Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate clinical outcomes after uncomplicated microincision biaxial cataract surgery and implantation of Incise intraocular lens (IOL).
Methods
This study included 47 eyes of 29 patients (mean age 62.2 ± 8.6 years), who underwent 1.4-mm biaxial cataract surgery with implantation of the Incise IOL (Bausch and Lomb). At third month, surgically induced astigmatism (SIA) was calculated. Three, 6 and 12 months postoperatively, uncorrected distance visual acuity (UDVA), corrected distance visual acuity (CDVA), corrected near visual acuity (CNVA) LogMAR ETDRS, spherical equivalent refraction (SER), photopic distance corrected contrast sensitivity (CS) with and without glare (85 cd/m2) (CSV-1000) were assessed. One year after surgery, late complications were assessed and subjects were questioned for subjective symptoms.
Results
Mean of SIA was equal 0.29 ± 0.16 D. Three months postoperatively: mean UDVA improved from 0.83 to 0.04 (p < 0.001), CDVA from 0.58 to −0.05 (p < 0.001) and CNVA from 0.58 to −0.02 (p < 0.001) and all were stable during 1-year follow-up. Three months postoperatively, the mean SER was equal 0.07 ± 0.61 D and was within ±0.5 D in 79%, and within 1 D in 88% of eyes. During follow-up period, corrected CS with and without glare for distance was found to be within normal limits. The only late complication was posterior capsule opacification (PCO). Subjective quality of vision was very high; none of patients complained about glare.
Conclusions
Biaxial cataract surgery with implantation of the Incise IOL provided excellent clinical outcomes by minimizing SIA, stable refraction and low incidence of PCO.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Microinvasive surgical methods determine the development direction of today’s ophthalmology. Examples of these trends are MIVS (microincision vitrectomy surgery), MIGS (microinvasive glaucoma surgery) and MICS (microincision cataract surgery).
The goal of MICS is to treat cataract using 2.0 or smaller corneal incision with the purpose of reducing surgical invasiveness, improving at the same time surgical outcomes [1]. MICS is divided into two methods: coaxial MICS (C-MICS) and biaxial MICS (B-MICS). C-MICS gives the possibility to implant the IOL through 1.8 mm incision. The method which reduces this size is B-MICS, which allows 1.4 mm cataract surgery and IOL implantation. B-MICS resulted from the interplay of several factors including microcorneal incisions, bimanuality, improved use of fluids, rapidly progressing instrumentation, and adequate use of low-energy ultrasound phacoemulsificators [2], including development of new sleeveless tip [3, 4]. Advantages for this procedure are lower surgically induced astigmatism (SIA), less postoperative higher-order corneal aberrations (HOA) and lower endothelial cell loss [5,6,7]. Furthermore, it seems reasonable to conclude that smaller incision size has lower impact on corneal biomechanics, shortens recovery time and reduces number of endophthalmitis, although until now there is no clear evidence to support these hypotheses.
The Incise monofocal intraocular lens (IOL, Bausch & Lomb) is the first innovative IOL that can be implanted without a convention tunnel preparation but through 1.4 mm paracentesis. In the available literature, only three promising study results with short follow-up period up to 6 months were published on clinical outcomes of this lens [5,6,7]. Above-mentioned studies were performed with biaxial technique with IOL implantation from 1.4 mm [5] and 1.6 mm [6] clear cornea incision and one with coaxial microincision (C-MICS), where the lens was implanted through 1.8 mm incision [7].
This is why we decided to assess clinical outcomes after B-MICS with implantation of these lenses in longer follow-up period of 12 months.
Methods
Patients
This consecutive prospective observational noncomparative clinical trial included 47 eyes of 29 patients, 18 women and 11 men. Informed consent was obtained prior to treatment from each patient. The patients’ mean age was equal 62.2 ± 8.6 (range 43–76 years). The cataract grade (LOCS III) ranged from No. 3–6 [8]. None of the eyes had associated ocular diseases that might affect the visual outcome postoperatively. The study adhered to the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the local ethics committee. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Biometry was performed on IOLMaster (Carl Zeiss). Ultrasound biometry was utilized in eyes in which IOLMaster could not be performed because of a dense cataract. The IOL power was calculated with SRK-T formula (A-constant 118.9) in eyes with the axial length (AL) of 22–24 mm. Hoffer Q formula (pACD = 5.61) was used in eyes with a shorter AL (<22 mm).
