Abstract
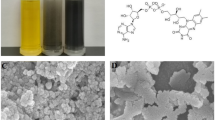
A novel electrochemical bioidentification system for determination of the Kirsten rat sarcoma virus oncogene (KRAS) gene derived from lung cancer was developed based on riboflavin 5′-(trihydrogen diphosphate) (RHP) functionalized WS2 nanosheets prepared by synchronous ultrasonication. RHP presented excellent performance for scattering the WS2 nanosheets into aqueous phase. The acquired WS2-RHP nanocomposite provided favorable interface for DNA sensing by means of electrochemical self-redox signal variation. The immobilization of the probe single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) on the nanocomposite through the non-covalent π–π interaction between the nucleic acid bases and conjugated nanostructure could bring about the decrease of the self-signal. The self-redox signal would regenerate owing to the release of the obtained double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) from the nanocomposite due to the burying of the base in dsDNA after the nucleic acid hybridization. The determination linear range of the complementary target DNA was achieved from 1.0 × 10−16 to 1.0 × 10−8 mol L−1 accompanied with a detection limit of 2.7 × 10−17 mol L−1. The constructed gene sensing system exhibited splendid specificity and magnificent long-term stableness at the same time. The proposed detection method was deserved to spread and employed to develop diverse sensing systems for biological species and molecules.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Korzeniecki C, Priefer R (2021) Targeting KRAS mutant cancers by preventing signaling transduction in the MAPK pathway. Eur J Med Chem 211:113006
Salgia R, Pharaon R, Mambetsariev I, Nam A, Sattler M (2021) The improbable targeted therapy: KRAS as an emerging target in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Cell Rep Med 2:100186
Meng MM, Zhong KY, Jiang T, Liu ZQ, Kwan HY, Su T (2021) The current understanding on the impact of KRAS on colorectal cancer. Biomed Pharmacother 140:111717
Otero F, Shortall K, Salaj-Kosla U, Tofail SAM, Magner E (2021) Electrochemical biosensor for the detection of a sequence of the TP53 gene using a methylene blue labelled DNA probe. Electrochim Acta 388:138642
Luo SH, Zhang Y, Huang GN, Situ B, Ye XY, Tao ML, Huang YF, Li B, Jiang XJ, Wang Q, Zheng L (2021) An enzyme-free amplification strategy for sensitive assay of circulating tumor DNA based on wheel-like catalytic hairpin assembly and frame hybridization chain reaction. Sens Actuators B 338:129857
Li ZB, Xu HW, Li SQ, Wu SJ, Mi XM (2021) Zettomole electrochemical HIV DNA detection using 2D DNA-Au nanowire structure, hemin/G-quadruplex and polymerase chain reaction multi-signal synergistic amplification. Anal Chim Acta 1159:338428
Han S, Liu WY, Zheng M, Wang RS (2020) Label-Free and ultrasensitive electrochemical DNA biosensor based on urchinlike carbon nanotube-gold nanoparticle nanoclusters. Anal Chem 92:4780–4787
Wang YQ, Hsine Z, Sauriat-Dorizon H, Mlika R, Korri-Youssoufi H (2020) Structural and electrochemical studies of functionalization of reduced graphene oxide with alkoxyphenylporphyrin mono- and tetra-carboxylic acid: application to DNA sensors. Electrochim Acta 357:136852
Chen KC, Zhao HL, Wang ZX, Lan MB (2021) A novel signal amplification label based on AuPt alloy nanoparticles supported by high-active carbon for the electrochemical detection of circulating tumor DNA. Anal Chim Acta 1169:338628
Chen M, Wu DM, Tu SH, Yang CY, Chen DJ, Xu Y (2021) CRISPR/Cas9 cleavage triggered ESDR for circulating tumor DNA detection based on a 3D graphene/AuPtPd nanoflower biosensor. Biosens Bioelectron 173:112821
Kıransan KD, Topcu E (2020) Conducting polymer-reduced graphene oxide sponge electrode for electrochemical detection based on DNA hybridization. ACS Appl Nano Mater 3:5449–5462
Liang QJ, Zhang Q, Zhao XX, Liu MZ, Wee ATS (2021) Defect engineering of two-dimensional transition-metal dichalcogenides: applications, challenges, and opportunities. ACS Nano 15:2165–2181
