Abstract
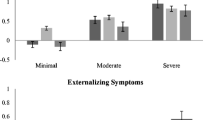
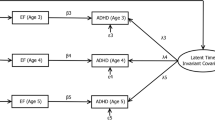
A population-based longitudinal sample of 489 twin pairs was assessed at six time points over ten years to examine the measurement invariance and stability of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) symptoms, as well as the developmental relations between inattention (IN), hyperactivity-impulsivity (HI), and multiple aspects of functional impairment. Parent ratings of ADHD symptoms and functional impairment were obtained in preschool and after the completion of kindergarten, first, second, fourth, and ninth grades. Results of the temporal and sex invariance models indicated that parent ratings of the 18 ADHD symptoms function in the same manner for females and males from early childhood into adolescence. In addition to establishing this prerequisite condition for the interpretation of longitudinal and between-sex differences in the IN and HI symptom dimensions, cross-lagged models indicated that both IN and HI were associated with increased risk for both concurrent and future overall, social, and recreational impairment, whereas only IN was uniquely associated with later academic impairment. Taken together, the current results demonstrate that IN and HI are highly stable from preschool through ninth grade, invariant between females and males, and indicative of risk for impairment in multiple areas, thereby providing strong support for the validity of the symptom dimensions among both sexes.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Psychiatric Association. (1994). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (4th ed.). Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association.
American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (5th ed.). Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association.
Arnett, A. B., Pennington, B. F., Willcutt, E. G., DeFries, J. C., & Olson, R. K. (2015). Sex differences in ADHD symptom severity. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 56, 632–639.
Barkley, R. A., & Murphy, K. (1998). Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder: A clinical workbook (Vol. 2nd). New York, NY: Guilford Press.
Bauermeister, J. J., Canino, G., Polanczyk, G., & Rohde, L. A. (2010). ADHD across cultures: Is there evidence for a bidimensional organization of symptoms? Journal of Clinical Child & Adolescent Psychology, 39(3), 362–372.
Brosco, J. P., & Bona, A. (2017). Changes in academic demands and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in young children. JAMA Pediatrics, 170(4), 396–397.
Burns, G. L., Walsh, J. A., Gomez, R., & Hafetz, N. (2006). Measurement and structural invariance of parent ratings of ADHD and ODD symptoms across gender for American and Malaysian children. Psychological Assessment, 18, 452–457.
Burns, G. L., Servera, M., Bernad, M. D. M., Carrillo, J. M., & Geiser, C. (2014). Ratings of ADHD symptoms and academic impairment by mothers, fathers, teachers, and aides: Construct validity within and across settings as well as occasions. Psychological Assessment, 26(4), 1247–1258.
Burns, G. L., Becker, S. P., Servera, M., Bernad, M. D. M., & Garcia-Banda, G. (2017). Sluggish cognitive tempo and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) inattention in the home and school contexts: Parent and teacher invariance and cross-setting validity. Psychological Assessment, 29(2), 209–220. https://doi.org/10.1037/pas0000325.
Byrne, B., Delaland, C., Fielding-Barnsley, R., Quain, P., Samuelsson, S., Hoien, T., et al. (2002). Longitudinal twin study of early reading development in three countries: Preliminary results. Annals of Dyslexia, 52, 49–73.
Chen, F. F. (2007). Sensitivity of goodness of fit indexes to lack of measurement invariance. Structural Equation Modeling, 14, 464–504.
Chen, F. F., Sousa, K. H., & West, S. G. (2005). Testing measurement invariance of second-order factor models. Structural Equation Modeling, 12, 471–492.
Christopher, M. E., Hulslander, J., Byrne, B., Samuelsson, S., Keenan, J. M., Pennington, B. F., et al. (2013). The genetic and environmental etiologies of individual differences in early reading growth in Australia, the United States, and Scandinavia. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 125, 453–467.
Christopher, M. E., Hulsander, J., Keenan, J., DeFries, J., Pennington, B. F., Byrne, B., et al. (2015). Genetic and environmental etiologies of the longitudinal relations between pre-reading skills and reading. Child Development, 86, 342–361.
Dittman, C. K. (2016). The impact of early classroom inattention on phonological processing and word-reading development. Journal of Attention Disorders, 20(8), 653–664.
Eid, M., Geiser, C., Koch, T., & Heene, M. (2017). Anomalous results in g-factor models: Explanations and alternatives. Psychological Methods, 22(3), 541–562.
Friedman-Weieneth, J. L., Doctoroff, G. L., Harvey, E. A., & Goldstein, L. H. (2009). The Disruptive Behavior Rating Scale-Parent Version (DBRS-PV): Factor analytic structure and validity among young preschool children. Journal of Attention Disorders, 13, 42–55.
Gaub, M., & Carlson, C. L. (1997). Gender differences in ADHD: A meta-analysis and critical review. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 36, 1036–1045.
Gershon, J. (2002). A meta-analytic review of gender differences in ADHD. Journal of Attention Disorders, 5, 143–154.
Hartung, C. M., Lefler, E. K., Canu, W. H., Stevens, A. E., Jaconis, M., LaCount, P. A., … Willcutt, E. G. (2016). DSM-5 and other symptom thresholds for ADHD: Which is the best predictor of impairment in college students? Advance online publication. Journal of Attention Disorders. https://doi.org/10.1177/1087054716629216.
Hinshaw, S. P. (2002). Preadolescent girls with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: I. Background characteristics, comorbidity, cognitive and social functioning, and parenting practices. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 70, 1086–1098.
