Abstract
Purpose
To compare intraocular pressure (IOP) measurements between Easyton transpalpebral tonometry and Perkins, iCare iC100 and Corvis ST. Also, to assess the influence of corneal characteristics and anterior scleral thickness (AST) on the IOP measurements.
Methods
Sixty-nine eyes from 69 healthy subjects were included. IOP was measured by Easyton, Perkins, iC100 and Corvis ST (corrected IOP, bIOP; and non-corrected IOP, IOPnct). Other variables studied were AST, axial length (AL), and Corvis parameters: Length 1, velocity 1, length 2, velocity 2, peak distance, radius, deformation amplitude, and central corneal thickness (CCT). Pearson correlation, limits of agreement (LoA), and multiple regression analysis were calculated.
Results
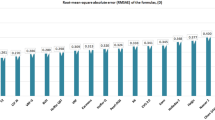
No significant differences in IOP between Easyton and Perkins, iC100, and bIOP were observed (all p > 0.05), being significant only between Perkins and IOPnct ( − 1.49 mmHg, p < 0.001). Bland–Altman graphs showed that the mean difference between Perkins and Easyton was 0.07 mmHg (p < 0.001), and LoA − 7.49 to + 7.39 mmHg. Significant correlations were found between the measurements of Perkins and iC100, IOPnct, bIOP (r = 0.710, 0.628, 0.539; p < 0.001 respectively), iC100 and IOPnct, bIOP (r = 0.627, 0.513; p < 0.001, respectively). The multivariate regression analysis revealed that differences between Perkins and Easyton (adjusted R2 = 0.25) were influenced by AL (B = 1.28, p < 0.008), length 1 (B = 3.13, p < 0.018), and the radius (B = 1.26, p < 0.010). Differences between Perkins and bIOP (adjusted R2 = 0.21) were affected by the CCT (B = 0.029, p < 0.003).
Conclusions
There are no significant differences in the IOP measurements between Perkins and Easyton, iC100 or bIOP. Length 1, radius, and CCT have limited influence on these differences, while AST did not show any effect.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Krieglstein GK, Waller WK (1975) Goldmann applanation versus hand-applanation and Schiötz indentation tonometry. Albrecht von Graefe’s Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 194:11–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00408271
Baskett JS, Goen TM, Terry JE (1986) A comparison of Perkins and Goldmann applanation tonometry. J Am Optom Assoc 57:832–834
Zhang Y, Bian A, Hang Q et al (2023) Corneal biomechanical properties of various types of glaucoma and their impact on measurement of intraocular pressure. Ophthalmic Res. https://doi.org/10.1159/000530291
Brown L, Foulsham W, Pronin S, Tatham AJ (2018) The influence of corneal biomechanical properties on intraocular pressure measurements using a rebound self-tonometer. J Glaucoma 27:511–518. https://doi.org/10.1097/IJG.0000000000000948
Tranchina L, Lombardo M, Oddone F et al (2013) Influence of corneal biomechanical properties on intraocular pressure differences between an air-puff tonometer and the Goldmann applanation tonometer. J Glaucoma 22:416–421. https://doi.org/10.1097/IJG.0b013e31824cafc9
Bao F, Huang W, Zhu R et al (2020) Effectiveness of the goldmann applanation tonometer, the dynamic contour tonometer, the ocular response analyzer and the Corvis ST in measuring intraocular pressure following FS-LASIK. Curr Eye Res 45:144–152. https://doi.org/10.1080/02713683.2019.1660794
Firat PG, Orman G, Doganay S, Demirel S (2013) Influence of corneal parameters in keratoconus on IOP readings obtained with different tonometers. Clin Exp Optom 96:233–237. https://doi.org/10.1111/cxo.12016
Mendez-Hernandez C, Arribas-Pardo P, Cuiña-Sardiña R et al (2017) Measuring intraocular pressure in patients with keratoconus with and without intrastromal corneal ring segments. J Glaucoma 26:71–76. https://doi.org/10.1097/IJG.0000000000000549
Bañeros-Rojas P, Martinez de la Casa JM, Arribas-Pardo P et al (2014) Comparison between Goldmann, Icare Pro and Corvis ST tonometry. Archivos de la Sociedad Espanola de Oftalmologia 89:260–264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oftal.2014.02.001
Karlova EV (2017) Application of the tonometer for intraocular pressure measurements: EASYTON in patients in the early postoperative recovery phase following penetrating keratoplasty. In: Almagia. Clinical study report. https://almagia.com/clinical-tests/easyton-in-patients-in-the-early/. Accessed 20 Aug 2022
Toker MI, Vural A, Erdogan H et al (2008) Central corneal thickness and Diaton transpalpebral tonometry. Graefe’s Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 246:881–889. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-008-0769-8
Doherty MD, Carrim ZI, O`Neill DP, (2012) Diaton tonometry: an assessment of validity and preference against Goldmann tonometry. Clin Exp Ophthalmol 40:171–175. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1442-9071.2011.02636.x
Lösch A, Scheuerle A, Rupp V et al (2005) Transpalpebral measurement of intraocular pressure using the TGDc-01 tonometer versus standard Goldmann applanation tonometry. Graefe’s Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 243:313–316. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-004-0971-2
Sandner D, Böhm A, Kostov S, Pillunat L (2005) Measurement of the intraocular pressure with the “transpalpebral tonometer” TGDc-01 in comparison with applanation tonometry. Graefe’s Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 243:563–569. https://doi.org/10.1007/S00417-004-1037-1
