Abstract
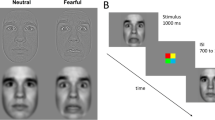
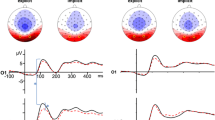
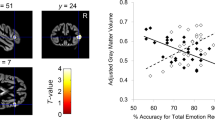
FMRI was performed with the dynamic facial expressions fear and happiness. This was done to detect differences in valence processing between 25 subjects with autism spectrum disorders (ASDs) and 27 typically developing controls. Valence scaling was abnormal in ASDs. Positive valence induces lower deactivation and abnormally strong activity in ASD in multiple regions. Negative valence increased deactivation in visual areas in subjects with ASDs. The most marked differences between valences focus on fronto-insular and temporal regions. This supports the idea that subjects with ASDs may have difficulty in passive processing of the salience and mirroring of expressions. When the valence scaling of brain activity fails, in contrast to controls, these areas activate and/or deactivate inappropriately during facial stimuli presented dynamically.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AS:
-
Asperger syndrome
- ADI-R:
-
Autism diagnostic interview-revised
- ADOS:
-
Autism diagnostic observation schedule
- ASDs:
-
Autism spectrum disorders
- ASSQ:
-
Autism spectrum screening questionnaire
- AROUSAL:
-
Dimension refers to the intensity of emotions, varying from very low to very high
- BOLD:
-
Blood oxygenation level-dependent
- EK:
-
Ekman’s collections
- fMRI:
-
Functional magnetic resonance imaging
- HFA:
-
High functioning autism
- K-SADS-PL:
-
Schedule for affective disorders and schizophrenia for school-age children-present and lifetime version
- MNS:
-
Mirror neuron system
- MNI:
-
Montreal neurological institute
- TD:
-
Typically developing
- TKK:
-
“Helsinki University of Technology (TKK) video sequence collection”
References
Adolphs, R. (2002). Recognizing emotion from facial expressions: Psychological and neurological mechanisms. Behavioral and Cognitive Neuroscience Reviews, 1, 21–62.
Adrien, J. L., Perrot, A., Sauvage, D., Leddet, I., Larmande, C., Hameury, L., et al. (1992). Early symptoms in autism from family home movies. Evaluation and comparison between 1st and 2nd year of life using I.B.S.E. scale. Acta Paedopsychiatrica, 55(2), 71–75.
Adrien, J. L., Lenoir, P., Martineau, J., Perrot, A., Hameury, L., Larmande, L., et al. (1993). Blind ratings of early symptoms of autism based upon family home movies. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 32(3), 617–626.
American Psychiatric Association (APA). (2000). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders: DSM-IV-TR (fourth edition, text revision). Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association.
Baranek, G. T. (1999). Autism during Infancy: A retrospective video analysis of sensory-motor and social behaviors at 9–12 months of age. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 29(3), 213–224.
Behrmann, M., Cibu, T., & Humphreys, K. (2006). Seeing it differently: Visual processing in autism. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 10(6), 259–264.
Best, C. T., Womer, J. S., & Queen, H. F. (1994). Hemispheric asymmetries in adults’ perception of infant emotional expressioins. Journal of Experimental Psychology Human Perc Performance, 20, 751–765.
Caron, M.-J., Mottron, L., Berthiaume, C., & Dawson, M. (2006). Cognitive mechanism, specificity and neural underpinnings of visuo-spatial peaks in autism. Brain, 129, 1789–1802.
Dahlgren, S. O., & Gillberg, C. (1989). Symptoms in the first two years of life. A preliminary population study of infantile autism. European Archives of Psychology and Neurological Sciences, 238, 169–174.
Dapretto, M., Davies, M. S., Pfeifer, J. H., Scott, A. A., Sigman, M., Bookheimer, S. Y., et al. (2006). Understanding emotions in others: Mirror neuron dysfunction in children with autism spectrum disorders. Natural Neuroscience, 9(1), 28–30.
Davidson, R. J., & Irwin, W. (1999). The functional neuroanatomy of emotion and affective style. Trends in cognitive sciences, 3(1), 11–21.
De Vignemont, F., & Singer, T. (2006). The empathic brain: How, when and why? Trends in Cognitive Science, 10(10), 435–441.
Deruelle, C., Hubert, B., Santos, A., & Wicker, B. (2008). Negative emotion does enhance recall skills in adults with autistic spectrum disorders. Autism Research, 1(2), 91–99.
