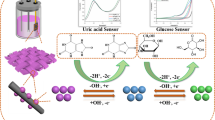
Abstract
In this contribution, a simple and novel non-enzymatic electrochemical sensor for the detection of glucose was successfully prepared by direct in situ growth of nickel hydroxide nanoparticles (Ni(OH)2NPs) onto a three-dimensional Inconel 625foam (IN625F) substrate through a facile electrochemical route, using cyclic voltammetry (CV) method in alkaline medium without addition of nickel salts. Then, surface characterization of modified Ni(OH)2/IN625F electrodes was carried out through advanced technologies, such as scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and X-ray diffraction (XRD). The electrochemical catalytic behavior of the fabricated electrodes was investigated using CV and amperometric methods. The results revealed that the novel modified sensor, Ni(OH)2/IN625F, showed the highest sensitivity of 5685 μAmM−1 cm−2 over a wide linear concentration range from 1 to10 mM, with lowest detection limit (LOD) of 2 μM (S/N = 3), and short response time within < 2 s. Therefore, the proposed non-enzymatic electrochemical sensor demonstrated high selectivity and stability, good reproducibility, and low cost. In addition, analysis of human blood samples was performed. Hence, the constructed glucose sensor, Ni(OH)2/IN625F, with suitable performance could be used as a promising material in real human blood samples.
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li H, Zhang L, Mao Y, Wen C, Zhao P (2019) A simple electrochemical route to access amorphous Co-Ni hydroxide for nonenzymatic glucose sensing. Nanoscale Res Lett 14:135. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-019-2966-2
Ojani R, Raoof JB, Fathi S (2012) Nickel/poly(o-aminophenol) film prepared in presence of sodium dodecyl sulfate: application for electrocatalytic oxidation of carbohydrates. J Chin Chem Soc 59:788–792. https://doi.org/10.1002/jccs.201100463
Wang Q, Zhang Y, Ye W, Wang C (2016) Ni(OH)2/MoSx nanocomposite electrodeposited on a flexible CNT/PI membrane as an electrochemical glucose sensor: the synergistic effect of Ni(OH)2 and MoSx. J Solid State Electrochem 20:133–142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-015-3002-9
King H, Aubert RE, Herman WH (1998) Global burden of diabetes, 1995–2025: prevalence, numerical estimates, and projections. Diabetes Care 21:1414–1431. https://doi.org/10.2337/diacare.21.9.1414
Zhe T, Sun X, Liu Y, Wang Q, Li F, Bu T, Jia P, Lu Q, Wang J, Wang L (2019) An integrated anode based on porous Ni/Cu(OH)2 nanospheres for nonenzymatic glucose sensing. Microchem J 151:104197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2019.104197
Rungsawang T, Punrat E, Adkins J, Henry C, Chailapakul O (2016) Development of electrochemical paper-based glucose sensor using cellulose-4-aminophenylboronic acid-modified screen-printed carbon electrode. Electroanalysis 28:462–468. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.201500406
Naik KK, Ratha S, Rout CS (2016) Phase and shape dependent non–enzymatic glucose sensing properties of nickel molybdate. Chemistry Select 1:5187–5195. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.201600795
Klonoff DC (2012) Overview of fluorescence glucose sensing: a technology with a bright future. J Diabetes Sci Technol 6:1242–1250. https://doi.org/10.1177/193229681200600602
Filip M, Vlassa M, Coman V, Halmagyi A (2016) Simultaneous determination of glucose, fructose, sucrose and sorbitol in the leaf and fruit peel of different apple cultivars by the HPLC–RI optimized method. Food Chem 199:653–659. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.12.060
Kremeskotter J, Wilson R (1995) Detection of glucose via electrochemiluminescence in a thin-layer cell with a planar optical waveguide. Meas Sci Technol 6:1325–1328. https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-0233/6/9/012
Morikawa MA, Kimizuka N (2002) New colorimetric detection of glucose by means of electron-accepting indicators: ligand substitution of [Fe(acac)3-n(phen)n]n+ complexes triggered by electron transfer from glucose oxidase. Chem Eur J 8:5580–5584. https://doi.org/10.1002/1521-3765(20021216)8:24%3c5580:AID-CHEM5580%3e3.0.CO;2-V
Li HB, Zhao P (2019) Amorphous Ni-Co-Fe hydroxide nanospheres for the highly sensitive and selective non-enzymatic glucose sensor applications. J Alloys Compd 800:261–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.05.264
