Abstract
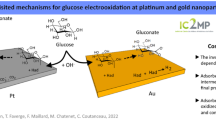
Glucose oxidation on platinum nanoparticles (Pt NPs) at varying potentials (from − 0.7 V to 0.2 V) was investigated using single entity electrochemistry. The active chemisorption model was found to be valid only at potentials below − 0.6 V, while the incipient hydrous oxide/adatom mediator (IHOAM) model was confirmed for potentials above − 0.6 V. In both cases, hydrous ions significantly improved glucose oxidation by freeing up active sites on the Pt NPs. The potential for glucose sensing at − 0.4 V, where continuous glucose oxidation took place, was assessed. Although the linearity was limited (0.1–0.6 mM), the high sensitivity of 423.056 µA mM− 1 cm− 2 and limit of detection (LOD) of 25.63 µM demonstrated promising prospects for glucose sensing at − 0.4 V, particularly for samples with low glucose concentrations.
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
IDF (2021) IDF Diabetes Atlas 10th edition.
Lee, I, Probst, D, Klonoff, D, Sode, K (2021) Continuous glucose monitoring systems - current status and future perspectives of the flagship technologies in biosensor research. Biosens Bioelectron 181, 113054.
Gnana kumar G, Amala G, Gowtham SM (2017) Recent advancements, key challenges and solutions in non-enzymatic electrochemical glucose sensors based on graphene platforms. RSC Adv 7:36949–36976
Hassan, MH, Vyas, C, Grieve, B, Bartolo, P (2021) Recent advances in enzymatic and non-enzymatic Electrochemical glucose sensing. Sensors (Basel) 21, 4672.
Wei, M, Qiao, Y, Zhao, H, Liang, J, Li, T, Luo, Y, Lu, S, Shi, X, Lu, W, Sun, X (2020) Electrochemical non-enzymatic glucose sensors: recent progress and perspectives. Chem. Commun. 56, 14553–14569.
Liu S, Zeng W, Guo Q, Li Y (2020) Metal oxide-based composite for non-enzymatic glucose sensors. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 31:16111–16136
Hwang, DW, Lee, S, Seo, M, Chung, TD (2018) Recent advances in electrochemical non-enzymatic glucose sensors - a review. Anal Chim Acta 1033, 1–34.
Mazurków, JM, Kusior, A, Radecka, M (2021) Electrochemical characterization of modified glassy Carbon Electrodes for non-enzymatic glucose sensors. Sensors 21, 7928.
Lin L, Weng S, Zheng Y, Liu X, Ying S, Chen F, You D (2020) Bimetallic PtAu alloy nanomaterials for nonenzymatic selective glucose sensing at low potential. J Electroanal Chem 865:114147
Olejnik, A, Karczewski, J, Dołęga, A, Siuzdak, K, Grochowska, K (2020) Insightful analysis of Phenomena arising at the metal polymer interphase of Au-Ti based non-enzymatic glucose sensitive electrodes covered by Nafion. Coatings 10, 810.
Teymourian, H, Barfidokht, A, Wang, J (2020) Electrochemical glucose sensors in diabetes management: an updated review (2010–2020). Chem Soc Rev 49, 7671–7709.
Park, S, Boo, H, Chung, TD (2006) Electrochemical non-enzymatic glucose sensors. Anal Chim Acta 556, 46–57.
Naikoo, GA, Salim, H, Hassan, IU, Awan, T, Arshad, F, Pedram, MZ, Ahmed, W, Qurashi, A (2021) Recent advances in non-enzymatic glucose sensors based on metal and metal oxide nanostructures for Diabetes Management- A Review. Front Chem 9, 748957.
Naik KM, Alagur MM, Nandibewoor ST (2013) Electrochemical response of hydroxyurea by different voltammetric techniques at carbon paste electrode. Anal Methods 5:6947
Naik KM, Nandibewoor ST (2014) Electroanalytical method for the determination of methylparaben. Sens Actuat A: Phys 212:127–132
Naik KM, Ashi CR, Nandibewoor ST (2015) Anodic voltammetric behavior of hydroxyurea and its electroanalytical determination in pharmaceutical dosage form and urine. J Electroanal Chem 755:109–114
Bard, AJ, Faulkner, LR (2001) Electrochemcial Methods, Fundamentals and Applications, 2nd Ed. New York: John Wiley & Sons.
