Abstract
Objective and design
The involvement of nitric oxide pathway in the antinociceptive activity of Lonchocarpus araripensis lectin (LAL) was investigated in the model of carragenan-induced hypernociception.
Methods
Swiss mice received LAL (0.01–10 mg/kg; i.v.) 30 min before s.c. injection of carragenan in the paws. For the involvement of nociceptive pathways, animals were previously treated with the blockers: NOS (L-NAME, aminoguanidine, 7-nitroindazole); soluble guanylyl cyclase (ODQ); channels of ATP-dependent K+ (glibenclamide); L-type Ca2+ (nifedipine), or Ca2+-dependent Cl− (niflumic acid). Participation of lectin domain was evaluated by injection of LAL associated with N-acetyl-glucosamine (GlcNAc). nNOS gene relative expression was evaluated in the paw tissues and nNOS immunostaining in dorsal root ganglia.
Results
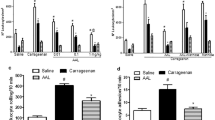
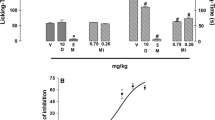
LAL at all doses inhibited carrageenan-induced hypernociception (4.12 ± 0.58 g), being maximal at 10 mg/kg (3 h: 59%), and reversed by GlcNAc. At this time, LAL effect was reversed by nifedipine (39%), niflumic acid (59%), L-NAME (59%), 7-nitroindazole (44%), ODQ (45%), and glibenclamide (34%), but was unaltered by aminoguanidine. LAL increased (95%) nNOS gene expression in mice paw tissues, but not its immunoexpression in the dorsal root ganglia.
Conclusion
The antinociceptive effect of Lonchocarpus araripensis lectin involves activation of the l-arginine/NO/GMPc/K+ATP pathway.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aley KO, McCarter G, Levine JD (1998) Nitric oxide signaling in pain and nociceptor sensitization in the rat. J Neurosci 18:7008–7014. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-020-00686-7
Amorim RMF, Pires AF, Nascimento TS, Cavada BS, Nascimento KS, Cajazeiras JB (2016) The leguminous lectin of Lonchocarpus araripensis promotes antinociception via mechanisms that include neuronal inhibition of Na+ currents. Inflamm Res 65:701–708. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-016-0951-0
Chaban VV, McRoberts JA, Ennes HS, Mayer EA (2001) Nitric oxide synthase inhibitors enhance mechanosensitive Ca2+ influx in cultured dorsal root ganglion neurons. Brain Res 903:74–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0006-8993(01)02407-6
Collin T, Chat M, Lucas MG, Moreno H, Racay P, Schwaller B et al (2005) Developmental changes in parvalbumin regulate presynaptic Ca2+ signaling. J Neurosci 25:96–107. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3748-04.2005
Cunha TM, Roman-Campos D, Lotufo CM, Duarte HL, Souza GR, Verri WAJR et al (2010) Morphine peripheral analgesia depends on activation of the PI3Kgamma/AKT/nNOS/NO/KATP signaling pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci 7:4442–4447. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0914733107
Cunha TM, Verri WA Jr, Vivancos GG, Moreira IF, Reis S et al (2014) An electronic pressure-meter nociception paw test for mice. Braz J Med Biol Res 37:401–407. https://doi.org/10.1590/s0100-879x2004000300018
Cury Y, Picolo G, Gutierrez VP, Ferreira SH (2011) Pain and analgesia: the dual effect of nitric oxide in the nociceptive system. Nitric Oxide 25:243–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.niox.2011.06.004
Ferreira SH, Duarte ID, Lorenzetti BB (1991) The molecular mechanism of action of peripheral morphine analgesia: stimulation of the cGMP system via nitric oxide release. Eur J Pharmacol 201:121–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-2999(91)90333-l
Hao JX, Xu XJ (1996) Treatment of a chronic allodynia-like response in spinally injured rats: effects of systemically administered nitric oxide synthase inhibitors. Pain 66:313–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-3959(96)03039-4
Hsu S, Raine L, Fanger H (1981) Use of avidin–biotin–peroxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem 29:577–580. https://doi.org/10.1177/29.4.6166661