Liu B, Li Z (2019) Electrochemical treating of a smooth Cu-Ni-Zn surface into layered micro-chips of rice grain-like Cu/Ni(OH)2 nanocomposites as a highly sensitive enzyme-free glucose sensor. J Electroanal Chem 855:113493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2019.113493
Wang L, Nie F, Zheng J (2013) Nickel hydroxide and intercalated graphene with ionic liquid nanocomposite modified electrode for sensing of glucose. J Chin Chem Soc 60:1062–1069. https://doi.org/10.1002/jccs.201200587
Chelaghmia ML, Nacef M, Affoune AM, Pontie M, Derabla T (2018) Facile synthesis of Ni(OH)2 modified disposable pencil graphite electrode and its application for highly sensitive non-enzymatic glucose sensor. Electroanalysis 30:1117–1124. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.201800002
Wang L, Lu X, Ye Y, Sun L, Song Y (2013) Nickel-cobalt nanostructures coated reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite electrode for nonenzymatic glucose biosensing. Electrochimi Acta 114:484–493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2013.10.125
Sim H, Kim JH, Lee SK, Song MJ, Yoon DH, Lim DS, Hong SI (2012) High-sensitivity non-enzymatic glucose biosensor based on Cu(OH)2 nanoflower electrode covered with boron-doped nanocrystalline diamond layer. Thin Solid Films 520:7219–7223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2012.08.011
Nacef M, Chelaghmia ML, Affoune AM, Pontié M (2019) Electrochemical investigation of glucose on a highly sensitive nickel-copper modified pencil graphite electrode. Electroanalysis 31:113–120. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.201800622
Boukharouba C, Nacef M, Chelaghmia ML, Kihal R, Drissi W, Fisli H, Affoune AM, Pontié M (2022) Dendritic Cu(OH)2 nanostructures decorated pencil graphite electrode as a highly sensitive and selective impedimetric non-enzymatic glucose sensor in real human serum blood samples. Monatsh Chemie 153:171–181. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00706-021-02883-8
Rinaldi AL, Sobral S, Carballo R (2017) Nickel hydroxide nanoparticles on screen printed electrodes as an impedimetric non-enzymatic glucose sensor. Electroanalysis 29:1961–1967. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.201700187
Marini S, Ben Mansour N, Hjiri M, Dhahri R, Mir El, Espro LC, Bonavita A, Galvagno S, Neri G, Leonardi SG (2018) Non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on nickel/carbon composite. Electroanalysis 30:727–733. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.201700687
Chelaghmia ML, Nacef M, Fisli H, Affoune AM, Pontié M, Makhlouf A, Derabla T, Khelifi O, Aissat F (2020) Electrocatalytic performance of Pt-Ni nanoparticles supported on an activated graphite electrode for ethanol and 2-propanol oxidation. RSC Adv 10:36941–36948. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0RA07331H
Wu X, Li F, Zhao C, Qian X (2018) One-step construction of hierarchical Ni(OH)2/ RGO/Cu2O on Cu foil for ultra-sensitive non-enzymatic glucose and hydrogen peroxide detection. Sens Actuators B Chem 274:163–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.07.141
Yang D, Gao L, Yang JH (2017) Facile synthesis of ultrathin Ni(OH)2-Cu2S hexagonal nanosheets hybrid for oxygen evolution reaction. J Power Sources 359:52–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2017.05.034
Liu P, Qin K, Wen S, Wang L, He F, Liu E, He C, Li CSJ, Li Q, Ma L, Zhao N (2018) In situ fabrication of Ni(OH)2/Cu2O nanosheets on nanoporous NiCu alloy for high performance supercapacitor. Electrochimi Acta 283:970–978. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2018.07.007
Kung CW, Cheng YH, Ho KC (2014) Single layer of nickel hydroxide nanoparticles covered on a porous Ni foam and its application for highly sensitive non-enzymatic glucose, sensor. Sens Actuators B 204:159–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2014.07.102
Chelaghmia ML, Nacef M, Affoune AM (2012) Ethanol electrooxidation on activated graphite supported platinum-nickel in alkaline medium. J Appl Electrochem 42:819–826. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-012-0440-2
Mao W, He H, Ye Z, Huang J (2019) Three-dimensional graphene foam integrated with Ni(OH)2 nanosheets as a hierarchical structure for non-enzymatic glucose sensing. J Electroanal Chem 832:275–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2018.11.016
