Abstract
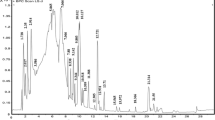
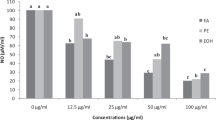
To characterise bioactive phenolics and confirm anti-inflammatory indicators in Porana sinensis stem, 23 phenolics were identified by UPLC-QTOF-MS/MS from crude extract (CE) prepared optimally with 80% methanol. Further fractionalisation using D101 macroporous resin resulted in predominant enrichment of total phenols and flavonoids into Fr.II. Correspondingly, the bioactive components-enriched Fr.II exhibited the lowest IC50 for scavenging DPPH and ABTS and the highest oxygen radical absorbance capacity or ORAC followed by Fractions Fr.I + Fr.II, CE and Fr.I, implying that certain phenolics possessing lower antioxidant activity completely remained in CE. Anti-inflammatory tests with LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells showed that CE possessed the highest inhibition of NO-production followed by Fr.II and Fr.I, meaning that CE might contain compounds that expressed higher anti-inflammatory but lower antioxidant activities or possessed synergistic interactions but were not fractionated together. Quantitative determination of nine major phenolics revealed that caffeic acid and 3-, 4- and 5-caffeoylquinic acids were concentrated into Fr.I, whereas scopolin, scopoletin and 3,5-, 3,4- and 4,5-dicaffeoylquinic acids were enriched into Fr.II. Further experiments with three selected major phenolics reduced the proposed synergistic interactions. Anti-inflammatory tests of the nine major phenolics evidenced that caffeic acid and the six caffeoylquinic acids produced higher, and the three dicaffeoylquinic acids at 140 μΜ showed even more significant activities in suppressing NO-production and mRNA expression of iNOS, TNF-α, COX-2, and IL-6, suggesting that these three dicaffeoylquinic acids could be indicators of the anti-inflammatory potential of P. sinensis stem. These findings provided novel insights for potential use of P. sinensis or liana, as an important source of natural antioxidants, against inflammation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Apel K, Hirt H (2004) Reactive oxygen species: metabolism, oxidative stress, and signal transduction. Annu Rev Plant Biol 55:373–399. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.55.031903.141701
Broadhurst RB, Jones WT (1978) Analysis of condensed tannins using acidified vanillin. J Sci Food Agric 29:788–794. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.2740290908
Cai H, Harrison DG (2000) Endothelial dysfunction in cardiovascular diseases: the role of oxidant stress. Circ Res 87:840–844. http://circres.ahajournals.org/content/87/10/840
Calixto JB, Otuki MF, Santos AR (2003) Anti-inflammatory compounds of plant origin. Part I. Action on arachidonic acid pathway, nitric oxide and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappaB). Planta Med 69:973–983. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2003-45141
Carciochi RA, Manrique GD, Dimitrov K (2015) Optimization of antioxidant phenolic compounds extraction from quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa) seeds. J Food Sci Tech 52:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-014-1514-4
Chavan Y, Singhal RS (2013) Ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE) of bioactives from arecanut (Areca catechu L.) and optimization study using response surface methodology. Innov Food Sci Emerg 17:106–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2012.10.001
Chen Z, Liao L, Zhang Z, Wu L, Wang Z (2013) Comparison of active constituents, acute toxicity, anti-nociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities of Erycibe obtusifolia Benth. and Erycibe schmidtii Craib. J Ethnopharmacol 150:501–506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2013.08.059
Chen Z, Liao L, Yang Y, Zhang Z, Wang Z (2015) Different fingerprinting strategies to differentiate Porana sinensis and plants of Erycibe by high-performance liquid chromatography with diode array detection, ultra high performance liquid chromatography with tandem quadrupole mass spectrometry, and chemometrics. J Sep Sci 38:231–238. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201400861