Eduard Klevtsov (2018) Bench testing of intraocular pressure tonometer TVGD-02 (“EASYTON”) to confirm accuracy, repeatability and reproducibility. In: Eurotechoptical. Accessed 21 Dec 2021
Iomdina EN, Kushnarevich NY (2022) Possibilities of monitoring intraocular pressure in children using EASYTON transpalpebral tonometer. Int Ophthalmol 42:1631–1638. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-021-02158-5
Salvetat ML, Zeppieri M, Tosoni C et al (2015) Corneal deformation parameters provided by the Corvis-ST pachy-tonometer in healthy subjects and glaucoma patients. J Glaucoma 24:568–574. https://doi.org/10.1097/IJG.0000000000000133
Li Y, Shi J, Duan X, Fan F (2010) Transpalpebral measurement of intraocular pressure using the Diaton tonometer versus standard Goldmann applanation tonometry. Graefe’s Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 248:1765–1770. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-009-1243-y
Cook JA, Botello AP, Elders A et al (2012) Systematic review of the agreement of tonometers with Goldmann applanation tonometry. Ophthalmology 119:1552–1557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ophtha.2012.02.030
Cacho I, Sanchez-Naves J, Batres L et al (2015) Comparison of intraocular pressure before and after laser in situ keratomileusis refractive surgery measured with perkins tonometry, noncontact tonometry, and transpalpebral tonometry. J Ophthalmol 2015:683895. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/683895
Troost A, Yun SH, Specht K et al (2005) Transpalpebral tonometry: reliability and comparison with Goldmann applanation tonometry and palpation in healthy volunteers. Br J Ophthalmol 89:280–283. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjo.2004.050211
Schlote T, Landenberger H (2005) Augeninnendruckmessung mit dem transpalpebralen tonometer TGDc-01 “PRA” im vergleich zur applanationstonometrie nach Goldmann bei glaukompatienten. Klin Monatsbl Augenheilkd 222:123–131. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2005-857881
Molero-Senosiaín M, Morales-Fernández L, Saenz-Francés F et al (2020) Analysis of reproducibility, evaluation, and preference of the new iC100 rebound tonometer versus iCare PRO and Perkins portable applanation tonometry. Eur J Ophthalmol 30:1349–1355. https://doi.org/10.1177/1120672119878017
Ye Y, Yang Y, Fan Y et al (2019) Comparison of biomechanically corrected intraocular pressure obtained by Corvis ST and Goldmann applanation tonometry in patients with open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension. J Glaucoma 28:922–928. https://doi.org/10.1097/IJG.0000000000001348
Nakao Y, Kiuchi Y, Okumichi H (2020) Evaluation of biomechanically corrected intraocular pressure using Corvis ST and comparison of the Corvis ST, noncontact tonometer, and Goldmann applanation tonometer in patients with glaucoma. PLoS ONE 15:e0238395. https://doi.org/10.1371/JOURNAL.PONE.0238395
Matsuura M, Murata H, Fujino Y et al (2020) Relationship between novel intraocular pressure measurement from Corvis ST and central corneal thickness and corneal hysteresis. Br J Ophthalmol 104:563–568. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjophthalmol-2019-314370
Leung CKS, Ye C, Weinreb RN (2013) An ultra-high-speed Scheimpflug camera for evaluation of corneal deformation response and its impact on IOP measurement. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 54:2885–2892. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.12-11563
Mark HH, Robbins KP, Mark TL (2002) Axial length in applanation tonometry. J Cataract Refract Surg 28:504–506. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0886-3350(01)01091-4
Liu Q, Pang C, Liu C et al (2022) Correlations among corneal biomechanical parameters, stiffness, and thickness measured using Corvis ST and pentacam in patients with ocular hypertension. J Ophthalmol 2022:7387581. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/7387581
Shen SR, Fleming GP, Jain SG, Roberts CJ (2023) A review of corneal biomechanics and scleral stiffness in topical prostaglandin analog therapy for glaucoma. Curr Eye Res 48:172–181. https://doi.org/10.1080/02713683.2022.2099903
Acknowledgements
Gratitude to patients, and members of the ophthalmology department who contribute to patient care and research.
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript. The easyton device was loaned by the company.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JMM-de-la-C contributed to the conception and design of the study. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by LS, JIF-V, YP, and EM. The first draft of the manuscript was written by LS-Q, LM-F, RS-del-H, JIF-V, JG-B, and JG-F. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The Authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Salazar-Quiñones, L., Fernández-Vigo, J.I., Pérez-Quiñones, Y. et al. Comparison of intraocular pressure measurements between Easyton transpalpebral tonometry and Perkins, iCare iC100 and Corvis ST, and the influence of corneal and anterior scleral thickness. Int Ophthalmol 43, 4121–4129 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-023-02814-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-023-02814-y