Abstract
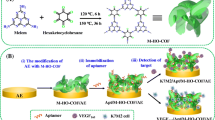
Designing and developing electrochemical DNA biosensors based on nanotechnology to solve the low hybridization efficiency of DNA has gained wide attention in recent years because nanomaterials can enhance surface area of electrode and increase amount of probe DNA immobilization. Herein, a new label-free electrochemical DNA biosensor was constructed for sensitive detection of kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene (KRAS) DNA. During this process, based on the large specific surface of hollow mesoporous silica (HMS), amino-functionalized hollow mesoporous silica (NH2-HMS) nanocomposite was synthesized, and then highly dispersed gold nanoparticles (Au NPs) were uniformly and stably anchored onto its surface to form Au NPs combined with amino-functionalized hollow mesoporous silica (NH2-HMS@Au), which was utilized as supporting material for decorating the electrode surface. The amino-terminated probe DNA was subsequently immobilized onto the modified electrode surface via Au–N bond and employed as probes to determine the target DNA (t-DNA). The synergetic effects of NH2-HMS with Au NPs achieved enhance of the analytical performance of biosensor. Under the optimized conditions, the prepared DNA biosensor possessed a wide linear range from 1 × 10−12 to 1 × 10−7 M with a low detection limit of 0.366 pM. Moreover, the DNA biosensor displayed satisfying selectivity, remarkable stability, which provided a promising application for clinical diagnosis and analysis.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang W, Dai Z, Liu X, Yang J (2018) High-performance electrochemical sensing of circulating tumor DNA in peripheral blood based on poly-xanthurenic acid functionalized MoS2 nanosheets. Biosens Bioelectron 105:116–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.01.038
Li F, Chen W, Zhang S (2008) Development of DNA electrochemical biosensor based on covalent immobilization of probe DNA by direct coupling of sol-gel and self-assembly technologies. Biosens Bioelectron 24:781–786. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2008.06.052
Malmir M, Arjomandi J, Khosroshahi AG, Moradi M, Shi H (2021) Label-free E-DNA biosensor based on PANi-RGO-G*NPs for detection of cell-free fetal DNA in maternal blood and fetal gender determination in early pregnancy. Biosens Bioelectron 189:113356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2021.113356
Gong Q, Wang Y, Yang H (2017) A sensitive impedimetric DNA biosensor for the determination of the HIV gene based on graphene-Nafion composite film. Biosens Bioelectron 89:565–569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.02.045
Liu Z, Su X (2017) A novel fluorescent DNA sensor for ultrasensitive detection of Helicobacter pylori. Biosens Bioelectron 87:66–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.07.061
Zuo L, Qu Q, Li L, Ran X, Gui J, Wang Q, Cui X, Jiang C (2018) Electrochemical DNA biosensor based on magnetite/multiwalled carbon nanotubes/chitosan nanocomposite for Bacillus cereus detection of potential marker for gold prospecting. Electroanal 30:910–920. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.201700801
Li F, Zhang H, Dever B, Li XF, Le XC (2013) Thermal stability of DNA functionalized gold nanoparticles. Bioconjug Chem 24:1790–1797. https://doi.org/10.1021/bc300687z
Liu B, Liu J (2017) Methods for preparing DNA-functionalized gold nanoparticles, a key reagent of bioanalytical chemistry. Anal Methods 9:2633–2643. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ay00368d
Han Z, Tang Z, Jiang K, Huang Q, Meng J, Nie D, Zhao Z (2020) Dual-target electrochemical aptasensor based on co-reduced molybdenum disulfide and Au NPs (rMoS2-Au) for multiplex detection of mycotoxins. Biosens Bioelectron 150:111894. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.111894
Noorbakhsh A, Salimi A (2011) Development of DNA electrochemical biosensor based on immobilization of ssDNA on the surface of nickel oxide nanoparticles modified glassy carbon electrode. Biosens Bioelectron 30:188–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2011.09.010
Bagheri E, Ansari L, Sameiyan E, Abnous K, Taghdisi SM, Ramezani M, Alibolandi M (2020) Sensors design based on hybrid gold-silica nanostructures. Biosens Bioelectron 153:112054. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2020.112054
Zheng Y, Wang D, Li Z, Sun X, Gao T, Zhou G (2018) Laccase biosensor fabricated on flower-shaped yolk-shell SiO2 nanospheres for catechol detection. Colloid Surface A 538:202–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2017.10.086
Deng C, Liu Y, Zhou F, Wu M, Zhang Q, Yi D, Yuan W, Wang Y (2021) Engineering of dendritic mesoporous silica nanoparticles for efficient delivery of water-insoluble paclitaxel in cancer therapy. J Colloid Interface Sci 593:424–433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2021.02.098
Guillet-Nicolas R, Wainer M, Marcoux L, Thommes M, Kleitz F (2020) Exploring the confinement of polymer nanolayers into ordered mesoporous silica using advanced gas physisorption. J Colloid Interface Sci 579:489–507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2020.05.103
Hochstrasser J, Juere E, Kleitz F, Wang W, Kubel C, Tallarek U (2021) Insights into the intraparticle morphology of dendritic mesoporous silica nanoparticles from electron tomographic reconstructions. J Colloid Interface Sci 592:296–309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2021.02.069