Examination protocol
All patients had preoperatively full complete ophthalmologic examination including monocular uncorrected distance visual acuity (UDVA), corrected distance visual acuity (CDVA) (4 m), corrected near visual acuity (CNVA) (LogMAR) (40 cm), measured on Early Treatment Diabetic Study (ETDRS) charts, 3, 6 and 12 months postoperatively following parameters were assessed: UDVA, CDVA and CNVA, spherical equivalent refraction (SER), photopic corrected contrast sensitivity (CS) with and without glare (85 cd/m2) (CSV-1000E instrument), measured at the distance of 2 m. At third month, surgically induced astigmatism was calculated using vector analysis based on the keratometry results, which was described by Dr. Saurabh Sawhney and Dr. Aashima Aggarwal [9, 10]. One year after surgery late complications were assessed. Additionally patients were questioned for subjective symptoms (modified National Eye Institute Visual Function Questionnaire-14; NEI VFQ-14).
Statistical analysis
Distribution of analyzed data was performed using the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test. All data presented in the current study were not normally distributed, and therefore nonparametric statistics were used. Wilcoxon ranked sum test was used to compare changes in visual acuities and astigmatism between preoperative and postoperative examinations, considering a significance level of p < 0.05. The statistical analysis was performed using Statistica StatSoft®.
The intraocular lens
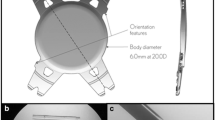
The Incise IOL (Bausch & Lomb) is a single piece aspheric hydrophilic, aberration free IOL and has sharp edge radius (less than 5 µm) and a continuous 360 square-edge profile—design features that help to prevent cell migration and decrease the incidence of posterior capsular opacification (PCO). The acrylic lens material has 22% of water content and contains more hydrophobic monomers than other acrylic IOL materials, making Incise resistant to tears and other surgical trauma. The combination of unique material and single-use injector system enables the IOL to be implanted through an incision as small as 1.4 mm.
Surgical technique
All surgeries were performed by one surgeon (WL). Topical (proxymetacaine hydrochloridum) and local (1% lidocaine) anesthesia was used. Low-power phacoemulsification systems were used to emulsify the cataract through 2 microincisions in the 2 and 10 o’clock positions using trapezoidal knife 1.2 × 1.4 mm. The continuous curvilinear capsulorhexis of 5 mm diameter, hydrodissection and hydrodelineation under protection with Discovisc® were performed. The Stellaris Vision Enhancement System (Bausch & Lomb, Rochester, N.Y., USA) was used for phacoemulsification with mean parameters: burst mode—mean power 4.69 ± 4.39% (SD), mean effective phacotime 0.78 ± 2.22 s (SD). Nucleus was divided into two or four pieces using Phaco PreChopper. The IOL was implanted through the clear cornea incision in superotemporal quadrant with a “wound-assist” technique [2]. The size of incisions after IOL implantation was measured with calipers (Asico).
Results
Corneal incision size
The mean corneal incision size used for the IOL implantation during the surgery with IOL implantation was 1.44 ± 0.1 mm (range 1.4–2.0 mm). Final incision diameter was 1.5 or smaller in 45 eyes and 1.7 mm in 1 eye. Through these incisions, all the intraocular maneuvers and IOL implantation were performed without the need for further enlargement (except for one case, described further on). The implantation process was estimated as difficult in one eye after the original incision (1.4 mm) had been made and cataract had been removed. In this case, IOL incarcerated in the wound and after incision enlargement the same IOL was implanted through 2.0 mm incision.
Surgically induced astigmatism (SIA)
Mean SIA measured at third month was equal 0.29 ± 0.16 D. Fifty-three percent of eyes had SIA lower than 0.25 D, in 34% of eyes SIA was between 0.25 and 0.5 D, and only in 13% of eyes SIA was higher than 0.5 D (Fig. 1). Before surgery, mean astigmatism was equal 0.67 ± 0.45 D, decreased to 0.64 ± 0.40 D postoperatively and the difference was not statistically significant (p > 0.05).
