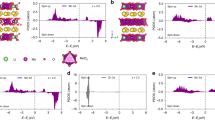
Abstract
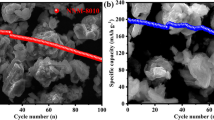
Birnessite MnO2, a hydrated layered manganese dioxide with a layered structure, is a promising candidate for sodium-ion batteries because of a significant interlayer distance for the reversible insertion of sodium ions. This work proposes to improve the electrochemical performance of layered manganese dioxide by metal cation doping. Nickel-doped layered MnO2 (0.05–0.15 wt%) prepared by a sol–gel method using a chelate agent of fumaric acid showed a gradual increase of interlayer distance with an increase of Ni-doping amount. Moreover, ex situ XRD results during the first cycle confirmed a stabilization of the layered structure during the sodium insertion. During the charge–discharge test, the initial capacity of 15% Ni layered MnO2 was 140 mAh/g, with small capacity fade over 20 cycles.
Graphical Abstract
Layered structure of MnO2 and sodium diffusion along [001] and [010] direction.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chabre Y, Pannetier J (1995) Structure and electrochemical properties of the proton/gamma-MnO2 system. Prog Solid State Chem 23:1–130
Euler K-J (1982) Battery manganese dioxide-a survey of its history and etymology. J Power Sources 8:133–141
Bach S, Henry M, Baffier N, Livage J (1990) Sol-gel synthesis of manganese oxide. J Solid State Chem 88:325–333
Pereira-Ramos JP, Baddour-Hadjean R, Bach S, Baffier N (1992) Electrochemical and structural characteristics of some lithium intercalation materials synthesized via a sol-gel process: V2O5 and manganese dioxides-based compounds. Solid State Ion 53–56:701–709
Franger S, Bach S, Fracy J et al (2002) Synthesis, structural and electrochemical characterization of the sol-gel birnessite MnO1.84·0.6H2O. J Power Sources 109:262–275
Ibarra Palos A, Anne M, Strobel P (2001) Electrochemical lithium intercalation in disordered manganese oxides. Solid State Ion 138:203–212
Mendiboure A, Delmas C, Hagenmuller P (1985) Electrochemical intercalation and deintercalation of NaxMnO2 bronzes. J Solid State Chem 57:323–331
Su D, Wang C, Ahn H, Wang G (2013) Single crystalline Na0.7MnO2 nanoplates as cathode materials for sodium-ion batteries with enhanced performance. Chem Eur J 19:10884–10889
Sauvage F, Laffont L, Tarascon J-M, Baudrin E (2007) Study of the insertion/deinsertion mechanism of sodium into Na0.44MnO2. Inorg Chem 46:3289–3294
Kim DJ, Rubha Ponraj AG, Kannan et al (2013) Diffusion behavior of sodium ions in Na0.44MnO2 in aqueous and non-aqueous electrolytes. J Power Sources 244:758–763
Ruffo R, Fathi R, Kim DJ et al (2013) Impedance analysis of Na0.44MnO2 positive electrode for reversible sodium batteries in organic electrolyte. Electrochim Acta 108:575–582
Bach S, Pereira-Ramos JP, Baffier N (1993) Electrochemical sodium insertion into the sol-gel birnessite manganese dioxide. Electrochim Acta 38:1695–1698
Renuka R, Ramamurthy S (2000) An investigation on layered birnessite type manganese oxides for battery applications. J Power Sources 87:144–152
Le Goff P, Baffier N, Bach S et al (1993) Structural and electrochemical characteristics of a lamellar sodium manganese oxide synthesized via a sol-gel process. Solid State Ion 61:309–315
Franger S, Bach S, Farcy J et al (2003) An electrochemical impedance spectroscopy study of new lithiated manganese oxides for 3 V application in rechargeable Li-batteries. Electrochim Acta 48:891–900
Bach S, Pereira-Ramos JP, Baffier N, Messina R (1991) Birnessite manganese dioxide synthesized via a sol–gel process: a new rechargeable cathodic material for lithium batteries. Electrochim Acta 36:1595–1603
Julien C, Massot M, Baddour-Hadjean R et al (2003) Raman spectra of birnessite manganese dioxides. Solid State Ion 159:345–356
Julien C, Massot M, Rangan S et al (2002) Study of structural defects in gamma-MnO2 by Raman spectroscopy. J Raman Spectrosc 33:223–228
Nam KW, Kim S, Yang E et al (2015) Critical role of crystal water for a layered cathode material in sodium ion batteries. Chem Mater 27:3721–3725
Ogata A, Komaba S, Baddour-Hadjean R et al (2008) Doping effects on structure and electrode performance of K-birnessite-type manganese dioxides for rechargeable lithium battery. Electrochim Acta 53:3084–3093
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Vietnam National University of Ho Chi Minh City through grant C2016-18-03.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen, V.H., Huynh, L.T.N., Nguyen, T.H. et al. Promising electrode material using Ni-doped layered manganese dioxide for sodium-ion batteries. J Appl Electrochem 48, 793–800 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-018-1196-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-018-1196-0