Guo Z, Chen Y, Wang S, Pang J, Liu Z (2021) Dendritic mesoporous silica nanospheres: toward the ultimate minimum particle size for ultraefficient liquid chromatographic separation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 13:22970–22977. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.1c03985
Gao Q, Xie W, Zhao L, Wang Y, Zhang W, Cai Q (2018) Synthesis of hierarchical sieve-like mesoporous silica nanoparticle aggregates via centrifugal method for drug delivery system. Chin Chem Lett 29:1804–1810. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2018.09.006
Teng Z, Li W, Tang Y, Elzatahry A, Lu G, Zhao D (2019) Mesoporous organosilica hollow nanoparticles: synthesis and applications. Adv Mater 31:1707612. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201707612
Gao Y, Liu Y, Qin X, Guo Z, Li D, Li C, Wan H, Zhu F, Li J, Zhang Z, He S (2021) Dual stimuli-responsive fungicide carrier based on hollow mesoporous silica/hydroxypropyl cellulose hybrid nanoparticles. J Hazard Mater 414:125513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125513
Tian M, Long Y, Xu D, Wei S, Dong Z (2018) Hollow mesoporous silica nanotubes modified with palladium nanoparticles for environmental catalytic applications. J Colloid Interface Sci 521:132–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2018.03.041
Chang Y, Li Y, Zhang C, Zhao T, Tuo X, Guo J, Gong Y (2019) Formaldehyde-controlled synthesis of multishelled hollow mesoporous SiO2 microspheres. Langmuir 35:14517–14521. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.9b00880
Li T, Geng T, Md A, Banerjee P, Wang B (2019) Novel scheme for rapid synthesis of hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles (HMSNs) and their application as an efficient delivery carrier for oral bioavailability improvement of poorly water-soluble BCS type II drugs. Colloid Surf B 176:185–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.01.004
Lin CY, Yang CM (2020) Study on the dissolution of hollow mesoporous silica nanosphere-supported nanosized platinum oxide in biorelevant media for evaluating its potential as chemotherapeutics. J Colloid Interface Sci 558:137–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2019.09.114
Yang L, Kaziem AE, Lin Y, Li C, Tan Y, Huang S, Cheng D, Xu H, Zhang Z (2021) Carboxylated beta-cyclodextrin anchored hollow mesoporous silica enhances insecticidal activity and reduces the toxicity of indoxacarb. Carbohydr Polym 266:118150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118150
Qian X, Tan S, Li Z, Qu Q, Li L, Yang L (2020) A robust host-guest interaction controlled probe immobilization strategy for the ultrasensitive detection of HBV DNA using hollow HP5-Au/CoS nanobox as biosensing platform. Biosens Bioelectron 153:112051. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2020.112051
Eldehna WM, Salem R, Elsayed ZM, Al-Warhi T, Knany HR, Ayyad RR, Traiki TB, Abdulla MH, Ahmad R, Abdel-Aziz HA, El-Haggar R (2021) Development of novel benzofuran-isatin conjugates as potential antiproliferative agents with apoptosis inducing mechanism in Colon cancer. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 36:1424–1435. https://doi.org/10.1080/14756366.2021.1944127
Wu L, Garrido-Maestu A, Guerreiro JRL, Carvalho S, Abalde-Cela S, Prado M, Dieguez L (2019) Amplification-free SERS analysis of DNA mutation in cancer cells with single-base sensitivity. Nanoscale 11:7781–7789. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9nr00501c
Xu H, Wu D, Li CQ, Lu Z, Liao XY, Huang J, Wu ZS (2017) Label-free colorimetric detection of cancer related gene based on two-step amplification of molecular machine. Biosens Bioelectron 90:314–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.12.003
Chen H, Xiang Y, Cai R, Zhang L, Zhang Y, Zhou N (2021) An ultrasensitive biosensor for dual-specific DNA based on deposition of polyaniline on a self-assembled multi-functional DNA hexahedral-nanostructure. Biosens Bioelectron 179:113066. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2021.113066
Jang K, Choi J, Park C, Na S (2017) Label-free and high-sensitive detection of Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog and epidermal growth factor receptor mutation using Kelvin probe force microscopy. Biosens Bioelectron 87:222–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.08.045
Li Q, Zhou D, Pan J, Liu Z, Chen J (2019) An ultrasensitive and simple fluorescence biosensor for detection of the Kras wild type by using the three-way DNA junction-driven catalyzed hairpin assembly strategy. Analyst 144:3088–3093. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9an00195f
Wang X, Yang M, Liu Q, Yang S, Geng X, Yang Y, Fa H, Wang Y, Hou C (2019) An ultrasensitive electrochemical DNA biosensor based on carboxylated multi-walled carbon nanotube/molybdenum disulfide composites for KRAS gene detection. Anal Sci 35:441–448. https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.18p518
Teng Z, Su X, Zheng Y, Sun J, Chen G, Tian C, Wang J, Li H, Zhao Y, Lu G (2012) Mesoporous silica hollow spheres with ordered radial mesochannels by a spontaneous self-transformation approach. Chem Mater 25:98–105. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm303338v
Hashkavayi AB, Raoof JB (2017) Design an aptasensor based on structure-switching aptamer on dendritic gold nanostructures/Fe3O4@SiO2/DABCO modified screen printed electrode for highly selective detection of epirubicin. Biosens Bioelectron 91:650–657. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2017.01.025
