Abstract
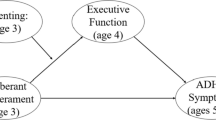
A culturally diverse sample of formerly homeless youth (ages 6–12) and their families (n = 223) participated in a cluster randomized controlled trial of the Early Risers conduct problems prevention program in a supportive housing setting. Parents provided 4 annual behaviorally-based ratings of executive functioning (EF) and conduct problems, including at baseline, over 2 years of intervention programming, and at a 1-year follow-up assessment. Using intent-to-treat analyses, a multilevel latent growth model revealed that the intervention group demonstrated reduced growth in conduct problems over the 4 assessment points. In order to examine mediation, a multilevel parallel process latent growth model was used to simultaneously model growth in EF and growth in conduct problems along with intervention status as a covariate. A significant mediational process emerged, with participation in the intervention promoting growth in EF, which predicted negative growth in conduct problems. The model was consistent with changes in EF fully mediating intervention-related changes in youth conduct problems over the course of the study. These findings highlight the critical role that EF plays in behavioral change and lends further support to its importance as a target in preventive interventions with populations at risk for conduct problems.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
August, G. J., Realmuto, G. M., Hektner, J. M., & Bloomquist, M. L. (2001). An integrative components intervention for aggressive elementary school children: The Early Risers Program. Journal of Counseling and Clinical Psychology, 69, 614–626. doi:10.1037/0022-006X.69.4.614.
August, G. J., Lee, S. S., Bloomquist, M. L., Realmuto, G. M., & Hektner, J. M. (2003). Dissemination of an evidence-based prevention innovation for aggressive children living in culturally diverse, urban neighborhoods: The Early Risers effectiveness study. Prevention Science, 4, 271–286. doi:10.1023/A:1026072316380.
August, G. J., Bloomquist, M. L., Lee, S. S., Realmuto, G. M., & Hektner, J. M. (2006). Can evidence-based prevention programs be sustained in community systems-of-care? The Early Risers advanced-stage effectiveness trial. Prevention Science, 7, 151–165. doi:10.1007/s11121-005-0024-z.
Baron, R. M., & Kenny, D. A. (1986). The moderator-mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 51, 1173–1182. doi:10.1037/0022-3514.51.6.1173.
Barringer, M. S., & Reynolds, C. R. (1995). Behavior ratings of frontal lobe dysfunction. Orlando: Paper presented at the annual meeting of the National Academy of Neuropsychology.
Bernat, D., August, G. J., Hektner, J. M., & Bloomquist, M. L. (2007). The Early Risers preventive intervention: Six year outcomes and mediational processes. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 35, 605–617. doi:10.1007/s10802-007-9116-5.
Bernier, A., Carlson, S. M., & Whipple, N. (2010). From external regulation to self- regulation: Early parenting precursors of young children’s executive functioning. Child Development, 81, 326–339. doi:10.1111/j.1467-8624.2009.01397.x.
Bierman, K. L., Domitrovich, C. E., Nix, R. L., Gest, S. D., Welsh, J. A., Greenberg, M. T., & Gill, S. (2008a). Promoting academic and social-emotional school readiness: The Head Start REDI program. Child Development, 79, 1802–1817. doi:10.1111/j.1467-8624.2008.01227.x.
Bierman, K. L., Nix, R. L., Greenberg, M. T., Blair, C., & Domitrovich, C. E. (2008b). Executive functions and school readiness intervention: Impact, moderation, and mediation in the Head Start REDI program. Development and Psychopathology, 20, 821–843. doi:10.1017/S0954579408000394.
Bloomquist, M. L., August, G. J., Lee, S. S., Lee, C.-Y. S., Realmuto, G. M., & Klimes-Dougan, B. (2013). Going-to-scale with the Early Risers conduct problems prevention program: Use of a comprehensive implementation support (CIS) system to optimize fidelity, participation and child outcomes. Evaluation and Program Planning, 38, 19–27. doi:10.1016/j.evalprogplan.2012.11.001.
Boisjoli, R., Vitaro, F., Lacourse, E., Barker, E. D., & Tremblay, R. E. (2007). Impact and clinical significance of a preventive intervention for disruptive boys: 15-year follow-up. The British Journal of Psychiatry, 191, 415–419. doi:10.1192/bjp.bp.106.030007.
Cheong, J., MacKinnon, D. P., & Khoo, S. T. (2003). Investigation of mediational processes using parallel process latent growth curve modeling. Structural Equation Modeling, 10, 238–262. doi:10.1207/S15328007SEM1002_5.
Cheung, G. W., & Rensvold, R. B. (2002). Evaluating goodness-of-fit indexes for testing measurement invariance. Structural Equation Modeling, 9, 233–255.