Jia L, Wei X, Lv L, Zhang X, Duan X, Xu Y, Liu K, Wang J (2018) Electrodeposition of hydroxyapatite on nickel foam and further modification with conductive polyaniline for non-enzymatic glucose sensing. Electrochim Acta 280:315–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2018.05.130
Zhang Y, Zhao D, Zhu W, Zhang W, Yue Z, Wang J, Wang R, Zhang D, Wang J, Zhang G (2018) Engineering multistage nickel oxide rod-on-sheet nanoarrays on Ni foam: A superior catalytic electrode for ultrahigh-performance electrochemical sensing of glucose. Sens Actuators B Chem 255:416–423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.08.078
Ramkumar KD, Abraham WS, Viyash V, Arivazhagan N, Rabel AM (2017) Investigations on the microstructure, tensile strength and high temperature corrosion behaviour of Inconel 625 and Inconel 718 dissimilar joints. J Manuf Process 25:306–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2016.12.018
Shakil M, Ahmad M, Tariq NH, Hasan BA, Akhter JI, Ahmed E, Mehmood M, Choudhry MA, Iqbal M (2014) Microstructure and hardness studies of electron beam welded Inconel 625 and stainless steel 304L. Vacuum 110:121–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2014.08.016
Carroll EB, Otis AR, Borgonia JP, Suh JO, Dillon PR, Shapiro AA, Hofmann DC, Liu ZK, Beese AM (2016) Functionally graded material of 304L stainless steel and inconel 625 fabricated by directed energy deposition: characterization and thermodynamic modeling. Acta Mater 108:46–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2016.02.019
Babu MS, Kiruba M, Dharuman N, Sundaravignesh S, Sankarapandian S, Prabu V, Berchmans LJ, Sreedhar G (2019) High-temperature oxidation and hot corrosion behavior of Er2Sn2O7+Inconel 625 composite. Ceram Int 45:17620–17629. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.05.327
Urso M, Torrisi G, Boninelli S, Bongiorno C, Priolo F, Mirabella S (2019) Ni(OH)2@Ni core-shell nanochains as low-cost high-rate performance electrode for energy storage applications. Sci Rep 9:7736. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-44285-1
Wu MS, Sie YJ, Yang SB (2019) Hollow mesoporous nickel dendrites grown on porous nickel foam for electrochemical oxidation of urea. Electrochim Acta 304:131–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2019.02.100
Nacef M, Chelaghmia ML, Khelifi O, Pontié M, Djelaibia M, Guerfa R, Bertagna V, Vautrin-Ul C, Aisset F, Affoune AM (2021) Electrodeposited Ni on pencil graphite electrode for glycerol electrooxidation in alkaline media. Int J Hydrog Energy 46:37670–37678. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.07.104
Veerasubramani GK, Krishnamoorthy K, Kim SJ (2016) Improved electrochemical performances of binder-free CoMoO4 nanoplate arrays@Ni foam electrode using redox additive electrolyte. J Power Sources 306:378–386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2015.12.034
Ferrari AGM, Foster CW, Kelly PJ, Brownson DAC, Banks CE (2018) Determination of the electrochemical area of screen-printed electrochemical sensing platforms. Biosensors 8:53. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios8020053
Jafarian M, Forouzandeh F, Danaee I, Gobal F, Mahjani MG (2009) Electrocatalytic oxidation of glucose on Ni and NiCu alloy modified glassy carbon electrode. J Solid State Electrochem 13:1171–1179. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-008-0632-1
Mathew M, Sandhyarani N (2013) A highly sensitive electrochemical glucose sensor structuring with nickel hydroxide and enzyme glucose oxidase. Electrochim Acta 108:274–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2013.07.010
Laviron E (1979) General expression of the linear potential sweep voltammogram in the case of diffusionnless electrochemical systems. J Electroanal Chem 101:19–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-0728(79)80075-3
Mao H, Cao Z, Guo X, Liu M, Sun D, Sun Z, Ge H, Zhang Y, Song XM (2019) Enhanced electrocatalytic performance for the oxidation of methanol by hierarchical NiS/Ni(OH)2@polypyrrole/graphene oxide nanosheets. Appl Surf Sci 471:355–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.11.188
