained for qualitative synthesis used more than one type of informant, not only parents but also the participants themselves, study staff and teachers (Table 2). Two studies reported only on questionnaires completed by parents and participants; five used socio-cognitive tasks and three used an idiomatic language task with participants. Four used self-report questionnaires in conjunction with a socio-cognitive or idiomatic language task. None used validated self-report questionnaires in conjunction with socio-cognitive tasks; participants are best placed to report on changes in their social knowledge, implying the GSSI studies reviewed here may not be capturing changes in this social skills dimension.
Two studies used teacher-report measures (SRS and SSRS). Two also used observation schedules to measure social performance. Participants were filmed interacting with confederate peers, one was blind-rated. The studies that used staff questionnaires administered satisfaction surveys that were not validated; the questionnaires were completed by non-blind observers.
Quality Assessment: Risk of Bias
A ‘risk of bias’ analysis was conducted on all the RCTs (Table 3). Two studies obtained a ‘high risk’ rating in four or more of the seven risk of bias criteria; these will be discussed separately. All others obtained a ‘low risk’ or ‘unclear’ rating for the sequence generation and allocation concealment criteria. The incomplete blinding of outcome by participants, personnel and outcome assessors conferred a ‘high risk’ for all of the studies. A few studies did employ observational outcome measures (where the coders were blind to the participants’ group status) but these were always used in conjunction with outcome measures where the assessors were not blind. The incomplete-outcome criteria were rated ‘high risk’ for two-thirds of the studies, because of participant attrition from either or both the waitlist control and the intervention groups. The selective-outcome reporting criterion was rated ‘low risk’ in all studies. No other sources of bias were detected.
Two studies, (Corbett et al. 2016; Waugh and Peskin 2015) obtained more ‘high risk’ ratings than others reviewed here. The Waugh and Peskin (2015) study scored ‘high risk’ for all except selective-outcome reporting criteria. The baseline measures were ‘high risk’ because SRS scores differed significantly at baseline between the control and experimental groups, and this study was excluded from the meta-analysis. The Corbett study obtained a ‘high risk’ rating for the baseline measurements criteria due to a discrepancy between control and experimental groups on two outcome measures (theory of mind and delayed faces memory). As this baseline discrepancy did not affect the SRS or SSRS scores, the Corbett study was retained for analysis.
Meta-analysis
Social Responsiveness Scale (SRS)
A comparison of the treatment and control groups’ post-intervention scores showed GSSI participants obtained better outcomes than controls, with a substantial reduction in SRS total scores (SMD = − 0.85, 95% CI [− 1.12,− 0.59], Z = 6.35, p = 0.000; Fig. 2; Table 4). This is a significant (p < 0.0001) and large effect size.
GSSI participants also improved on all SRS subscales, relative to controls (Table 5). The effect sizes for the social awareness (SMD = − 0.57, 95% CI [− 0.87,− 0.28], Z = 3.78, p = 0.000), social cognition (SMD = − 0.53, 95% CI [− 0.98,− 0.09], Z = 2.34, p = 0.019) and social motivation subscales (SMD = − 0.55, 95% CI [− 1.02,− 0.07], Z = 2.27, p = 0.023) were moderate. The effect sizes on the social communication (SMD = − 0.89, 95% CI [− 1.2,− 0.59], Z = 5.71, p = 0.000) and restricted interests and repetitive behaviours subscales (SMD = − 0.9, 95% CI [− 1.23,− 0.57], Z = 5.4, p = 0.000) were large. All subscale effect sizes were significant (p < 0.05).
Koning et al. (2013; Fig. 3) was the only study not to report improvement in the social cognition subscale.
Forest plot of SRS social cognition subscale scores. Schohl et al. 2014 cognition subscales were not included in the analysis as the source data was not available
Social Skills Rating System (SSRS)
GSSI participants improved relative to controls on the social skills subscale (SMD = 0.56, 95% CI [0.18,0.95], Z = 2.86, p = 0.004) and had better outcomes on the problem behaviours subscale (SMD = − 0.55, 95% CI [− 1.13,0.03], Z = 1.86, p = 0.06; Fig. 4). The effect size for both subscales was moderate, but only the social skills subscale effect was significant.
Moderator Analysis
Moderator analyses was conducted on the SRS. There were insufficient studies to conduct moderator analyses on the SSRS.
