Abstract
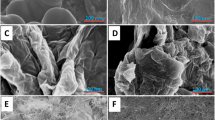
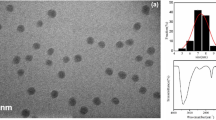
We describe here the manufacture of poly(aniline-co-o-anisidine)/graphene oxide nanocomposites, with the common abbreviation [PANI-co-PoAN/GO1−5], by the well-known in situ oxidative polymerization method with ultrasonic assistance. FE-SEM and TEM micrographs were utilized to examine the morphological characteristics of the composite materials. Moreover, FT-IR, XRD, TGA, and electrical conductivity measurements were used to investigate their complete performance. All the composites had almost equal final copolymer decomposition temperatures, which were in the range of 609.3–663.8 °C. Our essential objective is to study the electro selective application using gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) as a coating. Dopamine (DA) electrochemical sensor based on [AuNPs/PANI-co-PoAN/GO] nanocomposite covalently modified gold electrode was modified by an electroabsorption technique. The electrochemical behavior of the modified electrode towards the oxidation of DA was studied by square wave voltammetry (SWV) and cyclic voltammetry (CV) in pH 5.0 phosphate buffer solution. The sensor developed a current response to the oxidation of DA. Using SWV, the electrochemical sensor gave a linear relationship to DA in the concentration range of 5–100 µM with a limit of detection of 0.0334 µM. The modified electrode was highly stable, sensitive, and selective.
Graphical abstract


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ben AM, Bounab L, Choukairi M et al (2018) Selective and sensitive detection of dopamine in the presence of ascorbic acid and uric acid at a Sonogel-Carbon l-Histidine modified electrode. J Mater Environ Sci 9:66–76
Tukimin N, Abdullah J, Sulaiman Y (2018) Review—electrochemical detection of uric acid. Dopamine Ascorbic Acid 165:258–267. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0201807jes
Heien MLAV, Khan AS, Ariansen JL et al (2005) Real-time measurement of dopamine fluctuations after cocaine in the brain of behaving rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:10023–10028
Li W, Liu Z, Lin H et al (2010) Label-free colorimetric assay for methyltransferase activity based on a novel methylation-responsive. DNAzyme Strategy 82:4407–4413
Park J, Myung S, Kim I et al (2013) Simultaneous measurement of serotonin, dopamine and their metabolites in mouse brain extracts by high-performance liquid chromatography with mass spectrometry following derivatization with ethyl chloroformate. Biol Pharm Bull 36:252–258
Carrera V, Sabater E, Vilanova E, Sogorb MA (2007) A simple and rapid HPLC-MS method for the simultaneous determination of epinephrine, norepinephrine, dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine: application to the secretion of bovine chromaffin cell cultures. J Chromatogr 847:88–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2006.09.032
Qian C, Zhu S, Feng P et al (2015) Conjugated polymer nanoparticles for fluorescence imaging and sensing of neurotransmitter dopamine in living cells and the brains of Zebra fish larvae. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b04987
Kumbhat S, Shankaran DR, Kim SJ et al (2007) Surface plasmon resonance biosensor for dopamine using D3 dopamine receptor as a biorecognition molecule. Biosens Bioelectron 23:421–427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2007.05.004
Krishna VM, Somanathan T, Manikandan E et al (2018) Neurotransmitter dopamine enhanced sensing detection using fibre-like carbon nanotubes by chemical vapor deposition technique. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 18:5380–5389. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2018.15425
Yin ZZ, Cheng SW, Xu L, Bin et al (2018) Highly sensitive and selective sensor for sunset yellow based on molecularly imprinted polydopamine-coated multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Biosens Bioelectron 100:565–570. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2017.10.010
Cogal S (2018) Electrochemical determination of dopamine using graphene oxide-modified glassy carbon electrode electrochemical determination of dopamine using a. Anal Lett. https://doi.org/10.1080/00032719.2017.1387791
March G, Dung T, Piro B (2015) Modified electrodes used for electrochemical detection of metal ions in environmental analysis. Biosensors 5:241–275. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios5020241
Fan D, Wu S, Tian S, Zhou J, Ju Y, Ma C, Shi J (2014) Detection of dopamine on a poly(metanilic acid) decorated two-dimensional gold cavity array electrode. RSC Adv 4:49560–49568. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA07649D