Dinstein, I., Thomas, C., Behrmann, M., & Heeger, D. J. (2008). A mirror up to nature. Current Biology, 18(1), 13–18.
Ehlers, S., Gillberg, C., & Wing, L. (1999). A screening guestionnaire for asperger syndrome and other high-functioning autism spectrum disorders in school age children. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 29(2), 129–141.
Ekman, P., & Friesen, W. V. (1978). Pictures of facial affect. Palo Alto, CA: Consulting Psychologist Press.
Freyd, J. (1987). Dynamic mental representations. Psychological Review, 94, 427–438.
Gopnik, A., & Meltzoff, A. N. (1994). Minds, bodies and persons: Young children’s understanding of the self and others as reflected in imitation and “theory of mind” research. In S. Parker & R. Mitchell (Eds.), Self-awareness in animals and humans. New York: Cambridge University Press.
Hadjikhani, N., Joseph, R. M., Snyder, J., & Tager-Flusberg, H. (2006). Anatomical differences in the mirror neuron system and social cognition network in autism. Cerebral Cortex, 16(9), 1276–1282.
Hadjikhani, N., Joseph, R. M., Snyder, J., & Tager-Flusberg, H. (2007). Abnormal activation of the social brain during face perception in autism. Human Brain Mapping, 28(5), 441–449.
Hari, R., & Kujala, M. V. (2010). Brain basis of human social interaction: From concepts to brain imaging. Physiological Reviews, 89, 453–479. doi:10.1152/physrev.00041.2007.
Iacoboni, M. (2005). Neural mechanisms of imitation. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 15(6), 632–637.
Iacoboni, M., Woods, R. P., Brass, B., Bekkering, H., Mazziotta, J. C., & Rizzolatti, G. (1999). Cortical mechanisms of human imitation. Science, 286(5449), 2526–2528.
Jansson-Verkasalo, E., Kujala, T., Jussila, K., Mattila, M.-L., Moilanen, I., Näätänen, R., et al. (2005). Similarities in the phenotype of the auditory neural substrate in children with Asperger syndrome and their parents. European Journal of Neuroscience, 22(4), 986–990.
Jenkinson, M., & Smith, S. M. (2001). A Global optimisation method for robust affine registration of brain images. Medical Image Analysis, 5(2), 143–156.
Jenkinson, M., Bannister, P., Brady, M., & Smith, S. M. (2002). Improved optimization for the robust and accurate linear registration and motion correction of brain images. Neuroimage, 17, 825–841.
Johnson, M. H., Griffin, R., Csibra, G., Halit, H., Farroni, T., de Haan, M., et al. (2005). The emergence of the social brain network: Evidence from typical and atypical development. Development and Psychopathology, 17, 599–619.
Johnson-Frey, S., Maloof, F., Newman-Norlund, R., Farrer, C., Inati, S., & Grafton, S. (2003). Actions or hand-object interactions human inferior frontal cortex and action observation. Neuron, 39(6), 1053–1058.
Joseph, R. M., & Tanaka, J. (2003). Holistic and part-based face recognition in children with autism. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 34, 199–210.
Kadesjo, B., Gillberg, C., & Hagberg, B. (1999). Brief report: Autism and Asperger syndrome in seven-year-old children: A total population study. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 29, 327–331.
Kätsyri J. (2006). Human Recognition of Basic Emotions from Posed and Animated Dynamic Facial Expressions. Helsinki University of Technology. Dissertation in PDF format (ISBN 951-22-8538-X).
Kätsyri, J. &, Sams, M. (2008). The effect of dynamics on identifying basic emotions from synthetic and natural faces. International Journal of Human-Computer Studies, 66(4), 233–242. URL: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhcs.2007.10.001.
Kaufman, J., Birmaher, B., Brent, D., Rao, U., Flynn, C., Moreci, P., et al. (1997). Schedule for affective disorders and schizophrenia for school-age children-present and lifetime version (K-SADS-PL): Initial reliability and validity data. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 36(7), 980–988.
Kennedy, D. P., Redcay, E., & Courchesne, E. (2006). Failing to deactivate: Resting functional abnormalities in autism. PNAS, 103(21), 8275–8280.
Kientz, M. A., & Dunn, W. (1997). A comparison of the performance of children with and without autism on the sensory profile. American Journal of Occupational Therapy, 51(7), 530–537.
