Abstract
Background
QP001, a novel meloxicam formulation, has been developed to manage moderate to severe postoperative pain. This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of QP001 injections for moderate to severe pain following abdominal surgery.
Method
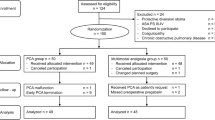
This prospective, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial enlisted patients experiencing moderate to severe pain following abdominal surgery. These patients were randomized to receive either QP001 injections (30 mg or 60 mg) or a placebo pre-surgery. The primary efficacy endpoint was the total morphine consumption within 24 h after the first administration.
Results
A total of 108 patients were enrolled, and 106 patients completed the study. The total morphine consumption in the QP001 30 mg group and 60 mg group, versus placebo group, were significantly lower over the following 24 h (5.11[5.46] vs 8.86[7.67], P = 0.011; 3.11[3.08] vs 8.86[7.67], P < 0.001), respectively. The total morphine consumption in the QP001 30 mg and 60 mg groups, versus placebo group, was also significantly decreased over the following 48 h, including the 24–48 h period (P ≤ 0.001). The QP001 30 mg and 60 mg groups, versus placebo, showed a significant decrease in the area under the curve for pain intensity-time as well as a significant decrease in the effective pressing times of the analgesic pump over the 24 h and 48 h periods (P < 0.05). The QP001 groups, versus placebo, show no significant different in Adverse Events or Adverse Drug Reactions (P > 0.05).
Conclusion
Preoperative/preemptive QP001 provides analgesia and reduces opioid consumption in patients with moderate to severe pain following abdominal surgery, while maintaining a favorable safety profile.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data sets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Amaechi O, Huffman MM, Featherstone K (2021) Pharmacologic Therapy for Acute Pain. Am Fam Physician 104:63–72
American Society of Anesthesiologists Task Force on Acute Pain M (2012) Practice guidelines for acute pain management in the perioperative setting: an updated report by the American Society of Anesthesiologists Task Force on Acute Pain Management. Anesthesiology 116:248–273. https://doi.org/10.1097/ALN.0b013e31823c1030
Anwari JS, Anjum S, Al-Khunain S (2008) Placebo controlled comparison of the opioid sparing effect of meloxicam and diclofenac after abdominal hysterectomy. Saudi Med J 29:379–383
Argoff CE (2014) Recent management advances in acute postoperative pain. Pain Pract 14:477–487. https://doi.org/10.1111/papr.12108
Barr LF, Boss MJ, Mazzeffi MA, Taylor BS, Salenger R (2020) Postoperative Multimodal Analgesia in Cardiac Surgery. Crit Care Clin 36:631–651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccc.2020.06.003
Buvanendran A, Fiala J, Patel KA, Golden AD, Moric M, Kroin JS (2015) The Incidence and Severity of Postoperative Pain following Inpatient Surgery. Pain Med 16:2277–2283. https://doi.org/10.1111/pme.12751
Chou R, Gordon DB, de Leon-Casasola OA et al (2016) Management of Postoperative Pain: A Clinical Practice Guideline From the American Pain Society, the American Society of Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine, and the American Society of Anesthesiologists’ Committee on Regional Anesthesia, Executive Committee, and Administrative Council. J Pain 17:131–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpain.2015.12.008
Coccolini F, Corradi F, Sartelli M et al (2022) Postoperative pain management in non-traumatic emergency general surgery: WSES-GAIS-SIAARTI-AAST guidelines. World J Emerg Surg 17:50. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13017-022-00455-7
Doleman B, Read D, Lund JN, Williams JP (2015) Preventive Acetaminophen Reduces Postoperative Opioid Consumption, Vomiting, and Pain Scores After Surgery: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Reg Anesth Pain Med 40:706–712. https://doi.org/10.1097/AAP.0000000000000311
Fiore JF, Jr., Olleik G, El-Kefraoui C, et al (2019) Preventing opioid prescription after major surgery: a scoping review of opioid-free analgesia. Br J Anaesth 123:627–636. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bja.2019.08.014
Glare P, Aubrey KR, Myles PS (2019) Transition from acute to chronic pain after surgery. Lancet 393:1537–1546. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30352-6
Grant AD, Miller MM, Anastas TM, Quinn P, Lok B, Hirsh AT (2022) Opioid-related risk perceptions in chronic pain: influence of patient gender and previous misuse behaviors. Pain 163:711–718. https://doi.org/10.1097/j.pain.0000000000002412
Hwang C, Park S, Park J, Cho J, Lee C, Lee D (2020) Sustained Postoperative Fever Without Evident Cause After Spine Instrumentation as an Indicator of Surgical Site Infection. The Journal of bone and joint surgery. American 102:1434–1444. https://doi.org/10.2106/jbjs.19.01490
Joshi GP, Kehlet H (2019) Enhanced Recovery Pathways: Looking Into the Future. Anesth Analg 128:5–7. https://doi.org/10.1213/ANE.0000000000003746
Kehlet H (2018) Postoperative pain, analgesia, and recovery-bedfellows that cannot be ignored. Pain 159(Suppl 1):S11–S16. https://doi.org/10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001243
Kehlet H, Dahl JB (1993) The value of “multimodal” or “balanced analgesia” in postoperative pain treatment. Anesth Analg 77:1048–1056. https://doi.org/10.1213/00000539-199311000-00030