SRS Group Analysis by Intervention
A post-hoc analysis analysed group differences on the total SRS scores by separating studies according to intervention type (Fig. 5). There was no statistical difference in the total SRS scores between the treatment and control group for the SENSE theatre (p = 0.06) or the CBT social skills intervention (p = 0.39), but sample size was small so there was a potential Type II error. The SENSE theatre intervention obtained a moderate effect size (SMD = − 0.72, 95% CI [− 1.46,0.03], Z = 1.88); the CBT intervention had a small effect size (SMD = − 0.45, 95% CI [− 1.48,0.58], Z = 0.86).
summerMAX was used in 3 studies and PEERS was used in 2 studies. Participants receiving these interventions obtained better outcomes than controls (p < 0.0001). Both summerMAX (SMD = − 0.93, 95% CI [− 1.36,− 0.5], Z = 4.22) and PEERS (SMD = − 0.84, 95% CI [− 1.32,− 0.37], Z = 3.49) obtained large and significant effect sizes.
SRS Group Analysis by Parent Involvement
A group analysis was conducted on the total SRS score according to parent involvement. Participants performed better than controls regardless of whether they took part in an intervention that delivered concurrent parent groups, both effect sizes were significant (parent group p < 0.0001; no parent group p = 0.04). The GSSIs that delivered parent groups had a large effect size (SMD = − 0.91, 95% CI [− 1.20,− 0.61], Z = 6.08) whereas the GSSI that did not deliver parent groups had a moderate effect size (SMD = − 0.63, 95% CI [− 1.23,− 0.02], Z = 2.03; Fig. 6).
SRS Group Analysis by Intensity and Duration
Group analyses were conducted for the intensity and duration of GSSIs on total SRS scores (Fig. 6). The effect sizes in both the intensity and duration group analyses were significant (p < 0.0001). The more intensive GSSIs which took a summer camp format had a large effect size (SMD = − 0.90, 95% CI [− 1.23,− 0.57], Z = 5.3), whereas the GSSI taking place once a week had a moderate effect size (SMD = − 0.77, 95% CI [− 1.21,− 0.34], Z = 3.35).
GSSIs groups to examine the effect of duration of intervention as a co-variate were created with a median split. The GSSIs which required over 40 h of contact time also had a large effect size (SMD> 40 h = − 0.93, 95% CI [− 1.36,− 0.50], Z = 4.22), whereas those requiring 40 h and under had a moderate effect size (SMD< 40 h = − 0.76, 95% CI [− 1.13,− 0.39], Z = 4.00; Fig. 6).
Heterogeneity
Heterogeneity was assessed using the I2 statistic. The heterogeneity in the data was low to moderate, ranging from 0 to 58.2%. However, results did not differ across random and fixed effect models.
Publication Bias
Egger’s regression test and the trim and fill method showed that there was no evidence of substantial publication bias.
Discussion
Our systematic review of RCTs using multi-modal GSSIs has shown that studies use a variety of social skills measures, assessment types and informants. There was a predominant reliance on parent-report and self-report assessments of effectiveness, both prone to expectancy bias. Even when evidence of outcome was obtained from external observers such as support staff or teachers, these observers were seldom blind to treatment group. In future, evaluations of GSSI should employ blind-rated observer-reports (of performance). There is currently a lack of validated participant self-reports (of increase in social skills knowledge), yet previous meta-analyses of social knowledge improvement indicate this may be one of the main gains from group social skills interventions (Gates et al. 2017).
Evidence of the effectiveness of interventions from the meta-analysis of the SRS indicated treatments do bring about a significant reduction in autistic traits as measured by total and subscale scores, by parental report. Large effect sizes were found in terms of improved Social Communication, and reduced Restricted Interests and Repetitive Behaviour (RRB). The Social Communication scale of the SRS is intended to capture ‘expressive social communication [and] “motoric” aspects of reciprocal social behaviour’ (Constantino and Gruber 2012). Both subscales were derived from clinical definitions, rather than factor analysis, and reflect the main components of DSM-5 diagnostic criteria for Autism Spectrum Disorders.
Moderate effect sizes for improvement following intervention, explicitly in terms of social skills, were found for the Social Skills subscale of the SSRS, which measures cooperation, empathy, assertion, self-control and responsibility. Unfortunately, there were insufficient data available to enable further analysis of the Social Skills subscale, as it would have been interesting to see which items contributed the most to the significant changes in behaviour. The Problem Behaviours subscale of the SSRS measures internalising and externalising behaviours, and hyperactivity; no significant change was found in these behaviours.