Patrice, FT, Qiu, K, Ying, Y-L, Long, Y-T (2019) Single nanoparticle Electrochemistry. Annual Rev. Anal. Chem. 12, 347–370.
Sun Z, Hafez ME, Ma W, Long Y-T (2019) Recent advances in nanocollision electrochemistry. Sci China Chem 62:1588–1600
Roehrich, B, Sepunaru, L (2020) Nanoimpacts at active and partially active electrodes: Insights and Limitations. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 59, 19184–19192.
Kim, SD, Park, JH, Ahn, H, Lee, J, Shin, C-H, Jang, W-D, Kim, B-K, Ahn, HS (2022) The discrete single-entity electrochemistry of Pickering emulsions. NANOSCALE 14, 6981–6989.
Chen Y, Wang D, Liu Y, Gao G, Zhi J (2021) Redox activity of single bacteria revealed by electrochemical collision technique. Biosens Bioelectron 176:112914
Gao R, Ying Y-L, Hu Y-X, Li Y-J, Long Y-T (2017) Wireless Bipolar Nanopore Electrode for single small molecule detection. Anal Chem 89:7382–7387
Dick, JE, Bard, AJ (2015) Recognizing single collisions of PtCl62– at Femtomolar concentrations on Ultramicroelectrodes by nucleating Electrocatalytic clusters. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 137, 13752–13755.
Liu Y, Austen BJJ, Cornwell T, Tilbury RD, Buntine MA, O’Mullane AP, Arrigan DWM (2017) Collisional electrochemistry of laser-ablated gold nanoparticles by electrocatalytic oxidation of glucose. Electrochem Commun 77:24–27
Hafez, ME, Ma, H, Ma, W, Long, YT (2019) Unveiling the intrinsic Catalytic Activities of single-gold-nanoparticle-based enzyme mimetics. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 58, 6327–6332.
Tang, H, Wang, H, Du, J, Zhao, D, Cao, M, Li, Y (2021) Intrinsic Catalytic Activities from single Enzyme@Metal-Organic frameworks by using a Stochastic Collision Electrochemical technique. J Phys Chem Lett 12, 5443–5447.
Popović KD, Marković NM, Tripković AV, Adžić RR (1991) Structural effects in electrocatalysis: oxidation of D-glucose on single crystal platinum electrodes in alkaline solution. J Electroanal Chem Interfacial Electrochem 313:181–199
Tian K, Prestgard M, Tiwari A (2014) A review of recent advances in nonenzymatic glucose sensors. Mater Sci Eng: C 41:100–118
Beden B, Largeaud F, Kokoh KB, Lamy C (1996) Fourier transform infrared reflectance spectroscopic investigation of the electrocatalytic oxidation of d-glucose: identification of reactive intermediates and reaction products. Electrochim Acta 41:701–709
Lei H-W, Wu B, Cha C-S, Kita H (1995) Electrooxidation of glucose on platinum in alkaline solution and selective oxidation in the presence of additives. J Electroanal Chem 382:103–110
Ramaswamy N, Mukerjee S (2011) Influence of inner- and outer-sphere Electron transfer mechanisms during Electrocatalysis of Oxygen Reduction in Alkaline Media. J Phys Chem C 115:18015–18026
Si P, Huang Y, Wang T, Ma J (2013) Nanomaterials for electrochemical non-enzymatic glucose biosensors. RSC Adv 3:3487
Favaro M, Valero-Vidal C, Eichhorn J, Toma FM, Ross PN, Yano J, Liu Z, Crumlin EJ (2017) Elucidating the alkaline oxygen evolution reaction mechanism on platinum. J Mater Chem A 5:11634–11643
Niu XH, Shi LB, Zhao HL, Lan MB (2016) Advanced strategies for improving the analytical performance of Pt-based nonenzymatic electrochemical glucose sensors: a minireview. Anal Methods 8:1755–1764
Toghill K, Compton R (2010) Electrochemical non-enzymatic glucose sensors: a perspective and an evaluation. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. Int J 5:1246–1301
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge funding from Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. LY21F050004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JL and SL wrote the main manuscript text. JW and WZ conducted all the experiments. DZ, QX and YZ conducted the data analyzing and prepared all the figures. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, J., Wang, J., Li, S. et al. The effect of hydroxide ions on the electrocatalysis of glucose at single platinum nanoparticles. J Appl Electrochem 53, 1991–1999 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-023-01905-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-023-01905-z