Abstract
Background
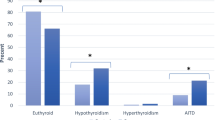
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory autoimmune disease characterized by joint swelling, pain, and deformation. RA patients have an increased risk of thyroid dysfunction, and drugs of RA treatment may have potential effects on thyroid function.
Methods
This is a single-center cross-sectional study including 281 inpatients with RA in the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine. The purpose of this study is to explore the correlation between RA therapeutic drugs and thyroid function. The medical records of 281 inpatients with RA were collected, including general data, laboratory examination, complications, and RA treatment. Spearman correlation analysis was used to explore the association of independent variables with thyroid function and antibodies in RA patients. Multinomial logistics and binary logistic regression were used for multivariate analysis. The statistically significance level was set as P < 0.05. SPSS 22.0 was used for statistical analysis.
Results
Patients taking methotrexate (OR = 0.067, 95%CI: 0.008–0.588, P = 0.015) had lower levels of total thyroxine (TT4) (TT4 < 78.38 nmol/L). There was a negative correlation between glucocorticoids (r = − 0.153, P = 0.010) and total triiodothyronine (TT3) level (TT3 ≥ 1.34 nmol/L), but it was not significant in the multivariate regression model of TT3, although the regression model was statistically significant (P = 0.001).
Conclusion
Methotrexate is associated with decreased TT4 levels in RA patients, and glucocorticoids is associated with decreased TT3 levels. Drugs of RA treatment may affect the thyroid function of patients while treating RA, which may be one of the causes of secondary thyroid diseases in RA patients.

Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All data are available for publication.
References
Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ et al (2010) 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum 62(9):2569–2581. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.27584
Alhefdhi A, Burke JF, Redlich A et al (2013) Leflunomide suppresses growth in human medullary thyroid cancer cells. J Surg Res 185(1):212–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2013.05.089
Atzeni F, Doria A, Ghirardello A et al (2008) Anti-thyroid antibodies and thyroid dysfunction in rheumatoid arthritis: prevalence and clinical value. Autoimmunity 41(1):111–115. https://doi.org/10.1080/08916930701620100
Biondi B, Cappola AR, Cooper DS (2019) Subclinical hypothyroidism: a review. JAMA 322(2):153–160. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2019.9052
Bliddal S, Borresen SW, Feldt-Rasmussen U (2017) Thyroid autoimmunity and function after treatment with biological antirheumatic agents in rheumatoid arthritis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 8:179. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2017.00179
Cañas CA, Tobón GJ, Arango LG et al (2009) Developing of granulomatous thyroiditis during etanercept therapy. Clin Rheumatol 28(Suppl 1):S17–S19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-008-1046-2
Chen YL, Lin JZ, Mo YQ et al (2018) Joint damage is amplified in rheumatoid arthritis patients with positive thyroid autoantibodies. PeerJ 6:e4216. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.4216
Dwivedi SN, Kalaria T, Buch H (2022) Thyroid autoantibodies. J Clin Pathol. https://doi.org/10.1136/jcp-2022-208290
Fraenkel L, Bathon JM, England BR et al (2021) 2021 American College of Rheumatology guideline for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol 73(7):1108–1123. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.41752
Genere N, Stan MN (2019) Current and emerging treatment strategies for Graves’ orbitopathy. Drugs 79(2):109–124. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-018-1045-9
Georges A, Charrié A, Raynaud S et al (2011) Thyroxin overdose due to rheumatoid factor interferences in thyroid-stimulating hormone assays. Clin Chem Lab Med 49(5):873–875. https://doi.org/10.1515/CCLM.2011.144
Hella Z, Hodinka L, Turbucz P et al (2017) Etanercept-induced subacute thyroiditis. Case report and literature review. Orv Hetil 158(39):1550–1554. https://doi.org/10.1556/650.2017.30796
Jing L, Zhang Q (2022) Intrathyroidal feedforward and feedback network regulating thyroid hormone synthesis and secretion. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 13:992883. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2022.992883
Kasono K, Hikino H, Fujino S et al (2001) Cross-reactive mechanism for the false elevation of free triiodothyronine in the patients treated with diclofenac. Endocr J 48(6):717–722. https://doi.org/10.1507/endocrj.48.717
Kjaergaard AD, Teumer A, Marouli E et al (2022) Thyroid function, pernicious anemia and erythropoiesis: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Hum Mol Genet 31(15):2548–2559. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddac052