Yan Z, Gan N, Li T, Cao Y, Chen Y (2016) A sensitive electrochemical aptasensor for multiplex antibiotics detection based on high-capacity magnetic hollow porous nanotracers coupling exonuclease-assisted cascade target recycling. Biosens Bioelectron 78:51–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2015.11.019
Shamsipur M, Emami M, Farzin L, Saber R (2018) A sandwich-type electrochemical immunosensor based on in situ silver deposition for determination of serum level of HER2 in breast cancer patients. Biosens Bioelectron 103:54–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2017.12.022
Wang X, Dong J, Liu X, Liu Y, Ai S (2014) A novel pH-controlled immunosensor using hollow mesoporous silica and apoferritin combined system for target virus assay. Biosens Bioelectron 54:85–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2013.10.051
Luo S, Liu Y, Rao H, Wang Y, Wang X (2017) Fluorescence and magnetic nanocomposite Fe3O4@SiO2@Au MNPs as peroxidase mimetics for glucose detection. Anal Biochem 538:26–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2017.09.006
Atchudan R, Edison T, Aseer KR, Perumal S, Karthik N, Lee YR (2018) Highly fluorescent nitrogen-doped carbon dots derived from Phyllanthus acidus utilized as a fluorescent probe for label-free selective detection of Fe3+ ions, live cell imaging and fluorescent ink. Biosens Bioelectron 99:303–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2017.07.076
Wan M, Zhao H, Peng L, Zou X, Zhao Y, Sun L (2020) Loading of Au/Ag bimetallic nanoparticles within and outside of the flexible SiO2 electrospun nanofibers as highly sensitive, stable, repeatable substrates for versatile and trace SERS detection. Polymers 12:3008. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12123008
Jeon H, Lee CS, Patel R, Kim JH (2015) Well-organized meso-macroporous TiO2/SiO2 film derived from amphiphilic rubbery comb copolymer. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:7767–7775. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b01010
Kumar DR, Kesavan S, Nguyen TT, Hwang J, Lamiel C, Shim J-J (2017) Polydopamine@electrochemically reduced graphene oxide-modified electrode for electrochemical detection of free-chlorine. Sensors Actuators B Chem 240:818–828. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.09.025
Ono LK, Behafarid F, Cuenya BR (2013) Nano-gold diggers: Au-assisted SiO2-decomposition and desorption in supported nanocatalysts. ACS Nano 7:10327–10334. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn404744b
Gholivand MB, Akbari A (2019) A sensitive electrochemical genosensor for highly specific detection of thalassemia gene. Biosens Bioelectron 129:182–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.01.017
Chen W, Zhang X, Li J, Chen L, Wang N, Yu S, Li G, Xiong L, Ju H (2020) Colorimetric detection of nucleic acids through triplex-hybridization chain reaction and DNA-controlled growth of platinum nanoparticles on graphene oxide. Anal Chem 92:2714–2721. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b04909
Li H, Tang Y, Zhao W, Wu Z, Wang S, Yu R (2019) Palindromic molecular beacon-based intramolecular strand-displacement amplification strategy for ultrasensitive detection of K-ras gene. Anal Chim Acta 1065:98–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2019.02.059
Chung CH, Kim JH (2018) One-step isothermal detection of multiple KRAS mutations by forming SNP specific hairpins on a gold nanoshell. Analyst 143:3544–3548. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8an00525g
Zhang Q, Liu Y, Nie Y, Liu Y, Ma Q (2019) Wavelength-dependent surface plasmon coupling electrochemiluminescence biosensor based on sulfur-doped carbon nitride quantum dots for K-RAS gene detection. Anal Chem 91:13780–13786. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b03212
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under the Grants 52061041, 51661033, 31660538, 51361028, and 51161025. This work was also supported by Workstation of Academician Chen Jing of Yunnan Province (No. 202105AF150012), Free exploration fund for academician (No. 202205AA160007). Authors thank Analysis and Measurement Center of Yunnan University for the sample testing service.
Funding
National Natural Science Foundation of China, 52061041, Qing Qu, 51661033, Qing Qu, 31660538, Qing Qu, 51361028, Qing Qu, 51161025, Qing Qu.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XB: involved in writing—original draft, experiment, investigation, and data curation; XL: involved in data management and investigation; SL: involved in investigation and data curation; EM: involved in investigation and data curation; YD: involved in investigation and data curation; LW: involved in supervision; LL: involved in supervision and resources; QQ: involved in conceptualization, supervision, and writing—review and editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Annela M. Seddon.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, X., Li, X., Li, S. et al. A stable Au–N bond controlled probe immobilization approach for the sensitive detection of kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene DNA using NH2-HMS@Au. J Mater Sci 57, 10328–10342 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-022-07314-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-022-07314-5