Despite the differences in the social skills domains taught in GSSIs, the syllabuses did overlap in some key areas. For instance, they all aimed to improve social communication skills, and evidence from this review that Social Communication does improve significantly could have been anticipated. However, improvements on the RRB subscale of the SRS were unexpected; no teaching materials reviewed here explicitly target RRB. Perhaps the cognitive and emotional skills taught during GSSIs, such as cognitive flexibility, problem solving or controlling emotional impulses are mediating this change. Consequently, participants become more confident and less anxious in social situations, which in turn reduces their anxiety-related restrictive and repetitive behaviours (Rodgers et al. 2012). Also, participants may learn that restrictive and repetitive behaviours are socially inappropriate, and consequently they conceal them, a hypothesis that is consistent with the moderate effect size obtained on the Social Awareness subscale. Evidence from previous meta-analyses of GSSI shows increases in social knowledge drive effect sizes in self-report measures of social skills (Gates et al. 2017).
Moderator analysis was only possible for studies in which the SRS was the outcome measure. A group analysis compared interventions that delivered concurrent parent groups, with those that did not. We found that GSSIs that included parent groups were more effective, associated with a large (compared with a moderate) effect size. Parents who attend GSSIs might display positive response biases (McMahon, Lerner et al., 2013), but parent involvement in treatment can nevertheless consolidate the social behaviours and knowledge acquired by their child, and help support the formation of appropriate peer networks (Laugeson and Frankel 2011).
Not all GSSI programmes reduced autistic traits (as measured by SRS total scores). The PEERS and summerMAX programmes obtained significant and large effect sizes compared to the SENSE Theatre and CBT social skills interventions (though associated with less power to detect benefit) which obtained small to moderate and non-significant effects effect sizes.
More intensive and longer-lasting interventions had slightly larger effect sizes. The cost-benefit comparison between programmes is hard to interpret. For instance, whereas the PEERS intervention is demanding in terms of participant and interventionist time, it may nevertheless be a more cost-effective choice as it is easier to implement with less resources than the summerMAX programme. Only one out of the six interventions employed a performance-based teaching strategy, therefore a comparison between didactic and performance based interventions was not possible.
Conclusion
A recent increase in methodological rigour in GSSI RCTs, and the use of common instruments to assess outcomes, has presented an opportunity to examine the effectiveness of social-skills interventions in a multi-dimensional context. Understanding what works for whom will be key to the future personalisation of GSSIs, improving the efficacy of GSSI programmes. Examining which social performance and social knowledge characteristics are responsive to specific GSSI design features is critical to unlocking our understanding of the active ingredients of social skills instruction. We need to develop more sensitive tools in order comprehensively to capture how treatments impact on the multi-dimensional nature of social skills.
References
American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (DSM-5®): American Psychiatric Pub.
Beelmann, A., Pfingsten, U., & Lösel, F. (1994). Effects of training social competence in children: A meta-analysis of recent evaluation studies. Journal of Clinical Child Psychology, 23(3), 260–271.
Cappadocia, M. C., & Weiss, J. A. (2011). Review of social skills training groups for youth with Asperger syndrome and high functioning autism. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders, 5(1), 70–78.
Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences Lawrence Earlbaum Associates. Hillsdale, NJ, pp. 20–26.
Coie, J., Terry, R., Lenox, K., Lochman, J., & Hyman, C. (1995). Childhood peer rejection and aggression as predictors of stable patterns of adolescent disorder. Development and Psychopathology, 7(04), 697–713.
Constantino, J., & Gruber, C. (2012). Social Responsiveness Scale, (SRS-2) (Western Psychological Services, Torrance, CA).
Corbett, B. A., Key, A. P., Qualls, L., Fecteau, S., Newsom, C., Coke, C., et al. (2016). Improvement in social competence using a randomized trial of a theatre intervention for children with autism spectrum disorder. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 46(2), 658–672.
Cordier, R., Speyer, R., Chen, Y.-W., Wilkes-Gillan, S., Brown, T., Bourke-Taylor, H., et al. (2015). Evaluating the psychometric quality of social skills measures: a systematic review. PLoS ONE, 10(7), e0132299.