Khalil NY, Aldosari KF (2020) Meloxicam. Profiles Drug Subst Excip Relat Methodol 45:159–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.podrm.2019.10.006
Kissin I (2000) Preemptive analgesia. Anesthesiology 93:1138–1143. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000542-200010000-00040
Ladha KS, Patorno E, Huybrechts KF, Liu J, Rathmell JP, Bateman BT (2016) Variations in the Use of Perioperative Multimodal Analgesic Therapy. Anesthesiology 124:837–845. https://doi.org/10.1097/ALN.0000000000001034
Manworren RC (2015) Multimodal pain management and the future of a personalized medicine approach to pain. AORN J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aorn.2014.12.009
Mitra S, Carlyle D, Kodumudi G, Kodumudi V, Vadivelu N (2018) New Advances in Acute Postoperative Pain Management. Curr Pain Headache Rep 22:35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11916-018-0690-8
Moore N, Scheiman JM (2018) Gastrointestinal safety and tolerability of oral non-aspirin over-the-counter analgesics. Postgrad Med 130:188–199. https://doi.org/10.1080/00325481.2018.1429793
Nir RR, Nahman-Averbuch H, Moont R, Sprecher E, Yarnitsky D (2016) Preoperative preemptive drug administration for acute postoperative pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Pain 20:1025–1043. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejp.842
Radi ZA, Khan KN (2019) Cardio-renal safety of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. J Toxicol Sci 44:373–391. https://doi.org/10.2131/jts.44.373
Rawal N (2005) Organization, function, and implementation of acute pain service. Anesthesiol Clin North Am 23:211–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atc.2004.11.012
Rechberger T, Mack RJ, McCallum SW, Du W, Freyer A (2019) Analgesic Efficacy and Safety of Intravenous Meloxicam in Subjects With Moderate-to-Severe Pain After Open Abdominal Hysterectomy: A Phase 2 Randomized Clinical Trial. Anesth Analg 128:1309–1318. https://doi.org/10.1213/ANE.0000000000003920
Ren L, Meng L, Yan H, Sun W, Yao D (2020) Preoperative meloxicam versus postoperative meloxicam for pain control, patients’ satisfaction and function recovery in hip osteoarthritis patients who receive total hip arthroplasty: a randomized, controlled study. Inflammopharmacology 28:831–838. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-020-00718-2
Ringold FG, Minkowitz HS, Gan TJ, Aqua KA, Chiang YK, Evashenk MA, Palmer PP (2015) Sufentanil sublingual tablet system for the management of postoperative pain following open abdominal surgery: a randomized, placebo-controlled study. Reg Anesth Pain Med 40:22–30. https://doi.org/10.1097/AAP.0000000000000152
Small C, Laycock H (2020) Acute postoperative pain management. Br J Surg 107:e70–e80. https://doi.org/10.1002/bjs.11477
Thompson JP, Sharpe P, Kiani S, Owen-Smith O (2000) Effect of meloxicam on postoperative pain after abdominal hysterectomy. Br J Anaesth 84:151–154. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.bja.a013395
(2020) FDA Drug Approval Package: ANJESO. U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2020/210583Orig1s000TOC.cfm. Accessed 10 June 2023
Vicente López N, Forés Cachón R, Iranzo Valero R, Lerma Verdejo A, Múñez Rubio E, Royuela Vicente A, Ramos Martínez A (2018) CD64 index as a marker of infection in patients with postoperative fever. Rev Esp Quimiot Public of Soc Esp Quimiot 31:493–498
Wilder-Smith OH (2000) Pre-emptive analgesia and surgical pain. Prog Brain Res 129:505–524. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0079-6123(00)29037-7
Xuan C, Yan W, Wang D, Li C, Ma H, Mueller A, Chin V, Houle TT, Wang J (2022) Efficacy of preemptive analgesia treatments for the management of postoperative pain: a network meta-analysis. Br J Anaesth 129:946–958. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bja.2022.08.038
Yu J, Wang Y, Wu Y et al (2022) Pharmacokinetics of Meloxicam Tablets in Healthy Chinese Adults in the Fasting and Fed States: A Single-Site, Single-Dose, Randomized, Open, 2-Period, 2-Sequence, Crossover Bioequivalence Study. Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev 11:71–79. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpdd.965
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the assistance and cooperation of staff from Zhichao Information Technology Co., Ltd.
Funding
The study received funding from the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (2021JJ31022), Nanjing Delova Biotech Co., Ltd. The sponsor had no role in the study design, including in the collection, analysis, or interpretation of the data or in the writing or submission of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YZ, SW and WO contributed to the study conception and design. YZ, KD, ZB, XH, MX, XL, YG, JL, MY, YZ, WZ, RD and YS performed the research. Data collection and analysis were performed by YZ, SW and BW. The first draft of the manuscript was written by YZ, BW and KD. ZW, YJ, SY and SW were responsible for the visualization of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Y., Wang, B., Duan, K. et al. Preemptive QP001, a fast-acting meloxicam formulation, provides analgesia and reduces opioid consumption following abdominal surgery: a randomized controlled trial. Inflammopharmacol 31, 2401–2410 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-023-01322-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-023-01322-w