Abstract
Aims
Activated microglia is known as a main mediator of inflammatory pain, but the possible mechanisms of its operation are poorly understood. Microglial cells have considered as one of the main sources of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the CNS. PTEN is one of the important targets of pro-inflammatory cytokines and the main mediator of apoptotic cell death. In this study, we investigated the possible effect of microglial activation on PTEN/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway and apoptosis in an inflammatory rat model of Complete Freund’s adjuvant (CFA).
Methods
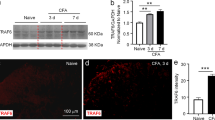
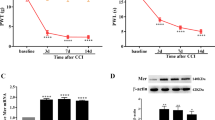
Persistent peripheral inflammation was induced by a subcutaneous injection of CFA into the rats’ right hind paw on day 0. Minocycline (a potent selective inhibitor of microglial) was administered intraperitoneally during days 1–21 after CFA injection. Hyperalgesia was assessed on days 0, 7, and 21 using plantar test, then lumbar spinal cord segments were isolated, and the amount of spinal Iba1 (microglial marker), PTEN, P.Akt, and cleaved caspase-3 (a marker of apoptosis activation) were analyzed using Western blot. The spinal TNF-α levels were assayed by ELISA and the microglia numbers were determined using immunohistochemical technique.
Results
Results revealed that increased hyperalgesia was concurrent with an increment of Iba1 (P < 0.001), TNF-α (P < 0.001), PTEN (P < 0.01), cleaved caspase-3 (P < 0.001), and a decrement of P.Akt (P < 0.01) during the acute phase of CFA-induced inflammation, while, at the same time as decreasing hyperalgesia during the chronic phase of study, Iba1 and TNF-α expression significantly decreased and PTEN, cleaved caspase-3, and P.Akt restored to baseline on day 0. Minocycline administration reduced the elevation of spinal Iba1 (P < 0.001), TNF-α (0.001), PTEN (P < 0.01), and cleaved caspase-3 (P < 0.001) expression induced by CFA injection, and also restored Akt activity to the baseline on day 0 (P < 0.001).
Conclusions
These results suggest that microglial-mediated pain following CFA injection might be related in part to increased spinal cell apoptosis which probably is mediated by PTEN/PI3K/Akt deregulation.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhtari Z, Zaringhalam J, Eidi A, Manaheji H, Tekieh E (2012) Bidirectional effects of serum TNF alpha level and spinal P38MAPK phosphorylation on hyperalgesia variation during CFA-induced arthritis. EXCLI J 11:373
Amin B, Abnous K, Motamedshariaty V, Hosseinzadeh H (2014) Attenuation of oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis by ethanolic and aqueous extracts of Crocus sativusL. stigma after chronic constriction injury of rats. An Acad Bras Ciênc 86:1821–1832
Amin B, Poureshagh E, Hosseinzadeh H (2016) The effect of verbascoside in neuropathic pain induced by chronic constriction injury in rats. Phytother Res 30:128–135
An K, Rong H, Ni H, Zhu C, Xu L, Liu Q, Chen Y, Zheng Y, Huang B, Yao M (2018) Spinal PKC activation—induced neuronal HMGB1 translocation contributes to hyperalgesia in a bone cancer pain model in rats. Exp Neurol 303:80–94
Cantley LC, Neel BG (1999) New insights into tumor suppression: PTEN suppresses tumor formation by restraining the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/AKT pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci 96:4240–4245
Chang N, El-Hayek YH, Gomez E, Wan Q (2007) Phosphatase PTEN in neuronal injury and brain disorders. Trends Neurosci 30:581–586