Hinshaw, S. P., Owens, E. B., Sami, N., & Fargeon, S. (2006). Prospective follow-up of girls with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder into adolescence: Evidence for continuing cross-domain impairment. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 74, 489–499.
Lahey, B. B., & Willcutt, E. G. (2010). Predictive validity of a continuous alternative to nominal subtypes of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder in DSM-IV. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 39, 761–775.
Lahey, B. B., Pelham, W. E., Stein, M. A., Loney, J., Trapani, C., Nugent, K., et al. (1998). Validity of DSM-IV attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder for younger children. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 37, 695–702.
Lahey, B. B., Pelham, W. E., Loney, J., Kipp, H., Ehrhardt, A., Lee, S. S., et al. (2004). Three-year predictive validity of DSM-IV attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children diagnosed at 4-6 years of age. American Journal of Psychiatry, 161, 2014–2020.
Lahey, B. B., Pelham, W. E., Loney, J., Lee, S. S., & Willcutt, E. (2005). Instability of the DSM-IV subtypes of ADHD from preschool through elementary school. Archives of General Psychiatry, 62, 896–902.
Little, T. D. (2013). Longitudinal structural equation modeling. New York: Guilford Press.
Little, T. D., Rhemtulla, M., Gibson, K., & Schoemann, A. M. (2013). Why the items versus parcels controversy needn’t be one. Psychological Methods, 18, 285–300.
McGee, R., Prior, M., Williams, S., Smart, D., & Sanson, A. (2002). The long-term significance of teacher-rated hyperactivity and reading ability in childhood: Findings from two longitudinal studies. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 43, 1004–1017.
Muthen, L. K., & Muthen, B. O. (2012). Mplus user's guide (7th ed.). Los Angeles: Muthen and Muthen.
Olson, R. K., Keenan, J. M., Byrne, B., Samuelsson, S., Coventry, W. L., Corley, R., et al. (2011). Genetic and environmental influences on vocabulary and reading development. Scientific Studies of Reading, 15, 26–46.
Owens, E. B., Hinshaw, S. P., Lee, S. S., & Lahey, B. B. (2009). Few girls with childhood attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder show positive adjustment during adolescence. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 38, 132–143.
Pham, A. V. (2016). Differentiating behavioral ratings of inattention, impulsivity, and hyperactivity in children: Effects on reading achievement. Journal of Attention Disorders, 20(8), 674–683.
Reynolds, C. R., & Kamphaus, R. W. (2004). Behavior assessment system for children (2nd ed.). Circle Pines: American Guidance Service.
Ros, R. & Graziano, P.A. (2017). Social functioning in children with or at risk for attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder: A meta-analytic review. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology. Advance online publication.
Spitzer, R. L., & Wakefield, J. C. (1999). DSM-IV diagnostic criterion for clinical significance: Does it help solve the false positives problem? American Journal of Psychiatry, 156, 1856–1864.
Toplak, M. E., Sorge, G. B., Flora, D. B., Chen, W., Banaschewski, T., Buitelaar, J., et al. (2012). The hierarchical factor model of ADHD: Invariant across age and national groupings? Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 53(3), 292–303.
Willcutt, E. G. (2012). The prevalence of DSM-IV attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: A meta-analytic review. Neurotherapeutics, 9, 490–499.
Willcutt, E. G., Betjemann, R. S., Pennington, B. F., Olson, R. K., DeFries, J. C., & Wadsworth, S. J. (2007a). Longitudinal study of reading disability and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: Implications for education. Mind, Brain, and Education, 1(4), 181–192. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1751-228X.2007.00019.x.
Willcutt, E. G., Betjemann, R. S., Wadsworth, S. J., Samuelsson, S., Corley, R., DeFries, J. C., et al. (2007b). Preschool twin study of the relation between attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and prereading skills. Reading and Writing, 20, 103–125.
Willcutt, E. G., Betjemann, R. S., McGrath, L. M., Chhabildas, N. A., Olson, R. K., DeFries, J. C., & Pennington, B. F. (2010). Etiology and neuropsychology of comorbidity between RD and ADHD: The case for multiple-deficit models. Cortex, 46, 1345–1361.
Willcutt, E. G., Boada, R., Riddle, M. W., Chhabildas, N., DeFries, J. C., & Pennington, B. F. (2011). Colorado learning difficulties questionnaire: Validation of a parent-report screening measure. Psychological Assessment, 23, 778–791.
Willcutt, E. G., Nigg, J. T., Pennington, B. F., Solanto, M. V., Rohde, L. A., Tannock, R., et al. (2012). Validity of DSM-IV attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder dimensions and subtypes. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 121, 991–1010.
Willoughby, M. T., Blanton, Z. E., & Family Life Project Investigators. (2015). Replication and external validation of a bi-factor parameterization of attention deficit/hyperactivity symptomatology. Journal of Clinical Child & Adolescent Psychology, 44, 68–79.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by grants from the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (R01 HD38526 and R01 HD68728). The authors were also supported by NIH grants F31 HD091967, P50 HD27802, and R24 HD75460 during the preparation of this report. We also gratefully acknowledge the participants, their caregivers, and the research staff that have made this ongoing project possible.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
All participants and parents read and agreed to the informed consent or assent document prior to their initial enrollment in the study and at each follow-up assessment.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 1072 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leopold, D.R., Christopher, M.E., Olson, R.K. et al. Invariance of ADHD Symptoms Across Sex and Age: a Latent Analysis of ADHD and Impairment Ratings from Early Childhood into Adolescence. J Abnorm Child Psychol 47, 21–34 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-018-0434-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-018-0434-6