Crowe, L., Beauchamp, M., Catroppa, C., & Anderson, V. (2011). Social function assessment tools for children and adolescents: A systematic review from 1988 to 2010. Clinical Psychology Review, 31(5), 767–785.
Egger, M., Smith, G. D., Schneider, M., & Minder, C. (1997). Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ, 315(7109), 629–634.
Elliott, S. N., & Gresham, F. M. (1987). Children’s social skills: Assessment and classification practices. Journal of Counseling & Development, 66(2), 96–99.
Elliott, S. N., Malecki, C. K., & Demaray, M. K. (2001). New directions in social skills assessment and intervention for elementary and middle school students. Exceptionality, 9(1–2), 19–32.
Ferraioli, S. J., & Harris, S. L. (2011). Treatments to increase social awareness and social skills. Evidence-based practices and treatments for children with autism (pp. 171–196). Springer, New York.
Gantman, A., Kapp, S. K., Orenski, K., & Laugeson, E. A. (2012). Social skills training for young adults with high-functioning autism spectrum disorders: A randomized controlled pilot study. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 42(6), 1094–1103.
Gates, J. A., Kang, E., & Lerner, M. D. (2017). Efficacy of group social skills interventions for youth with autism spectrum disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clinical Psychology Review.
Gresham, F. M. (1986). Conceptual issues in the assessment of social competence. In Children’s social behavior: Development, assessment, and modification (pp. 143–179). Elsevier, New York.
Gresham, F. M. (1997). Social competence and students with behavior disorders: Where we’ve been, where we are, and where we should go. Education and Treatment of Children, 233–249.
Gresham, F. M., & Elliott, S. N. (1990). Social skills rating system: Manual: American Guidance Service.
Higgins, J. (2016). Green S. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. The Cochrane Collaboration. 2011. Version.
Higgins, J. P., Thompson, S. G., Deeks, J. J., & Altman, D. G. (2003). Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ: British Medical Journal, 327(7414), 557.
Kaat, A. J., & Lecavalier, L. (2014). Group-based social skills treatment: a methodological review. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders, 8(1), 15–24.
Kasari, C., Rotheram-Fuller, E., Locke, J., & Gulsrud, A. (2012). Making the connection: Randomized controlled trial of social skills at school for children with autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 53(4), 431–439.
Koenig, K., De Los Reyes, A., Cicchetti, D., Scahill, L., & Klin, A. (2009). Group intervention to promote social skills in school-age children with pervasive developmental disorders: Reconsidering efficacy. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 39(8), 1163–1172.
Koning, C., Magill-Evans, J., Volden, J., & Dick, B. (2013). Efficacy of cognitive behavior therapy-based social skills intervention for school-aged boys with autism spectrum disorders. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders, 7(10), 1282–1290.
Laugeson, E. A., & Frankel, F. (2011). Social skills for teenagers with developmental and autism spectrum disorders: The PEERS treatment manual. Routledge.
Laugeson, E. A., Frankel, F., Mogil, C., & Dillon, A. R. (2009). Parent-assisted social skills training to improve friendships in teens with autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 39(4), 596–606.
Laugeson, E. A., Gantman, A., Kapp, S. K., Orenski, K., & Ellingsen, R. (2015). A randomized controlled trial to improve social skills in young adults with autism spectrum disorder: The UCLA PEERS® Program. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 45(12), 3978–3989.
Lerner, M. D., & Mikami, A. Y. (2012). A preliminary randomized controlled trial of two social skills interventions for youth with high-functioning autism spectrum disorders. Focus on Autism and Other Developmental Disabilities, 27(3), 147–157.
Lerner, M. D., & White, S. W. (2015). Moderators and mediators of treatments for youth with autism spectrum disorders. Moderators and mediators of youth treatment outcomes, 146.
Lerner, M. D., White, S. W., & McPartland, J. C. (2012). Mechanisms of change in psychosocial interventions for autism spectrum disorders. Dialogues in Clinical Neuroscience, 14(3), 307.
Lopata, C., Thomeer, M. L., Volker, M. A., Toomey, J. A., Nida, R. E., Lee, G. K., et al. (2010). RCT of a manualized social treatment for high-functioning autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 40(11), 1297–1310.
Matson, J. L., Matson, M. L., & Rivet, T. T. (2007). Social-skills treatments for children with autism spectrum disorders an overview. Behavior Modification, 31(5), 682–707.