Ikeda H, Stark J, Fischer H, Wagner M, Drdla R, Jager T et al (2006) Synaptic amplifier of inflammatory pain in the spinal dorsal horn. Science 312:1659–1662. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1127233
Lewin MR, Walters ET (1999) Cyclic GMP pathway is critical for inducing long-term sensitization of nociceptive sensory neurons. Nat Neurosci 2:18–23. https://doi.org/10.1038/4520
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 22DDCT method. Methods 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Loeser JD, Melzack R (1999) Pain: an overview. Lancet 353:1607–1609. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(99)01311-2
Maihöfner C, Euchenhofer C, Tegeder I, Beck KF, Pfeilschifter J, Geisslinger G (2000) Regulation and immunohistochemical localization of nitric oxide synthases and soluble guanylyl cyclase in mouse spinal cord following nociceptive stimulation. Neurosci Lett 290:71–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0304-3940(00)01302-1
Miyamoto T, Dubin AE, Petrus MJ, Patapoutian AA (2009) TRPV1 and TRPA1 mediate peripheral nitric oxide-induced nociception in mice. PLoS ONE 4:e7596. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0007596
Napimoga MH, Cavada BS, Alencar NM, Mota ML, Bittencourt FS et al (2007) Lonchocarpus sericeus lectin decreases leukocyte migration and mechanical hypernociception by inhibiting cytokine and chemokines production. Int Immunopharmacol 7:824–835. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2007.02.001
Nascimento KS, Silva MTL, Oliveira MV, Lossio CF, Pinto-Junior VR, Osterne VJ, Cavada BS (2020) Dalbergieae lectins: a review of lectins from species of a primitive Papilionoideae (leguminous) tribe. Int J Biol Macromol 144:509–526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.12.117
Pires AF, Rodrigues NV, Soares PM, Ribeiro RA, Aragao KS et al (2016) A novel N-acetyl-glucosamine lectin of Lonchocarpus araripensis attenuates acute cellular inflammation in mice. Inflamm Res 65:43–52. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-015-0889-7
Pires AF, Almeida LM, Silva DHM, Marques GFO, Cajazeiras JB et al (2017) The lectin isolated from Lonchocarpus araripensis seed elicits endothelium-dependent vasorelaxation. J Health Biol Sci 5:306–310. https://doi.org/10.12662/2317-3076jhbs.v5i4.1351.p306-310.2017
Pires AF, Bezerra MM, Amorim RMF, Nascimento FLF, Marinho MM et al (2019) Lectin purified from Lonchocarpus campestris seeds inhibits inflammatory nociception. Int J Biol Macromol 125:53–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.11.233
Sachs D, Cunha FQ, Ferreira SH (2004) Peripheral analgesic blockade of hypernociception: activation of arginine/NO/cGMP/protein kinase G/ATP-sensitive K+ channel pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci 101:3680–3685. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0308382101
Schmidtko A, Tegeder I, Geisslinger G (2009) No NO, no pain? The role of nitric oxide and cGMP in spinal pain processing. Trends Neurosci 32:339–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2009.01.010
Su YS, Sun WH, Chen CC (2014) Molecular mechanism of inflammatory pain. World J Anesthesiol 3:71–81. https://doi.org/10.5313/wja.v3.i1.71
Wang LJ, Wang Y, Chen MJ, Tian Z-P, Lu BH et al (2017) Effects of niflumic acid on γ-aminobutyric acid-induced currents in isolated dorsal root ganglion neurons of neuropathic pain rats. Exp Ther Med 14:1373–1380. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2017.4666
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico-CNPq, Fundação Cearense de Amparo a Pesquisa-FUNCAP and Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior-CAPES. Cavada BS and Assreuy AM are senior investigators of CNPq.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Assreuy, A.M.S., Amorim, R.M.F., Martins, S.L. et al. Antinociceptive effect of Lonchocarpus araripensis lectin: activation of l-arginine/NO/cGMP/K+ATP signaling pathway. Inflammopharmacol 28, 1623–1631 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-020-00729-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-020-00729-z