Conduct Problems Prevention Research Group. (2011). The effects of the Fast Track Preventive Intervention on the development of conduct disorder across childhood. Child Development, 82, 331–345. doi:10.1111/j.1467-8624.2010.01558.x.
Diamond, A., & Lee, K. (2011). Interventions shown to aid executive function development in children 4 to 12 years old. Science, 333, 959–964. doi:10.1126/science.120452910.1126/science.1204529.
Diamond, A., Barnett, S., Thomas, J., & Munro, S. (2007). Executive function can be improved in preschoolers by regular classroom teachers. Science, 318, 1387–1388. doi:10.1126/science.1151148.
Duncan, T. E., Duncan, S. C., Albert, A., Hops, H., Stoolmiller, M., & Muthen, B. (1997). Latent variable modeling of longitudinal and multilevel substance use data. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 32, 275–318. doi:10.1207/s15327906mbr3203_3.
Feingold, A. (2009). Effect sizes for growth-modeling analysis for controlled clinical trials in the same metric as for classical analysis. Psychological Methods, 14, 43–53. doi:10.1037/a0014699.
Forgatch, M. S., & DeGarmo, D. S. (1999). Parenting through change: an effective prevention program for single mothers. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 67, 711–724. doi:10.1037/0022-006X.67.5.711.
Garcia-Barrera, M. A., Kamphaus, R. W., & Bandalos, D. (2011). Theoretical and statistical derivation of a screener for the behavioral assessment of executive functions in children. Psychological Assessment, 23, 64–79. doi:10.1037/a0021097.
Gewirtz, A. (2007). Promoting children’s mental health in family supportive housing: a community-university partnership for formerly homeless children and families. Journal of Primary Prevention, 28, 359–374. doi:10.1007/s10935-007-0102-z.
Gewirtz, A., & Taylor, T. (2009). Participation of homeless and abused women in a parent training program. In M. F. Hindsworth & T. B. Lang (Eds.), Community participation and empowerment (pp. 97–114). Hauppage: Nova.
Gewirtz, A. H., Hart-Shegos, E., & Medhanie, A. (2008). Psychosocial status of children and youth in supportive housing. American Behavioral Scientist, 51, 810–823.
Gewirtz, A., DeGarmo, D., Plowman, E., August, G., & Realmuto, G. (2009). Parenting, parental mental health, and child functioning in families residing in supportive housing. American Journal of Orthopsychiatry, 79, 336–347. doi:10.1037/a0016732.
Gewirtz, A. H., DeGarmo, D. S., Lee, S. S., & August, G. A. (2013). Twenty-four month outcomes of the early risers prevention trial with formerly homeless families residing in supportive housing. Manuscript submitted for publication.
Giancola, P. R., Moss, H. B., Martin, C. S., Kirisci, L., & Tarter, R. E. (1996). Executive cognitive functioning predicts reactive aggression in boys at high risk for substance abuse: a prospective study. Alcoholism: clinical and experimental research, 20, 740–744. doi:10.1111/j.1530-0277.1996.tb01680.x.
Hinshaw, S. P. (2002). Intervention research, theoretical mechanisms, and causal processes related to externalizing behavior patterns. Developmental and Psychopathology, 14, 789–818. doi:10.1017/S0954579402004078.
Hu, L.-t., & Bentler, P. M. (1999). Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: Conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Structural Equation Modeling, 6, 1–55.
Kline, R. B. (2005). Principles and practice of structural equation modeling (2nd ed.). New York: Guilford Press.
Knutson, N. M., Forgatch, M. S., Rains, L. A., & Sigmarsdóttir, M. (2009). Fidelity of implementation rating system (FIMP): The manual for PMTO™ (Revised ed.). Eugene: Oregon Social Learning Center.
Kusché, C. A., & Greenberg, M. T. (1994). The PATHS curriculum. Seattle: Developmental Research and Programs, Inc.
Lee, C., August, G., Realmuto, G., Horowitz, J., Bloomquist, M., & Klimes-Dougan, B. (2008). Fidelity at a distance: Assessing implementation fidelity of the early risers prevention program in a going-to-scale intervention trial. Prevention Science, 9, 215–229. doi:10.1007/s11121-008-0097-6.
Lee, S. S., August, G. J., Gewirtz, A. H., Klimes-Dougan, B., Bloomquist, M. L., & Realmuto, G. M. (2010). Identifying unmet mental health needs in children of formerly homeless mothers living in a supportive housing community sector of care. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 38, 421–432. doi:10.1007/s10802-009-9378-1.
Lochman, J. E., & Wells, K. C. (2004). The Coping Power Program for preadolescent aggressive boys and their parents: Outcome effects at the 1-year follow-up. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 72, 571–578. doi:10.1037/0022-006X.72.4.571.