Distance visual acuity
Comparisons of UDVA and CDVA preoperative and 3, 6, 12 months postoperatively are shown in Table 1.
On the first day after the surgery, mean CDVA was already equal 0.13 ± 0.18. Distance visual acuity was very good in the third month and was stable up to 12-month follow-up examination.
Significant increase of UDVA and CDVA was obtained 3, 6 and 12 months postoperatively in comparison with values before surgery (Table 1).
At third month, UDVA was 0.2 or better in 83% of cases, BDVA was 0.2 or better in 87% of cases (Fig. 2).
Near visual acuity
Corrected near visual acuity in third, sixth and 1 year postoperatively was significantly better compared to preoperative value (Table 2).
Absolute refractive error
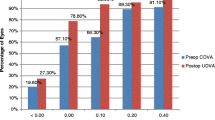
The mean SER was equal 0.07 ± 0.61 D 3 months postoperatively; −0.03 ± 0.64 D 6 months postoperatively and −0.02 ± 0.66 D 12 months after the operation. Regarding predictability, the SER was within ±0.5 D in 79% of eyes and within ±1 D in 88% of eyes at the postoperative third month. Twelve months after surgery in 79% of eyes SER was lower than 0.75 D (Fig. 3).
Contrast sensitivity
During follow-up period, corrected CS with and without glare for distance was found to be within normal limits in comparison with the normal population in the range of 50–75 years [11]. Corrected CSs were almost equal between follow-up visits (Fig. 4).
Patient’s satisfaction and subjective symptoms
Patient’s satisfaction was very high (Table 3). None of patients complained about glare.
Complications
The incident of corneal wound leakage was noticed in one case at first day after the cataract surgery. It was treated with contact lens and in day 4 the wound was stable without need for additional treatment. During 1-year follow-up, no incident of PCO which was a cost of visual acuity was noticed and there was no need for Nd: Yag procedure.
Discussion
Microincision cataract surgery develops rapidly. New techniques like B-MICS and C-MICS procedures significantly lowered mean phacoemulsification time, mean phacoemulsification power and surgically induced astigmatism when compared with standard coaxial phacoemulsification [12]. In B-MICS technique, irrigation and aspiration are performed separately. Through two opposite 1.2–1.4 mm paracentesis, the phacotip without sleeve and the irrigation tip are inserted into the anterior chamber. C-MICS technique requires tunnel and two additional paracentesis and the only difference from traditional coaxial phaco is the use of 21-gauge phacotip. During B-MICS procedure, the tip without sleeve is used and it is possible to damage the cornea around the wound because of possible thermal burn [13]. It may cause “leaky wound” and in consequences opens the way to bacterial infiltration from conjunctival sac. In the present work, one incident of corneal leakage at first day after the cataract surgery was noticed. It was treated with contact lens, and in day 4 the wound was stable without need for additional treatment. Other authors report anterior chamber instability during the surgery [5]. In our series of patients, where the Stellaris Phaco System with forced infusion was used, we did not observe above-mentioned problem. During one operation, there was need for wound enlargement and the lens was implanted through 2.0 mm incision. Even though in our study, no sign of intraoperative or postoperative inflammation could be seen, which indicates that this technique seems to be safe.
It is widely known that the smaller the incision the lower SIA [14, 15]. In comparison with coaxial surgery biaxial surgery shows significantly less SIA [14, 15]. B-MICS procedure allows sub-1.8 mm incisions, which effectively decrease the induction or changes in corneal SIA during cataract surgery in comparison with C-MICS [14]. Alio et al. [16] suspect that “2.0 mm is the limit around which no optical changes are induced by cataract surgery in the human cornea.” In present study SIA was equal 0.29 ± 0.16 D and was very similar to the Jimenez et al. result: 0.31 ± 0.22 D, p > 0.05 [8]. There was a statistically significant difference between our and Sonnleithner et al. [5] and Toygar et al. [7] results, where SIA was equal 0.45 ± 0.29 and 0.45 ± 0.28, respectively (p < 0.05). Probable reasons behind these differences might be the wound stretching during IOL implantation [5] and the incision size, which was equal 1.8 mm in Toygar et al. [7] study. Cavallini et al. [17] demonstrated that more posterior wound retraction is observed in 1.8-mm incisions compared to that in 1.4-mm incision (53 vs. 47%). It seems that the limit around which no optical changes are induced by cataract surgery is lower and might be sub-1.8 mm.