Yuhong S, Jia P, Bai Y, Liao S, Wang S, Zheng Z (2013) A simple and novel strategy for the simultaneous determination of dopamine, aceelectrodetamidophenol and tryptophan based on poly(new coccine) film modified carbon paste. Anal Methods 5:5737–5745. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ay41058g
Ding A, Wang B, Zheng J et al (2018) Sensitive dopamine sensor based on three dimensional and macroporous carbon aerogel microelectrode. Int J Electrochem Sci 13:4379–4389. https://doi.org/10.20964/2018.05.43
Wang X, Lu M, Wang H et al (2015) Three-dimensional graphene aerogels—mesoporous silica frameworks for superior adsorption capability of phenols. Sep Purif Technol 153:7–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2015.08.030
Li J, Wang Y, Sun Y et al (2016) A novel ionic liquid functionalized graphene oxide supported gold nanoparticle composite fi lm for sensitive electrochemical detection of dopamine. RSC Adv 7:2315–2322. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA25627A
Wang W, Cheng Y, Yan L et al (2015) Analytical methods highly sensitive electrochemical sensor for dopamine with a double-stranded. Anal Methods 7:1878–1883. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4AY03008G
Baig N, Kawde A (2016) RSC Advances electrode decorated with alternating layers of Au NPs for the simultaneous detection of dopamine and uric acid in human urine. RSC Adv 6:80756–80765. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA10055D
Pandey S, Annapoorni S, Malhotra BD (1993) Synthesis and characterization of poly(ani1ine-co-o-anisidine): a processable conducting copolymer. Macromolecules 26:3190–3193
Wang J, Keene FR (1996) Mechanism of mediation of the electrochemical oxidation of K4Fe(CN)6 at poly-[tris(3-{ω-[4-(2,2′-bipyridyl)] alkyl}-thiophene)iron(II)]-film modified electrodes in aqueous solutions. Electrochim Acta 41:2563–2569
Zhuang Z, Li J, Xu R, Xiao D (2011) Electrochemical detection of dopamine in the presence of ascorbic acid using overoxidized polypyrrole/graphene modified electrode. Int J Electrochem Sci 6:2149–2161
Kulandainathan M, Gorlea D (2016) Electrochemical sensing of dopamine at the surface of a dopamine grafted graphene oxide/poly(methylene blue) composite modified electrode. RSC Adv 6:19982–19991. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA25541D
He X, Wu Y, Cui L, Liu Y, Lv G, Pu T, Liu D (2013) A dopamine sensor based on a methoxypolyethylene glycol polymer covalently modified glassy carbon electrode. Analyst 138:1204–1211. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2AN36349F
Li F, Yang L, Zhaoa C, Du Z (2011) Electroactive gold nanoparticles/polyaniline/polydopamine hybrid composite in neutral solution as high-performance sensing platform. Anal Methods 3:1601–1606. https://doi.org/10.1039/C1AY05126A
Shi G, Yu X, Shenga K (2014) A three-dimensional interpenetrating electrode of reduced graphene oxide for selective detection of dopamine. Analyst 139:4525–4531. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4AN00604F
Pruneanua S, Biris A, Pogaceana F, Socacia C, Coros M, Rosua M, Watanabe F, Biris A (2015) The influence of uric and ascorbic acid on the electrochemical detection of dopamine using graphene-modified electrodes. Electrochimica Acta 154:197–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2014.12.046
Srivastava R, Kaur B, Satpatib B (2015) Synthesis of NiCo2O4/Nano-ZSM-5 nanocomposite material with enhanced electrochemical properties for the simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine, uric acid and tryptophan. New J Chem 39:1115–1124. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4NJ01360C
Yang X, Liu X, Zhua H (2014) An electrochemical sensor for dopamine based on poly(ophenylenediamine) functionalized with electrochemically reduced graphene oxide. RSC Adv 4:3706–3712. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3RA45234D
Recco L, Crulhas B, Parraa J, Pedrosa V (2016) A new strategy for detecting dopamine in human serum using polymer brushes reinforced with carbon nanotubes. RSC Adv 6:47134–47137. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA05151K
Acknowledgements
This article contains the results and findings of a research project funded by King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology (KACST) Grant No. PS-38-27.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ganash, A.A., Alqarni, S.A. & Hussein, M.A. Poly(aniline-co-o-anisidine)/graphene oxide Au nanocomposites for dopamine electrochemical sensing application. J Appl Electrochem 49, 179–194 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-018-1260-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-018-1260-9