Kuusikko, S., Pollock-Wurman, R., Jussila, K., Carter, A. S., Mattila, M. L., Ebeling, H., et al. (2008). Social anxiety in high-functioning children and adolescents with autism and asperger syndrome. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 38(9), 1697–1709.
Kuusikko, S., Haapsamo, H., Jansson-Verkasalo, E., Hurtig, T., Mattila, M. L., Ebeling, H., et al. (2009). Emotion recognition in children and adolescents with autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 39(6), 938–945.
LaBar, K. S., Crupain, M. J., Voyvodic, J. T., & McCarthy, G. (2003). Dynamic perception of facial affect and identity in the human brain. Cerebral Cortex, 13(10), 1023–1033.
Lord, C., Rutter, M., & LeCouteur, A. (1995). Autism diagnostic interview–revised (3rd ed.). Los Angeles: Western psychological services.
Lord, C., Rutter, M., DiLavore, P. C., & Risi, S. (2000). Autism diagnostic observation schedule (ADOS). Los Angeles: Western Psychological Services.
Mattila, M. L., Kielinen, M., Jussila, K., Linna, S. L., Bloigu, R., Ebeling, H., et al. (2007). An epidemiological and diagnostic study of Asperger syndrome according to four sets of diagnostic criteria. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 46(5), 636–646.
Mattila, M. L., Jussila, K., Kuusikko, S., Kielinen, M., Linna, S. L., Ebeling, H., et al. (2009). When does the autism spectrum screening questionnaire (ASSQ) predict autism spectrum disorders in primary school-aged children? European Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 18(8), 499–509.
Mattila, M. L., Hurtig, T., Haapsamo, H., Jussila, K., Kuusikko-Gauffin, S., Kielinen, M., et al. (2010). Comorbid psychiatric disorders associated with asperger syndrome/high-functioning autism: A community- and clinic-based study. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 40(9), 1080–1093.
Mattila, M. L., Kielinen, M., Linna, S. L., Jussila, K., Ebeling, H., Bloigu, R., et al. (2011). Autism spectrum disorders according to DSM-IV-TR and comparison with DSM-5 draft criteria: An epidemiological study. Journal of the American Academy Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 50(6), 583–592.
Morris, J., Ohman, A., & Dolan, R. (1998). Conscious and unconscious emotional learning in the human amygdala. Nature, 393, 467–470.
Morris, J. S., Ohman, A., & Dolan, R. J. (1999). A subcortical pathway to the right amygdale mediating “unseen” fear. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, 96, 1680–1685.
Nomura, M., Ohira, H., Haneda, K., Iidaka, T., Sadato, N., Okada, T., et al. (2004). Functional association of the amygdala and ventral prefrontal cortex during cognitive evaluation of facial expressions primed by masked angry faces: An event-related fMRI study. NeuroImage, 21(1), 352–363.
Osterling, J., & Dawson, G. (1994). Early recognition of children with autism: A study of first birthday home videotapes. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorder, 24, 247–257.
Paakki, J. J., Rahko, J., Long, X., Moilanen, I., Tervonen, O., Nikkinen, J., et al. (2010). Alterations in regional homogeneity of resting-state brain activity in autism spectrum disorders. Brain Research, 1321, 169–179.
Pelphrey, K. A., Morris, J. P., McCarthy, G., & Labar, K. L. (2007). Perception of dynamic changes in facial affect and identity in autism. Social cognitive and affective neuroscience, 2(2), 140–149.
Pfeifer, J. H., Iacoboni, M., Mazziotta, J. C., & Dapretto, M. (2008). Mirroring others’ emotions relates to empathy and interpersonal competence in children.”. NeuroImage, 39(4), 2076–2085.
Rahko, J., Paakki, J. J., Starck, T., Nikkinen, J., Remes, J., Hurtig, T., et al. (2010). Functional mapping of dynamic happy and fearful facial expression processing in adolescents. Brain Imaging and Behavior, 4(2), 164–176.
Rubenstein, J. L., & Merzenich, M. M. (2003). Model of autism: Increased ratio of excitation/inhibition in key neural systems. Genes Brain Behaviour, 2, 255–267.
Russell, J. A., & Barrett, L. F. (1999). Core affect, prototypical emotional episodes, and other things called emotion: Dissecting the elephant. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 76, 805–829.
Sato, W., & Aoki, S. (2006). Right hemispheric dominance in processing of unconscious negative emotion. Brain Cognitive, 62(3), 261–266.
Sato, W., Kochiyama, T., Yoshikawa, S., Naito, E., & Matsumura, M. (2004). Enhanced neural activity in response to dynamic facial expressions of emotion: An fMRI study. Cognitive Brain Research, 20, 81–91.