Crawford G, Le W, Smith R, Xie W, Stefani E, Appel SH (1992) A novel N18TG2 x mesencephalon cell hybrid expresses properties that suggest a dopaminergic cell line of substantia nigra origin. J Neurosci 12:3392–3398
Datta SR, Brunet A, Greenberg ME (1999) Cellular survival: a play in three Akts. Genes Dev 13:2905–2927
Di Cristofano A, Pandolfi PP (2000) The multiple roles of PTEN in tumor suppression. Cell 100:387–390
D'Mello R, Dickenson A (2008) Spinal cord mechanisms of pain. Br J Anaesth 101:8–16
Franciosi S, Ryu JK, Shim Y, Hill A, Connolly C, Hayden MR, McLarnon JG, Leavitt BR (2012) Age-dependent neurovascular abnormalities and altered microglial morphology in the YAC128 mouse model of Huntington disease. Neurobiol Dis 45:438–449
Fu H, Li F, Thomas S, Yang Z (2017) Hyperbaric oxygenation alleviates chronic constriction injury (CCI)-induced neuropathic pain and inhibits GABAergic neuron apoptosis in the spinal cord. Scand J Pain 17:330–338
Garraway SM, Woller SA, Huie JR, Hartman JJ, Hook MA, Miranda RC, Huang Y-J, Ferguson AR, Grau JW (2014) Peripheral noxious stimulation reduces withdrawal threshold to mechanical stimuli after spinal cord injury: role of tumor necrosis factor alpha and apoptosis. PAIN® 155:2344–2359
Gary DS, Mattson MP (2002) PTEN regulates Akt kinase activity in hippocampal neurons and increases their sensitivity to glutamate and apoptosis. Neuromol Med 2:261–269
Gazerani S, Zaringhalam J, Manaheji H, Golabi S (2016) The role of C fibers in spinal microglia induction and possible relation with TRPV3 expression during chronic inflammatory Arthritis in rats. Basic Clin Neurosci 7:231
Ghasemzadeh MR, Amin B, Mehri S, Mirnajafi-Zadeh SJ, Hosseinzadeh H (2016) Effect of alcoholic extract of aerial parts of Rosmarinus officinalis L. on pain, inflammation and apoptosis induced by chronic constriction injury (CCI) model of neuropathic pain in rats. J Ethnopharmacol 194:117–130
Hoogland IC, Houbolt C, van Westerloo DJ, van Gool WA, van de Beek D (2015) Systemic inflammation and microglial activation: systematic review of animal experiments. J Neuroinflamm 12:114
Hu B, Xu G, Zhang X, Xu L, Zhou H, Ma Z, Shen X, Zhu J, Shen R (2018) Paeoniflorin attenuates inflammatory pain by inhibiting microglial activation and Akt-NF-κB signaling in the central nervous system. Cell Physiol Biochem 47:842–850
Huang S-H, Wu S-H, Lee S-S, Chang K-P, Chai C-Y, Yeh J-L, Lin S-D, Kwan A-L, Wang H-MD, Lai C-S (2015a) Fat grafting in burn scar alleviates neuropathic pain via anti-inflammation effect in scar and spinal cord. PLoS ONE 10:e0137563
Huang S-Y, Sung C-S, Chen W-F, Chen C-H, Feng C-W, Yang S-N, Hung H-C, Chen N-F, Lin P-R, Chen S-C (2015b) Involvement of phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted from chromosome 10 in rodent model of neuropathic pain. J Neuroinflamm 12:59
Hylden JL, Nahin RL, Traub RJ, Dubner R (1989) Expansion of receptive fields of spinal lamina I projection neurons in rats with unilateral adjuvant-induced inflammation: the contribution of dorsal horn mechanisms. Pain 37:229–243
Joseph EK, Levine JD (2004) Caspase signalling in neuropathic and inflammatory pain in the rat. Eur J Neurosci 20:2896–2902
Kim W, Kim SK (2016) Neural circuit remodeling and structural plasticity in the cortex during chronic pain. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol 20:1–8
Kim SH, Nam JS, Choi DK, Koh WW, Suh JH, Song JG, Shin JW, Leem JG (2011) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha and apoptosis following spinal nerve ligation injury in rats. Korean J Pain 24:185–190
Ledeboer A, Sloane EM, Milligan ED, Frank MG, Mahony JH, Maier SF, Watkins LR (2005) Minocycline attenuates mechanical allodynia and proinflammatory cytokine expression in rat models of pain facilitation. Pain 115:71–83