Chunying L, Wang X, Ge G, Lian W, Yongxin L, Chengjun S (2013) Identification and quantification of free, conjugate and total phenolic compounds in leaves of 20 sweet potato cultivars by HPLC-DAD and HPLC-ESI-MS/MS. Food Chem 141:2697–2706. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.05.009
Clifford MN, Knight S, Kuhnert N (2005) Discriminating between the six isomers of dicaffeoylquinic acid by LC–MSn. J Agric Food Chem 53:3821–3832. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf050046h
Cui YQ, Jia YJ, Zhang T, Zhang QB, Wang XM (2012) Fucoidan protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced rat neuronal damage and inhibits the production of proinflammatory mediators in primary microglia. CNS Neurosci Ther 18:827–833. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1755-5949.2012.00372.x
Dawa Z, Zhou Y, Bai Y, Gesang S, Bai B, Ding L (2008) Development of an HPLC-DAD-ESI-MSn method for quantitative analysis of Saussurea tridactyla. J Pharm Biomed 48:1076–1081. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2008.08.016
Fang X, Wang J, Hao J, Li X, Guo N (2015) Simultaneous extraction, identification and quantification of phenolic compounds in Eclipta prostrata, using microwave-assisted extraction combined with HPLC-DAD-ESI-MS/MS. Food Chem 188:527–536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.05.037
Faqueti LG, Sandjo LP, Biavatti MW (2017) Simultaneous identification and quantification of polymethoxyflavones, coumarin and phenolic acids in ageratum conyzoides, by UPLC-ESI-QToF-MS and UPLC-DAD. J Pharm Biomed 145:621–628. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2017.07.034
Feron O, Dessy C (2004) pathophysiological roles of nitric oxide: in the heart and the coronary vasculature. Curr Med Chem 3:207–216. https://doi.org/10.2174/1568014043355348
Fujioka K, Shibamoto T (2008) Chlorogenic acid and caffeine contents in various commercial brewed coffees. Food Chem 106:217–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2007.05.091
Furukawa S, Fujita T, Shimabukuro M, Iwaki M, Yamada Y, Nakajima Y (2017) Increased oxidative stress in obesity and its impact on metabolic syndrome. J Clin Invest 114:1752–1761. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI21625
Hirakura K, Morita M, Nakajima K, Sugama K, Takagi K, Niitsu K (1997) Phenolic glucosides from the root of Pueraria lobate. Phytochemistry 46:921–928. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-9422(97)00371-3
Hsu YW, Chi KH, Huang WC, Lin WW (2001) Ceramide inhibits lipopolysaccharide-mediated nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 induction in macrophages: effects on protein kinases and transcription factors. J Immunol 166:5388–5397. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.166.9.5388
Huang WY, Cai YZ, Zhang Y (2009) Natural phenolic compounds from medicinal herbs and dietary plants: potential use for cancer prevention. Nutr Cancer 62:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1080/01635580903191585
Ickes GR, Fong HH Jr, Schiff PL, Perdue RE Jr, Farnsworth NR (2010) Antitumor activity and preliminary phytochemical examination of Tagetes minuta (Compositae). J Pharm Sci-US 62:1009–1011. https://doi.org/10.1002/jps.2600620635
Lee SR, Lee S, Moon E, Park HJ, Park HB, Kim KH (2017) Bioactivity-guided isolation of anti-inflammatory triterpenoids from the sclerotia of Poria cocos using LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells. Bioorg Chem 70:94–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2016.11.012
Longo W, Panesar N, Mazuski J, Kaminski D (1998) Contribution of cyclooxygenase-1 and cyclooxygenase-2 to prostanoid formation by human enterocytes stimulated by calcium ionophore and inflammatory agents. Prostag Oth Lipid M 56:325–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0090-6980(98)00058-6
Lotulung PD, Minarti Kardono LB, Kawanishi K (2008) Antioxidant compound from the rhizomes of Kaempferia rotunda L. Pak J Biol Sci 11:2447–2450. https://doi.org/10.3923/pjbs.2008.2447.2450
Markesbery WR (1997) Oxidative stress hypothesis in alzheimer’s disease. Free Radical Bio Med 23:134–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0891-5849(96)00629-6
Mihara M, Hashizume M, Yoshida H, Suzuki M, Shiina M (2012) IL-6/IL-6 receptor system and its role in physiological and pathological conditions. Clin Sci 122:143–159. https://doi.org/10.1042/CS20110340