Schultz, R. T., & Robert, T. (2005). Developmental deficits in social perception in autism: The role of the amygdala and fusiform face area. International Journal of Developmental Neuroscience: The Official Journal of the International Society for Developmental Neuroscience, 23(2–3), 125–141.
Schultz, R., Gauthier, I., Klin, A., Fulbright, R., Anderson, A., Volkmar, F., et al. (2000). Abnormal ventral temporal cortical activity during face discrimination among individuals with autism and Asperger syndrome. Archives of General Psychiatry, 57, 331–340.
Sigman, M., Dijamco, A., Gratier, M., & Rozga, A. (2004). Early detection of core deficits in autism. Mental retardation and developmental disabilities research reviews, 10(4), 221–233.
Smith, S. (2002). Fast robust automated brain extraction. Human Brain Mapping, 17(3), 143–155.
Sridharan, D., Levitin, D. J., & Menon, V. (2008). A critical role for the right fronto-insular cortex in switching between central-executive and default-mode networks. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 105(34), 12569–12574.
Stroop, J. (1935). Studies of interference in serial-verbal reaction. Journal of Experimental Psychology, 18, 643–662.
Talairach, J., & Tournoux, P. (1998). Co-planar stereotaxic atlas of the human brain. Stuttgart: Thieme, 122.
Teunisse, J. P., & de Gelder, B. (2003). Face processing in adolecents with autistic disorder: The inversion and composite effects. Brain Cognitive, 52, 285–294.
Trautmann, S. A., Fehr, T., & Herrmann, M. (2009). Emotions in motion: Dynamic compared to static facial expressions of disgust and happiness reveal more widespread emotion-specific activations. Brain Research, 1284, 100–115.
Uddin, L. Q., & Menon, V. (2009). The anterior insula in autism: Under-connected and under-examined. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 33(8), 1198–1203.
Uddin, L. Q., Davies, M. S., Scott, A. A., Zaidel, E., Bookheimer, S. Y., Iacoboni, M., et al. (2008). Neural basis of self and other representation in autism: An fMRI study of self-face recognition. PLoS One, 3(10), e3526.
Viinikainen, M., Jääskeläinen, I. P., Alexandrov, Y., Balk, M. H., Autti, T., & Sams, M. (2010). Nonlinear relationship between emotional valence and brain activity: Evidence of separate negative and positive valence dimensions. Human Brain Mapping, 31(7), 1030–1040. URL: http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/hbm.20915.
Wechsler, D. (1991). Wechsler intelligence scale for children (WISC-III) (3rd ed.). New York: The Psychological Corporation.
Weiss, L. A., Arking, D. E., Gene Discovery Project of Johns Hopkins, the Autism Consortium, Daly, M., & Chakravarti, A. (2009). A genome-wide linkage and association scan reveals novel loci for autism. Nature, 461(7265), 802–808.
Wicker, B., Keysers, C., Plailly, J., Royet, J. P., Gallese, V., & Rizzolatti, G. (2003). Both of us disgusted in My insula: The common neural basis of seeing and feeling disgust. Neuron, 40(3), 655–664.
Woolrich, M. W., Behrens, T. E. J., Beckmann, C. F., Jenkinson, M., & Smith, S. M. (2004). Multilevel linear modelling for FMRI group analysis using Bayesian inference. NeuroImage, 21(4), 1732–1747.
Acknowledgments
We thank the participants and their parents, who graciously gave their time to participate in this study. This study received financial support from the Alma and K. A. Snellman Foundation, Oulu, Finland; the Emil Aaltonen Foundation, Finland; Northern Ostrobothnia Hospital District; the Sigrid Jusélius Foundation, Finland; the Thule Institute, Oulu University Hospital, Finland; the Lundbeck Foundation, Turku, Finland. This study was also funded by Finnish Academy Grants #117111 and #123772 and Finnish Medical Foundation grants. The Graduate School of Circumpolar Wellbeing, Health and Adaptation is acknowledged for its support. We would also like to thank the National Alliance for Autism Research for financial support granted to David Pauls.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rahko, J.S., Paakki, JJ., Starck, T.H. et al. Valence Scaling of Dynamic Facial Expressions is Altered in High-Functioning Subjects with Autism Spectrum Disorders: an fMRI Study. J Autism Dev Disord 42, 1011–1024 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-011-1332-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-011-1332-8