Li L, Liu F, Salmonsen RA, Turner TK, Litofsky NS, Di Cristofano A, Pandolfi PP, Jones SN, Recht LD, Ross AH (2002) PTEN in neural precursor cells: regulation of migration, apoptosis, and proliferation. Mol Cell Neurosci 20:21–29
Li L, Liu F, Ross AH (2003) PTEN regulation of neural development and CNS stem cells. J Cell Biochem 88:24–28
Li K, Fu K-Y, Light AR, Mao J (2010) Systemic minocycline differentially influences changes in spinal microglial markers following formalin-induced nociception. J Neuroimmunol 221:25–31
May A (2008) Chronic pain may change the structure of the brain. PAIN® 137:7–15
McDowell ML, Das A, Smith JA, Varma AK, Ray SK, Banik NL (2011) Neuroprotective effects of genistein in VSC4. 1 motoneurons exposed to activated microglial cytokines. Neurochem Int 59:175–184
Nakajima K, Kohsaka S (2001) Microglia: activation and their significance in the central nervous system. J Biochem 130:169–175
Nasseri B, Nazemian V, Manaheji H, Zaringhalam J (2016) Microglia are involved in pain related behaviors during the acute and chronic phases of arthritis inflammation. J Cell Mol Anesth 1:137–145
Nasseri B, Zaringhalam J, Daniali S, Manaheji H, Abbasnejad Z, Nazemian V (2019) Thymulin treatment attenuates inflammatory pain by modulating spinal cellular and molecular signaling pathways. Int Immunopharmacol 70:225–234
Nazemian V, Nasseri B, Manaheji H, Zaringhalam J (2016) Effects of mesenchymal stem cells conditioned medium on behavioral aspects of inflammatory arthritic pain induced by CFA adjuvant. J Cell Mol Anesth 1:47–55
Nazemian V, Kalanaky S, Manaheji H, Houshmandi E, Mohammadi M, Zaringhalam J, Mirjafai S (2019) Anti-hyperalgesia effect of nanchelating based nano particle, RAc1, can be mediated via liver hepcidin expression modulation during persistent inflammation. Int Immunopharmacol 69:337–346
Ni J, Hou X, Wang X, Shi Y, Xu L, Zheng X, Liu N, Qiu A, Zhuang S (2019) 3-deazaneplanocin A protects against cisplatin-induced renal tubular cell apoptosis and acute kidney injury by restoration of E-cadherin expression. Cell Death Dis 10:355
Ohtake Y, Hayat U, Li S (2015) PTEN inhibition and axon regeneration and neural repair. Neural Regen Res 10:1363
Qin G, Fan X, Chen L, Shen C, Gui B, Tan G, Zhou J (2012) Preventive effects of AdR-siPTEN through the regulation of NMDA receptor NR2B subunit in trigeminal ganglia of migraine rats. Neurol Res 34:998–1006
Qin G, Xie J, Chen L, Wu B, Gui B, Zhou J (2016) PTEN inhibition preserves trigeminal nucleus caudalis neuron activation through tyrosine phosphorylation of the NR2B subunit at Tyr1472 of the NMDA receptor in a rat model of recurrent migraine. Neurol Res 38:320–326
Raghavendra V, DeLeo JA (2003) The role of astrocytes and microglia in persistent pain. Adv Mol Cell Biol 31:951–966
Scholz J, Broom DC, Youn D-H, Mills CD, Kohno T, Suter MR, Moore KA, Decosterd I, Coggeshall RE, Woolf CJ (2005) Blocking caspase activity prevents transsynaptic neuronal apoptosis and the loss of inhibition in lamina II of the dorsal horn after peripheral nerve injury. J Neurosci 25:7317–7323
Sekiguchi Y, Kikuchi S, Myers RR, Campana WM (2003) ISSLS prize winner: erythropoietin inhibits spinal neuronal apoptosis and pain following nerve root crush. Spine 28:2577–2584
Sekiguchi M, Sekiguchi Y, Konno S-i, Kobayashi H, Homma Y, Kikuchi S-i (2009) Comparison of neuropathic pain and neuronal apoptosis following nerve root or spinal nerve compression. Eur Spine J 18:1978
