Abstract
Implicit authentication is an efficient tool focusing on achieving identity authentication during the transmitting ciphertext or signed message without extra authentication information. As quantum cryptography is emerging as a means to provide true randomness between quantum smart devices, it is imperative and crucial to solve the problem that computational cryptography could be cracked in the future. In this article, a novel quantum mutual implicit authentication key protocol (QMIAK) is proposed, which is based on single photon and key recycling for improving efficiency without entanglement. QMIAK guarantees the fairness of the trusted parties by mutually determining the base for encoding and decoding the authentication key. Besides, the fusion coding used in this scheme can effectively prevent Eve from intercepting and analyzing the authentication key, which greatly enhances the security of the proposed protocol. For increasing the utilization of the quantum bits, we adopt key recycling mechanism. In addition, the content of security proof and efficiency analysis also demonstrate our protocol is suitable for efficiently protecting authentication keys and feasible to implement.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The raw/processed data required to reproduce these findings cannot be shared at this time as the data also forms part of an ongoing study.
References
Yuan, H., Liu, Y.-M., Pan, G.-Z., Zhang, G., Zhou, J., Zhang, Z.-J.: Quantum identity authentication based on ping-pong technique without entanglements. Quantum Inf. Process. 13(11), 2535–2549 (2014)
Zawadzki, P.: Quantum identity authentication without entanglement. Quantum Inf. Process. 18(1), 7 (2019)
Ma, H., Huang, P., Bao, W., Zeng, G.: Continuous-variable quantum Identity authentication based on quantum teleportation. Quantum Inf. Process. 15(6), 2605–2620 (2016)
McEliece, R.J.: A public-key cryptosystem based on algebraic coding theory. DSN progress report 42(44), 114–116 (1978)
Bernstein, D. J.: Introduction to post-quantum cryptography. In: Post-quantum cryptography, pp. 1–14. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin, Heidelberg (2009)
Regev, O.: On lattices, learning with errors, random linear codes, and cryptography. J. ACM 56(6), 1–40 (2009)
Bernstein, D. J., Hopwood, D., H¨ulsing, A., Lange, T., Niederhagen, R., Papachristodoulou, L., Schwabe, P., Wilcox-O’Hearn, Z.: SPHINCS: practical state-less hash-based signatures. Tech Report, October (2014) https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-46800-5_15
Eisenbarth, T., Maurich, I. V., Ye, X.: Faster hash-based signatures with bounded leakage. In Selected Areas in Cryptography – SAC 2013, Springer LNCS, pages 223–243. (2014)
Hong, C.H., Heo, J., Jang, J.G., Kwon, D.: Quantum identity authentication with single photon. Quantum Inf. Process. 16, 1–20 (2017)
Bennet, C. H., Brassard, G.: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computers, Systems, and Signal Processing, IEEE, New York, p. 175 (1984)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G.: Quantum cryptography: public key distribution and coin tossing. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Computers, Systems and Signal Processing, New York, pp. 175–179 (1984)
Cleve, R., Gottesman, D., Lo, H.K.: How to Share a Quantum Secret. Phys. Rev. Lett. 83, 648 (1999)
Long, G.L., Liu, X.S.: Theoretically efficient high-capacity quantum-key-distribution scheme. Phys. Rev. A 65, 032302–032304 (2002)
Créau, C., Salvail, L.: Advances in Cryptology In: Proceedings of Eurocrypt’ 95, p. 133. Springer, Berlin (1995)
Dušek, M., Haderka, O., Hendrych, M., & Myška, R.: Quantum identification system. Phys. Rev. A 60(1), 149 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.60.149
Zeng, G., Zhang, W.: Identity verification in quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 61, 022303 (2000)
Ljunggren, D., Bourennane, M., Karlsson, A.: Authority-based user authentication in quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 62, 022305 (2000)