MacKinnon, D. P. (2008). Introduction to statistical mediation analysis. Mahwah: Erlbaum.
Masten, A. S., & Cicchetti, D. (2010). Developmental cascades. Development and Psychopathology, 22, 491–495. doi:10.1017/S0954579410000222.
Masten, A. S., & Coatsworth, J. D. (1998). The development of competence in favorable and unfavorable environments: lessons from research on successful children. American Psychologist, 53, 205–220. doi:10.1037/0003-066X.53.2.205.
Masten, A. S., Herbers, J. E., Desjardins, C. D., Cutuli, J. J., McCormick, C. M., Sapienza, J. K., & Zelazo, P. D. (2012). Executive function skills and school success in young children experiencing homelessness. Educational Researcher, 41, 375–384.
McCrea, S. M., Mueller, J. H., & Parilla, R. K. (1999). Quantitative analyses of schooling effects on executive function in young children. Child Neuropsychology, 5, 242–250.
Moffitt, T. E. (1993). The neuropsychology of conduct disorder. Development and Psychopathology, 5, 135–151. doi:10.1017/S0954579402004078.
Muthén, L. K., & Muthén, B. O. (2010). Mplus user’s guide (6th ed.). Los Angeles: Muthén & Muthén.
Noble, K. G., McCandliss, B. D., & Farah, M. J. (2007). Socioeconomic gradients predict individual differences in neurocognitive abilities. Developmental Science, 10, 464–480. doi:10.1111/j.1467-7687.2007.00600.x.
Preacher, K. J., Zyphur, M. J., & Zhang, Z. (2010). A general multilevel SEM framework for assessing multilevel mediation. Psychological Methods, 15, 209–233.
Rafferty, Y., & Shinn, M. (1991). The impact of homelessness on children. American Psychologist, 46, 1170–1179. doi:10.1037/0003-066X.46.11.1170.
Reynolds, C. R., & Kamphaus, R. W. (2004). Behavior assessment system for children (2nd ed.). Circle Pines: American Guidance Service.
Riggs, N. R., Blair, C. B., & Greenberg, M. T. (2003). Concurrent and 2-year longitudinal relations between executive function and the behavior of 1st and 2nd grade children. Child Neuropsychology, 9, 267–276. doi:10.1076/chin.9.4.267.23513.
Riggs, N. R., Greenberg, M. T., Kusché, C. A., & Pentz, M. A. (2006a). The meditational role of neurocognition in the behavioral outcomes of a social-emotional prevention program in elementary school students: Effects of the PATHS Curriculum. Prevention Science, 7, 91–102. doi:10.1007/s11121-005-0022-1.
Riggs, N. R., Jahromi, L. B., Razza, R. P., Dillworth-Bart, J. E., & Mueller, U. (2006b). Executive function and the promotion of social-emotional competence. Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology, 27, 300–309. doi:10.1016/j.appdev.2006.04.002.
Rogosa, D., Brandt, D., & Zimowski, M. (1982). A growth curve approach to the measurement of change. Psychological Bulletin, 92, 726–748. doi:10.1037/0033-2909.92.3.726.
Sullivan, J. R., & Riccio, C. A. (2006). An empirical analysis of the BASC frontal lobe/executive control scale with a clinical sample. Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology, 21, 49–501.
Teichner, G., & Golden, C. J. (2000). The relationship of neuropsychological impairment to conduct disorder in adolescence: a conceptual review. Aggression and Violent Behavior, 5, 509–528. doi:10.1016/S1359-1789(98)00035-4.
Toplak, M. E., West, R. F., & Stanovich, K. E. (2013). Practitioner review: do performance-based measures and ratings of executive function assess the same construct? Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 54, 131–143. doi:10.1111/jcpp.12001.
Vygotsky, L. S. (1978). Mind in society: the development of higher psychological processes. Cambridge: Harvard University Press.
Zelazo, P. D., & Muller, U. (2002). Executive function in typical and atypical development. In U. Goswami (Ed.), Handbook of childhood cognitive development (pp. 445–469). Oxford: Blackwell.
Author Note
This research was supported by grants to Gerald J. August from the National Institute of Mental Health (MH074610 and P20 MH085987). The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institute Of Mental Health or the National Institutes of Health. The authors would like to thank Nicole Morrell, the project manager, for her major contribution to this effort, as well as David DeGarmo for his generous statistical consultation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Piehler, T.F., Bloomquist, M.L., August, G.J. et al. Executive Functioning as a Mediator of Conduct Problems Prevention in Children of Homeless Families Residing in Temporary Supportive Housing: A Parallel Process Latent Growth Modeling Approach. J Abnorm Child Psychol 42, 681–692 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-013-9816-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-013-9816-y