Chelaghmia ML, Fisli H, Nacef M, Brownson DAC, Affoune AM, Satha H, Banks CE (2021) Disposable non-enzymatic electrochemical glucose sensors based upon screen-printed graphite macroelectrodes modified via a facile methodology with Ni, Cu, and Ni/Cu hydroxides are shown to accurately determine glucose in real human serum blood samples. Anal Methods 13:2812–2822. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1AY00056J
Dong M, Hu H, Ding S, Wang C (2021) High-performance non-enzymatic glucose-sensing electrode fabricated by a-nickel hydroxide-reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite on nickel foam substrate. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 32:19327–19338. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06451-y
Wang L, Xie Y, Wei C, Lu X, Li X, Song Y (2015) Hierarchical NiO superstructures/foam Ni electrode derived from Ni metal-organic framework flakes on foam Ni for glucose sensing. Electrochim Acta 174:846–852. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2015.06.086
Zhaoa Y, Gub G, Youa S, Jic R, Suota H, Zhaota C, Liu F (2015) Preparation of Ni(OH)2 nanosheets on Ni foam via direct precipitation method for highly sensitive non-enzymatic glucose sensor. RSC Adv 5:53665–53670. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA06664F
Xiao Q, Wang X, Huang S (2017) Facile synthesis of Ni(OH)2 nanowires on nickel foam via one step low-temperature hydrothermal route for non-enzymatic glucose sensor. Mater Lett 198:19–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2017.03.172
Joa HJ, Shita A, Jhonc HS, Park SY (2020) Highly sensitive non-enzymatic wireless glucose sensor based on Ni–Co oxide nanoneedle-anchored polymer dots. J Ind Eng Chem 89:485–493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2020.06.028
Lu W, Qin X, Asiri AM, Al-Youbi AO, Sun X (2013) Ni foam: a novel three-dimensional porous sensing platform for sensitive and selective nonenzymatic glucose detection. Analyst 138:417–420. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2AN36138H
Huo H, Zhao Y, Xu C (2014) 3D Ni3S2 nanosheet arrays supported on Ni foam for high-performance supercapacitor and nonenzymatic glucose detection. J Mater Chem A 2:15111–15117. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TA02857K
Kumar S, Fu YP (2021) PANI/g-C3N4 composite over ZnCo2O4/Ni-foam, a bi-functional electrode as a supercapacitor and electrochemical glucose sensor. Sustain Energy Fuels 5:3987–4001. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1SE00491C
Iwu KO, Lombardo A, Sanz R, Scire S, Mirabella S (2016) Facile synthesis of Ni nanofoam for flexible and low-cost non-enzymatic glucose sensing. Sens Actuators B: Chem 224:764–771. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2015.10.109
Wang X, Wang M, Feng S, He D, Jiang P (2020) Controlled synthesis of flower-like cobalt phosphate microsheet arrays supported on Ni foam as a highly efficient 3D integrated anode for non-enzymatic glucose sensing. Inorg Chem Front 7:108–116. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9QI00948E
Xia K, Yang C, Chenb Y, Tianb L, Sub Y, Wang J, Li L (2017) In situ fabrication of Ni(OH)2 flakes on Ni foam through electrochemical corrosion as high sensitive and stable binder-free electrode for glucose sensing. Sens Actuators B 240:979–987. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.09.077
Guo Q, Zeng W, Li Y (2019) Highly sensitive non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on porous NiCo2O4 nanowires grown on nickel foam. Mater Lett 256:126603. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2019.126603
Chandrasekaran NI, Matheswaran M (2019) A sensitive and selective non-enzymatic glucose sensor with hollow Ni-AlMn layered triple hydroxide nanocomposites modified Ni foam. Sens Actuators B: Chem 288:188–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.02.102
Acknowledgements
The financial support within the General Direction of Scientific Research and Technology Development of the Algerian Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research is greatly acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kihal, R., Fisli, H., Chelaghmia, M.L. et al. A novel and ultrasensitive non-enzymatic electrochemical glucose sensor in real human blood samples based on facile one-step electrochemical synthesis of nickel hydroxides nanoparticles onto a three-dimensional Inconel 625 foam. J Appl Electrochem 53, 315–329 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-022-01757-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-022-01757-z