Mihara, T.: Quantum identification schemes with entanglements. Phys. Rev. A 65(5), 052326 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.65.052326
Zhou, N., Zeng, G.H., Zeng, W.J., Zhu, F.C.: Cross-center quantum identification scheme based on teleportation and entanglement swapping. Opt. Commun. 254, 380 (2005)
Wang, J., Zhang Q., Tang, C. J.: Authenticated Multiuser Quantum Direct Communication using Entanglement Swapping. e-prints: quant-ph/0605006, (2006)
Zhang, Z., Zeng, G., Zhou, N., Xiong, J.: Quantum identity authentication based on ping-pong technique for photons. Phys. Lett. A 356, 199 (2006)
Lo, H.-K.: Quantum key distribution with vacua or dim pulses as decoy states. In: Proceedings of IEEE ISIT. IEEE, p. 137 (2004)
Lo, H.-K., Ma, X., Chen, K.: Decoy state quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 230504 (2005)
Wang, X.-B.: Beating the pns attack in practical quantum cryptography. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 230503 (2005)
Wang, X.-B.: A decoy-state protocol for quantum cryptography with 4 intensities of coherent states. Phys. Rev. A 72, 012322 (2005)
Hwang, W.-Y.: Quantum key distribution with high loss: toward global secure communication. Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 057901 (2003)
Lo, H.K., Chau, H.F., Ardehali, M.: Efficient quantum key distribution scheme and a proof of its unconditional security. J. Cryptol. 18, 133–165 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00145-004-0142-y
Damgard, I. B., Pedersen, T. B., Salvail, L.: A quantum cipher with near optimal key-recycling. In: Shoup, Advances in Cryptology. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 3621. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. (2005)
Gao, F., Qin, S.J., Wen, Q.Y.: A simple participant attack on the Bradler-Dusek protocol. Quantum Inf. Comput. 7, 329–334 (2007)
Rao, B.D., Jayaraman, R.: A novel quantum identity authentication protocol without entanglement and preserving pre-shared key information. Quantum Inf. Processing (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-023-03832-6
Abulkasim, H., Hamad, S., El Bahnasy, K., Rida, S.Z.: Authenticated quantum secret sharing with quantum dialogue based on Bell states. Phys. Scr. 91(8), 085101 (2016)
Shi, W.-M., Zhang, J.-B., Zhou, Y.-H., Yang, Y.-G.: A novel quantum deniable authentication protocol without entanglement. Quantum Inf. Process. 14(6), 2183–2193 (2015)
Morchon, O. G., Rietman, R., Sharma, S., Tolhuizen, L., Torre-Arce, J. L.: Dtls-himmo: Achieving dtls certificate security with symmetric key overhead. In ESORICS (2015)
Zheng, Xiaoyi, Chang, Kuang, Liang, Wen-Zhen.: Controlled Quantum Dialogue with Authentication Protocol on A Basis of GHZ-like State. Quantum Inf. Processing 19(8), 251 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-020-02745-y
Cabello, A.: Quantum key distribution in the Holevo limit. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85(26), 5635 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.85.5635
Lizama-Perez, L.A.: Reverse reconciliation for optimal error correction in quantum key distribution. Symmetry 15(3), 710 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15030710
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China: Research on Precision PCR Instrument Model and Its Application in Genetic Engineering (Grant No. 62172330).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
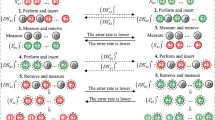
Yuguang Xu: Creativity and Verification, and prepared Fig. 1. Lu Zhang: Writing the main manuscript text Hongfeng Zhu: Design the protocol All authors reviewed the manuscript and discussed some main problems.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declared that they have no conflicts of interest to this work.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Y., Zhang, L. & Zhu, H. Quantum Mutual Implicit Authentication Key Agreement Protocol without Entanglement with Key Recycling. Int J Theor Phys 62, 244 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-023-05501-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-023-05501-x