Nascimento AM, Maria-Ferreira D, Dal Lin FT, Kimura A, de Santana-Filho AP, Mfp W (2017) Phytochemical analysis and anti-inflammatory evaluation of compounds from an aqueous extract of Croton cajucara Benth. J Pharmaceut Biomed 145:821–830. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2017.07.032
Nathan C (2002) Points of control in inflammation. Nature 420:846–852. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01320
Nathan C, Ding A (2010) Nonresolving inflammation. Cell 140:871–882. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2010.02.029
Pan XH, Shi XJ, Zhang XF, Jin-Ping SI (2012) Constituents of Chimonanthus salicifolius and their antioxidant activity. Chin J Exp Tradit Med Formulae 18:99–101. https://doi.org/10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.2012.01.039
Protti M, Gualandi I, Mandrioli R, Zappoli S, Tonelli D, Mercolini L (2017) Analytical profiling of selected antioxidants and total antioxidant capacity of goji (lycium spp.) berries. J Pharmaceut Biomed 143:252–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2017.05.048
Santos DR, Calixto JB, Souza GEP (2003) Effect of a kinin B2, receptor antagonist on LPS- and cytokine-induced neutrophil migration in rats. Brit J Pharmacol 139:271–278. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjp.0705236
Soobrattee MA, Neergheen VS, Luximon-Ramma A, Aruoma OI, Bahorun T (2005) Phenolics as potential antioxidant therapeutic agents: mechanism and actions. Mutat Res 579:200–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2005.03.023
Valko M, Rhodes CJ, Moncol J, Izakovic M, Mazur M (2006) Free radicals, metals and antioxidants in oxidative stress-induced cancer. Chem-Biol Interact 160:1–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2005.12.009
Valko M, Leibfritz D, Moncol J, Cronin MT, Mazur M, Telser J (2007) Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease. Int J Biochem Cell B 39:44–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2006.07.001
Wu L, Zhu E, Zhang Z, Wang Z (2005) Investigating original plant of Caulis Erycibes in Guangxi and identifying mainstream variety of Caulis Erycibes in market. Chin Trad Herb Drugs 36:1398–1400
Xue Q, Fan H, Li K, Yang L, Sun L, Liu Y (2017) Comparative evaluations on phenolic antioxidants of nine adulterants and anti-inflammation of four alternatives with their original herb Erycibe schmidtii. RSC Adv 7:51151–51161. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA10767F
Yu T, Yi YS, Yang Y, Oh J, Jeong D, Cho JY (2012) The pivotal role of TBK1 in inflammatory responses mediated by macrophages. Mediat Inflamm 2012:979105. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/979105
Zhang L, Ravipati AS, Koyyalamudi SR, Jeong SC, Reddy N, Smith PT, Bartlett J, Shanmugam K, Münch DG, Wu MJ (2011) Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of selected medicinal plants containing phenolic and flavonoid compounds. J Agric Food Chem 59:12361–12367. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf203146e
Zhang JY, Zhang Q, Li N, Wang ZJ, Lu JQ, Qiao YJ (2013) Diagnostic fragment-ion-based and extension strategy coupled to DFIs intensity analysis for identification of chlorogenic acids isomers in Flos Lonicerae Japonicae by HPLC-ESI-MS(n). Talanta 104:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2012.11.012
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by the China Special Fund for Forestry Research in the Public Interest (Grant No. 201504606).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
QX, LS, and YL designed the study, performed the research and drafted the manuscript. PY, KL, HF, LY, and XC participated in the experiments. YL provided the facilities and reviewed the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that there were no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xue, Q., Yin, P., Li, K. et al. Identification of bioactive phenolics from Porana sinensis Hemsl. stem by UPLC-QTOF-MS/MS and the confirmation of anti-inflammatory indicators using LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells. Inflammopharmacol 27, 1055–1069 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-018-00558-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-018-00558-1