Smith RG, Alexianu ME, Crawford G, Nyormoi O, Stefani E, Appel SH (1994) Cytotoxicity of immunoglobulins from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients on a hybrid motoneuron cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci 91:3393–3397
Smith JA, Zhang R, Varma AK, Das A, Ray SK, Banik NL (2009) Estrogen partially down-regulates PTEN to prevent apoptosis in VSC4. 1 motoneurons following exposure to IFN-γ. Brain Res 1301:163–170
Sun X, Zeng H, Wang Q, Yu Q, Wu J, Feng Y, Deng P, Zhang H (2018) Glycyrrhizin ameliorates inflammatory pain by inhibiting microglial activation-mediated inflammatory response via blockage of the HMGB1-TLR4-NF-kB pathway. Exp Cell Res 369:112–119
Vasudevan KM, Gurumurthy S, Rangnekar VM (2004) Suppression of PTEN expression by NF-κB prevents apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol 24:1007–1021
Wang L-Y, Li X, Han Y-Z (2015a) Neuroprotection by epigallo catechin gallate against bupivacaine anesthesia induced toxicity involves modulation of PI3/Akt/PTEN signalling in N2a and SH-SY5Y cells. Int J Clin Exp Med 8:15065
Wang Y-L, Li F, Chen X (2015b) Pten inhibitor-bpV ameliorates early postnatal propofol exposure-induced memory deficit and impairment of hippocampal LTP. Neurochem Res 40:1593–1599
Xu J, Yeon JE, Chang H, Tison G, Chen GJ, Wands J, De la Monte S (2003) Ethanol impairs insulin-stimulated neuronal survival in the developing brain role of pten phosphatase. J Biol Chem 278:26929–26937
Yoon S-Y, Patel D, Dougherty PM (2012) Minocycline blocks lipopolysaccharide induced hyperalgesia by suppression of microglia but not astrocytes. Neuroscience 221:214–224
Zanjani TM, Sabetkasaei M, Mosaffa N, Manaheji H, Labibi F, Farokhi B (2006) Suppression of interleukin-6 by minocycline in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Eur J Pharmacol 538:66–72
Zaringhalam J, Tekieh E, Manaheji H, Akhtari Z (2013) Cellular events during arthritis-induced hyperalgesia are mediated by interleukin-6 and p38 MAPK and their effects on the expression of spinal mu-opioid receptors. Rheumatol Int 33:2291–2299
Zaringhalam J, Akhtari Z, Eidi A, Ruhani AH, Tekieh E (2014a) Relationship between serum IL10 level and p38MAPK enzyme activity on behavioral and cellular aspects of variation of hyperalgesia during different stages of arthritis in rats. Inflammopharmacology 22:37–44
Zaringhalam J, Hormozi A, Tekieh E, Razavi J, Khanmohammad R, Golabi S (2014b) Serum IL-10 involved in morphine tolerance development during adjuvant-induced arthritis. J Physiol Biochem 70:497–507
Zhu S, Stavrovskaya IG, Drozda M, Kim BY, Ona V, Li M, Sarang S, Liu AS, Hartley DM, Gullans S (2002) Minocycline inhibits cytochrome c release and delays progression of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in mice. Nature 417:74
Zimmermann M (1983) Ethical guidelines for investigations of experimental pain in conscious animals. Pain 16:109–110
Zimmermann M (2001) Pathobiology of neuropathic pain. Eur J Pharmacol 429:23–37
Acknowledgements
This article has been extracted from the PhD thesis written by Mrs "Mansoureh Baniasadi" in School of Medicine, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences (Registration No: 304), and supported by Iran National Science Foundation (INSF) (No. 95840128) and Neurophysiology Research Center of Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences (No. 742).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baniasadi, M., Manaheji, H., Maghsoudi, N. et al. Microglial-induced apoptosis is potentially responsible for hyperalgesia variations during CFA-induced inflammation. Inflammopharmacol 28, 475–485 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-019-00623-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-019-00623-3