In our study, CDVA before surgery improved significantly from 0.58 ± 0.57 to −0.05 ± 0.06 in third month and was stable during 12-month follow-up. These results were significantly better compared with other study results on Incise IOL (p < 0.05) [5,6,7]. Jiménez et al. [6] reported improvement of mean DCVA from 0.57 ± 0.15 to 0.16 ± 0.13 3 months postoperatively, Sonnleithner et al. [5] from 0.4 ± 0.27 to 0.05 ± 0.07 4 weeks after surgery, Toygar et al. [7] from 0.52 ± 0.42 to 0.01 ± 0.02 logMAR 6 months postoperatively.
In present study, 1 year after the surgery mild PCO was observed especially in the peripheral part of the capsule, but the center was clear in all eyes. In consequences, no one patient needed YAG-capsulotomy 1 year after surgery. It is reasonable to conclude that lack of significant PCO was connected with design of the IOL: continuous 360 square-edge profile, which prevents PCO formation. According to study results of Nanavaty et al. [18] who evaluated 3 different IOLs: 2 aspheric microincision hydrophilic IOLs (Acri.Smart 36A and Akreos MI-60) and conventional single piece hydrophobic acrylic spheric IOL (AcrySof SN60AT; Alcon Laboratories), there is a trend in hydrophilic IOLs toward progression over the 2-year follow-up. At 2 years, the mean PCO score was lower than 11% for the conventional AcrySof IOL and 23% for the Akreos MI-60 IOL. Longer observation time is necessary to assess frequency of significant PCO formation.
Incise IOL has high level of predictability and is comparable with other IOLs [19]. Toygar et al. [7] reported 6 month after surgery 94% of eyes were within 1.0 D from calculated refraction in comparison with our 90% 1 year after surgery.
Other advantage of microincision is low number of higher-order aberration (HOA). It is commonly known that HOA might be caused of decreased visual acuity and contrast sensitivity [5]. In study, results by Sonnleithner et al. [5] outcome in terms of Incise IOL HOA were very satisfying and comparable to other aspheric IOLs (Akreos MI60, Tecnis ZCB00, CT Asphina). In our study, the results of contrast sensitivity for distance were within normal limits of healthy people in the same range of age indicated very good performance of this type of IOL. Our results agree with those in other study [6] on Incise IOL. Additionally, the follow-up period was 6 months longer in our study.
The patients were highly satisfied with the quality of performed procedures and implanted lenses due to the fact that they received mostly very good, uncorrected visual acuity for distance. None of patients complained about glare. In our experiences with other IOL implanted using B-MICS procedure [20, 21], glare effect was also not observed.
In summary, the results of presented study suggest that B-MICS with Incise lens implantation is a procedure which provides for the patient very good visual function as well as high patient’s satisfaction. So, we would recommend the B-MICS and this type of IOLs for the cataract surgeons and patients. It seems reasonable to expect that Incise lens might be a good platform for introduction for multifocal IOL.