Matson, J. L., & Wilkins, J. (2009). Psychometric testing methods for children’s social skills. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 30(2), 249–274.
McFall, R. M. (1982). A review and reformulation of the concept of social skills. Behavioral Assessment.
McMahon, C. M., Lerner, M. D., & Britton, N. (2013). Group-based social skills interventions for adolescents with higher-functioning autism spectrum disorder: a review and looking to the future. Adolescent Health, Medicine and Therapeutics, 4(23), 9.
Merrell, K. W., & Gimpel, G. (2014). Social skills of children and adolescents: Conceptualization, assessment, treatment: Psychology Press, Hove.
Nangle, D. W., Grover, R. L., Holleb, L. J., Cassano, M., & Fales, J. (2010). Defining competence and identifying target skills. Practitioner’s Guide to Empirically Based Measures of Social Skills (pp. 3–19). Springer, New York.
Rao, P. A., Beidel, D. C., & Murray, M. J. (2008). Social skills interventions for children with Asperger’s syndrome or high-functioning autism: A review and recommendations. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 38(2), 353–361.
Reichow, B., Steiner, A. M., & Volkmar, F. (2012). Social skills groups for people aged 6 to 21 with autism spectrum disorders (ASD). Evidence-Based Child Health: A Cochrane Review Journal, 7, 266–315.
Reichow, B., & Volkmar, F. R. (2010). Social skills interventions for individuals with autism: Evaluation for evidence-based practices within a best evidence synthesis framework. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 40(2), 149–166.
Rodgers, J., Glod, M., Connolly, B., & McConachie, H. (2012). The relationship between anxiety and repetitive behaviours in autism spectrum disorder. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 42(11), 2404–2409.
Schneider, B. H. (1992). Didactic methods for enhancing children’s peer relations: A quantitative review. Clinical Psychology Review, 12(3), 363–382.
Schneider, B. H., & Byrne, B. M. (1989). Parents rating children’s social behavior: How focused the lens? Journal of Clinical Child Psychology, 18(3), 237–241.
Schohl, K. A., Van Hecke, A. V., Carson, A. M., Dolan, B., Karst, J., & Stevens, S. (2014). A replication and extension of the PEERS intervention: Examining effects on social skills and social anxiety in adolescents with autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 44(3), 532–545.
Spence, S. H. (1995). Social skills training: Enhancing social competence with children and adolescents: Nfer-Nelson, Windsor.
Thomeer, M. L., Lopata, C., Donnelly, J. P., Booth, A., Shanahan, A., Federiconi, V., et al. (2016). Community effectiveness RCT of a comprehensive psychosocial treatment for high-functioning children with ASD. Journal of Clinical Child & Adolescent Psychology, 1–12.
Thomeer, M. L., Lopata, C., Volker, M. A., Toomey, J. A., Lee, G. K., Smerbeck, A. M., et al. (2012). Randomized clinical trial replication of a psychosocial treatment for children with high-functioning autism spectrum disorders. Psychology in the Schools, 49(10), 942–954.
Thompson, S. G., & Higgins, J. (2002). How should meta-regression analyses be undertaken and interpreted? Statistics in Medicine, 21(11), 1559–1573.
Volkmar, F. R., Lord, C., Bailey, A., Schultz, R. T., & Klin, A. (2004). Autism and pervasive developmental disorders. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 45(1), 135–170.
Waugh, C., & Peskin, J. (2015). Improving the social skills of children with HFASD: An intervention study. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 45(9), 2961–2980.
White, S. W., Keonig, K., & Scahill, L. (2007). Social skills development in children with autism spectrum disorders: A review of the intervention research. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 37(10), 1858–1868.
Acknowledgments
Thank you to the Child Health Research CIO for supporting this research.
Funding
This study was funded by the Child Health Research Charitable Incorporated Organisation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JW, WM and DS designed and directed the study. JW and EK conducted the systematic review screening. JW and LR conducted the statistical analysis. JW and DS wrote the manuscript. JW, SR, WM and DS contributed to critical revisions.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Wolstencroft, J., Robinson, L., Srinivasan, R. et al. A Systematic Review of Group Social Skills Interventions, and Meta-analysis of Outcomes, for Children with High Functioning ASD. J Autism Dev Disord 48, 2293–2307 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-018-3485-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-018-3485-1