Abstract
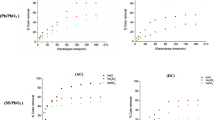
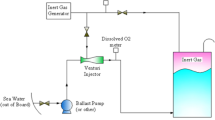
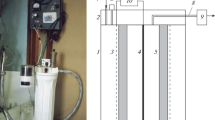
The feasibility of a quick electrochemical process for on board zero-reagent treatment of ballast water by anodic and cathodic production of oxidants was proposed. The process has been tested in the inactivation of the marine dinoflagellates Alexandrium minutum and A. taylori, both responsible for algal blooms and toxin-producing, and against the marine bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a Gram-negative pathogenic micro-organism. A complete inactivation of both dinoflagellates was quickly achieved with electro-generated active chlorine, while higher resistance to oxidising agents was verified for P. aeruginosa. A combined sequential treatment involving anodic oxidation followed by extended exposure time in the absence of current, and a final cathodic treatment was proposed. The cathodically electro-generated hydrogen peroxide contributed to the reduction of treatment time and the removal of residual species.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nanayakkara KGN, Zheng Y-M, Alam AKMK, Zou S, Chen JP (2011) Mar Pollut Bull 63:119–123
McCarthy SA, Khambaty FM (1994) Appl Environ Microbiol 60:2597–2601
Ruiz GM, Rawlings TK, Dobbs FC, Drake LA, Mullady T, Huq A, Colwell RR (2000) Nature 408:49–50
Gregg MD, Hallegraeff GM (2007) Harmful Algae 6:567–584
Haberkorn H, Hégaret H, Marie D, Lambert C, Soudant P (2011) Harmful Algae 10:463–471
Hallegraeff GM (1998) Mar Ecol Prog Ser 168:297–309
Hallegraeff GM, Bolch CJ (1992) J Plankton Res 14:1067–1084
Chu KH, Tam PF, Fung CH, Chen QC (1997) Hydrobiologia 352:201–206
Galil BS, Hulsmann N (2002) In: Leppa-koski E, Gollasch S, Olenin S (eds) Invasive aquatic species of Europe. Distribution, impacts and management. Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, pp 508–511
McCarthy HP, Crowder LB (2000) Biol Invasions 2:221–222
IMO (2004) International convention for the control and management of ships’ ballast water and sediments. BWM/CONF/36. p 36
Kuzirian AM, Terry ECS, Bechtel DL, James PL (2001) Biol Bull 201:297–299
Cangelosi A (2002) In: Leppakoski E, Gollasch S, Olenin S (eds) Invasive aquatic species of Europe. Distribution, impacts and management. Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, pp 511–519
Rigby GR, Hallegraeff GM, Taylor AH (2004) J Mar Environ Eng 7:217–230
Oemcke DJ, van Leeuwen J (2005) Water Res 39:5119–5125
Tsolaki E, Diamadopoulos E (2010) J Chem Technol Biotechnol 85:19–32
Da Pozzo A, Petrucci E, Merli C (2008) J Appl Electrochem 38:997–1003
Petrucci E, Montanaro D, Di Palma L (2012) Chem Eng Trans 28:91–96
Jeong J, Kim C, Yoon J (2009) Water Res 43:895–901
Da Pozzo A, Di Palma L, Merli C, Petrucci E (2005) J Appl Electrochem 35:413–419
Alonso JL, Mascellaro S, Moreno M, Ferrús MA, Hernández J (2002) Appl Environ Microbiol 68:5151–5154
Lahtinen SJ, Gueimonde M, Reinikainen JP, Salminen SJ (2009) Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 84:1137–1147
Veldhuis MJW, Kraay GW, Timmermans KR (2001) Eur J Phycol 36:167–177
Veldhuis MJW, Fuhr F, Boon JP, Ten Hallers-Tjabbers CC (2006) Environ Technol 27:909–921
Garvey M, Moriceau B, Passow U (2007) Mar Ecol Prog Ser 352:17–26
Llaveria G, Figueroa RI, Garcés E, Berdale E (2009) J Phycol 45:1106–1115
Drake LA, Steinberg MK, Riley SC, Robbins SH, Nelson BN, Lemieux E (2010) Development of a method to determine the number of living organisms ≥10 μm and <50 μm (nominally protists) in ships’ ballast water: a combination of two vital, fluorescent stains. Naval Research Laboratory, Washington, pp 20375–25320
Booth BC (1987) Bot Marina 30:101–108
Pouneva I (1997) Bul J Plant Physiol 23:67–76
Kester DR, Duedall IW, Connors DN, Pytkowicz RM (1967) Limnol Oceanogr 12:176–179
Guillard RRL (1975) In: Smith WL, Chanley MH (eds) Culture of marine invertebrate animals. Plenum, New York, pp 26–60
Gilbert F, Galgani F, Cadiou Y (1992) Mar Biol 112:199–205
Jones KH, Senft JA (1985) J Histochem Cytochem 33:77–79
Reavie ED, Cangelosi AA, Allinger LE (2010) J Great Lakes Res 36:540–547
Yu W, Dodds WK, Banks MK, Skalsky J, Strauss EA (1995) Appl Environ Microbiol 61:3367–3372
Dorsey J, Yentsch CM, Mayo S, McKenna C (1989) Cytometry 10:622–628
Held M, Halko DJ, Hurst JK (1978) J Am Chem Soc 100:5732–5740
Oh BS, Oh SG, Hwang YY, Yu HW, Kang J-W, Kim IS (2010) Sci Total Environ 408:5958–5965
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Italian Ministry of University and Research (PRIN 2008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Petrucci, E., Di Palma, L., De Luca, E. et al. Biocides electrogeneration for a zero-reagent on board disinfection of ballast water. J Appl Electrochem 43, 237–244 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-012-0507-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-012-0507-0