Hemanth NR, Kim T, Kim B, Jadhav AH, Lee K, Chaudhari NK (2021) Transition metal dichalcogenide-decorated MXenes: promising hybrid electrodes for energy storage and conversion applications. Mater Chem Front 5:3298–3321
Chowdhury T, Sadler EC, Kempa TJ (2020) Progress and prospects in transition-metal dichalcogenide research beyond 2D. Chem Rev 120:12563–12591
Tian SF, Tang Q (2021) Activating transition metal dichalcogenide monolayers as efficient electrocatalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction via single atom doping. J Mater Chem C 9:6040–6050
Hoang AT, Qu KR, Chen X, Ahn JH (2021) Large-area synthesis of transition metal dichalcogenides via CVD and solution-based approaches and their device applications. Nanoscale 13:615–633
Fu XH, Li XM, Han DB, Yang W, Liu CJ, Fan L, Ding SJ, Ma YP (2021) Ultrasensitive electrochemical biosensor for des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin analysis based on core-shell Pd@PtCu-alloy loaded on WS2 nanosheet. J Electroanal Chem 888:115213
Hong GL, Chen RT, Xu LY, Lu X, Yang ZQ, Zhou GB, Li L, Chen W, Peng HP (2020) One-pot ultrasonic synthesis of multifunctional Au nanoparticle-ferrocene-WS2 nanosheet composite for the construction of an electrochemical biosensing platform. Anal Chim Acta 1099:52–59
Kumari R, Osikoya AO, Opoku F, Anku WW, Shukla SK, Govender PP (2020) Composite 2D nanointerfaces for electrochemical biosensing: an experimental and theoretical study. ACS Appl Bio Mater 3:8676–8687
Zhang J, Han D, Wang S, Zhang XD, Yang RQ, Ji YC, Yu X (2019) Electrochemical detection of adenine and guanine using a three-dimensional WS2 nanosheet/graphite microfiber hybrid electrode. Electrochem Commun 99:75–80
Wang Q, Yin HS, Zhou YL, Wang J, Ai SY (2021) Photoelectrochemical biosensor for 5-formylcytosine deoxyribonucleoside detection based on BiIO4-WS2/CuO ternary heterojunction. Sens Actuators B 341:130019
Yang JM, Yin XS, Xia M, Zhang W (2018) Tungsten disulfide nanosheets supported poly (xanthurenic acid) as a signal transduction interface for electrochemical genosensing applications. RSC Adv 8:39703–39709
Hu YW, Yang T, Wang XX, Jiao K (2010) Highly sensitive indicator-free impedance sensing of DNA hybridization based on poly(m-aminobenzenesulfonic acid)/TiO2 nanosheet membranes with pulse potentiostatic method preparation. Chem Eur J 16:1992–1999
Zhang W, Dai ZC, Liu X, Yang JM (2018) High-performance electrochemical sensing of circulating tumor DNA in peripheral blood based on poly-xanthurenic acid functionalized MoS2 nanosheets. Biosens Bioelectron 105:116–120
Huang KJ, Liu YJ, Zhang JZ, Liu YM (2015) A sequence-specific DNA electrochemical sensor based on acetylene black incorporated two-dimensional CuS nanosheets and gold nanoparticles. Sens Actuators B 209:570–578
Avelino KYPS, Frias IAM, Lucena-Silva N, Gomes RG, de Melo CP, Oliveira MDL, Andrade CAS (2016) Attomolar electrochemical detection of the BCR/ABL fusion gene based on an amplifying self-signal metal nanoparticle-conducting polymer hybrid composite. Colloids Surf B 148:576–584
Gong QJ, Wang YD, Yang HY (2017) A sensitive impedimetric DNA biosensor for the determination of the HIV gene based on graphene-Nafion composite film. Biosens Bioelectron 89:565–569
Zhu LM, Luo LQ, Wang ZX (2012) DNA Electrochemical biosensor based on thionine-graphene nanocomposite. Biosens Bioelectron 35:507–511
Yang T, Meng L, Wang XX, Wang LL, Jiao K (2013) Direct electrochemical DNA detection originated from the self-redox signal of sulfonated polyaniline enhanced by graphene oxide in neutral solution. ACS Appl Mater Inter 5:10889–10894
Acknowledgements
This work was financed by the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (No. ZR2021MB131 and ZR2021MB105).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that can inappropriately influence our work.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, J., Hu, X. & Zhang, W. Electrochemical self-signal identification of Kirsten rat sarcoma virus oncogene based on riboflavin 5′-(trihydrogen diphosphate) functionalized WS2 nanosheets. J Appl Electrochem 53, 19–27 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-022-01739-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-022-01739-1