References
Alió JL, Rodriguez-Prats JL, Galal A (2004) Micro-incision cataract surgery. Highlights of Ophthalmology International, Miami
Weikert MP (2006) Update on bimanual microincisional cataract surgery. Curr Opin Ophthalmol 17:62–67
Pandey SK, Werner L, Agarwal A, Agarwal A, Lal V, Patel N et al (2002) Phakonit. Cataract removal through a sub-1.0 mm incision and implantation of the ThinOptX rollable intraocular lens. J Cataract Refract Surg 28:1710–1713
Liu YZ, Jiang YZ, Liu YH, Wu MX (2004) A preliminary report on bimanual microphacoemulsification. Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi 40:302–305
Sonnleithner C, Bergholz R, Gonnermann J, Klamann MK, Torun N, Bertelmann E (2015) Clinical results and higher-order aberrations after 1.4 mm biaxial cataract surgery and implantation of a new aspheric intraocular lens. Ophthalmic Res 53:8–14
Jiménez R, Valero A, Fernández J, Anera RG, Jiménez JR (2016) Optical quality and visual performance after cataract surgery with biaxial microincision intraocular lens implantation. J Cataract Refract Surg 42:1022–1028
Toygar B, Yabas Kiziloglu O, Toygar O, Hacimustafaoglu AM (2016) Early clinical outcome with a new monofocal microincision intraocular lens. Int Ophthalmol 36:657–664
Chylack LT Jr, Wolfe JK, Friend J, Khu PM, Singer DM, McCarthy D, del Carmen J, Rosner B (1993) Quantitating cataract and nuclear brunescence, the Harvard and LOCS systems. Optom Vis Sci 70:886–895
Holladay JT, Dudeja DR, Koch DD (1998) Evaluating and reporting astigmatism for individual and aggregate data. J Cataract Refract Surg 24:57–65
Basak SK, Basak S, Chowdhury AR (2008) SIA-Soft: a new software to calculate surgically induced astigmatism in comparison with manual mathematics by vector method. Indian J Ophthalmol 56:170
Pomeranie G, Evans D (1994) Test- retest reliability of the CSV-1000 contrast test and its relationship to glaucoma therapy. Incest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 35:3357–3361
Alió J, Rodríguez-Prats JL, Galal A, Ramzy M (2005) Outcomes of microincision cataract surgery versus coaxial phacoemulsification. Ophthalmology 112:1997–2003
Al-Muammar A (2009) Bimanual microincisional cataract surgery technique and clinical outcome. Saudi J Ophthalmol 23:149–155
Dick HB (2012) Controlled clinical trial comparing biaxial microincision with coaxial small incision for cataract surgery. Eur J Ophtalmol 22:739–750
Yao K, Tang X, Ye P (2006) Corneal astigmatism, high order aberrations, and optical quality after cataract surgery: microincision versus small incision. J Refract Surg 22:1079–1082
Alió JL, Elkady B, Ortiz D (2010) Corneal optical quality following sub 1.8 mm micro-incision cataract surgery versus 2.2 mm mini-incision coaxial phacoemulsification. Middle East Afr J Ophthalmol 17:94–99
Cavallini GM, Campi L, Torlai G, Forlini M, Fornasari E (2012) Clear corneal incisions in bimanual microincision cataract surgery: long-term wound-healing architecture. J Cataract Refract Surg 38:1743–1748
Nanavaty MA, Spalton DJ, Gala KB, Dhital A, Boyce J (2013) Fellow-eye comparison of posterior capsule opacification between 2 aspheric microincision intraocular lenses. J Cataract Refract Surg 39:705–711
Alió JL, Rodriguez-Prats JL, Vianello A, Galal A (2005) Visual outcome of microincision cataract surgery with implantation of an Acri. Smart lens. J Cataract Refract Surg 31:1549–1556
Podborączyńska-Jodko K, Lubiński W (2012) Bimanual microincision cataract surgery with implantation of an Akreos MI60 lens—1 year follow-up. Klin Oczna 114:245–248
Lubiński W, Podborączyńska-Jodko K, Barnyk K, Karczewicz D (2007) Microincision cataract surgery with implantation of an Acri. Smart 48S lens. Klin Oczna 109:267–271
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest (such as honoraria; educational grants; participation in speakers’ bureaus; membership, employment, consultancies, stock ownership, or other equity interest; and expert testimony or patent-licensing arrangements), or non-financial interest (such as personal or professional relationships, affiliations, knowledge or beliefs) in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Lubiński, W., Kirkiewicz, M. & Podborączyńska-Jodko, K. Clinical results after microincision biaxial cataract surgery and implantation of an Incise intraocular lens. Int Ophthalmol 38, 1977–1983 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-017-0686-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10792-017-0686-0