Komatsu N, Takayanagi H (2022) Mechanisms of joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis - immune cell-fibroblast-bone interactions. Nat Rev Rheumatol 18(7):415–429. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41584-022-00793-5
Liu YJ, Miao HB, Lin S et al (2022) Association between rheumatoid arthritis and thyroid dysfunction: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 13:1015516. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2022.1015516
Liu Y, Li Z, Yang T et al (2022) Impaired sensitivity to thyroid hormones and carotid plaque in patients with coronary heart disease: a RCSCD-TCM study in China. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 13:940633. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2022.940633
Raterman HG, Jamnitski A, Lems WF et al (2011) Improvement of thyroid function in hypothyroid patients with rheumatoid arthritis after 6 months of adalimumab treatment: a pilot study. J Rheumatol 38(2):247–251. https://doi.org/10.3899/jrheum.100488
Re RN, Kourides IA, Ridgway EC et al (1976) The effect of glucocorticoid administration on human pituitary secretion of thyrotropin and prolactin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 43(2):338–346. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem-43-2-338
Selmanoğlu G, Koçkaya EA, Akay MT et al (2006) Subacute toxicity of celecoxib on thyroid and testis of rats: hormonal and histopathological changes. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 22(1):85–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2005.12.004
Sipkova Z, Insull EA, David J et al (2018) Early use of steroid-sparing agents in the inactivation of moderate-to-severe active thyroid eye disease: a step-down approach. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 89(6):834–839. https://doi.org/10.1111/cen.13834
Siriwardhane T, Krishna K, Ranganathan V et al (2018) Exploring systemic autoimmunity in thyroid disease subjects. J Immunol Res 2018:6895146. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/6895146
Strianese D, Rossi F (2019) Interruption of autoimmunity for thyroid eye disease: B-cell and T-cell strategy. Eye (Lond) 33(2):191–199. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41433-018-0315-9
Supronik J, Szelachowska M, Kretowski A et al (2022) Rituximab in the treatment of Graves’ orbitopathy: latest updates and perspectives. Endocr Connect 11(12):e220303. https://doi.org/10.1530/EC-22-0303
Tokumaru M, Ohba K, Kakudo K et al (2021) Importance of imaging procedures in the evaluation of methotrexate-associated lymphoproliferative disorder of the thyroid gland: a case study. Eur Thyroid J 10(5):434–436. https://doi.org/10.1159/000507826
Waldenlind K, Saevarsdottir S, Bengtsson C et al (2018) Risk of thyroxine-treated autoimmune thyroid disease associated with disease onset in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. JAMA Netw Open 1(6):e183567. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2018.3567
Waldenlind K, Delcoigne B, Saevarsdottir S et al (2020) Does autoimmune thyroid disease affect rheumatoid arthritis disease activity or response to methotrexate? RMD Open 6(2):e001282. https://doi.org/10.1136/rmdopen-2020-001282
Wang J, Li R, Lin H et al (2019) Accumulation of cytosolic dsDNA contributes to fibroblast-like synoviocytes-mediated rheumatoid arthritis synovial inflammation. Int Immunopharmacol. 76:105791. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2019.105791
Wang Q, Xu X, Ren H et al (2023) Prevalence and risk factors of thyroid dysfunction in outpatients with overweight or obese first-episode and drug-naïve major depressive disorder. J Affect Disord 328:135–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2023.02.068
Funding
There was no funding for the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SL-C conceived the study, collected the data, and drafted the manuscript. QX participated in designing and writing this manuscript. CS-L reviewed and revised this manuscript. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical statement
This study does not involve identifiable personal information and meets the criteria of exempting patients’ informed consent from the Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine (FAHGUCM). The commitment to protect the privacy of subjects has been submitted to the Ethics Committee. This study has been approved by the Ethics Committee of FAHGUCM (NO. JY [2021]063).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, SL., Xu, Q. & Lin, CS. Methotrexate is associated with decreased total thyroxine in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Inflammopharmacol 31, 2383–2392 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-023-01299-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-023-01299-6