Abstract
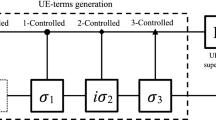
Quantum control is an important field for quantum computing and quantum simulation. The key of quantum control is to realize quantum logic operators with high fidelity. In this work, based on spin-1/2 system, the optimal simulation of three Pauli logic operators are carried out by using quantum optimal control theory. Under Pauli z spin-presentation, the results show that under the given quantum initial state, the Pauli operators achieve the expected target quantum state with fidelity (0.9999). When the control pulse is applied on x-axis, the number of iterations required to optimize Pauli x operator to achieve the target state is the least, and the number of iterations required to optimize Pauli z operator is the most. In addition, the comparison shows that when the fidelity reach 0.9999, the population of the quantum final state can reach the ideal theoretical expectation. Besides, the optimization fidelity of Hadamard gate can also reach 0.9999 based on spin-1/2 system. Finally, the study on the phase evolution of quantum states shows that the phase difference between the initial and final quantum states of optimized Pauli x and Pauli z logic operator are π/2 respectively, and there is no phase difference between the final quantum state and the initial quantum state after the evolution of optimized Pauli y operator.



















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data generated and/or analysed during the current study are not publicly available for legal/ethical reasons but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Barenco, A., Bennett, C.H., Cleve, R., DiVincenzo, D.P., Margolus, N., Shor, P., Sleator, T., Smolin, J.A., Weinfurter, H.: Elementary gates for quantum computation. Phys. Rev. A 52, 3457 (1995)
Campbell, E.T., Terhal, B.M., Vuillot, C.: Roads towards fault-tolerant universal quantum computation. Nature 549, 173 (2017)
Huang, C.-H., Goan, H.-S.: Robust quantum gates for stochastic time-varying noise. Phys. Rev. A 95, 062325 (2017)
Nielsen, M.A., Chuang, I.L.: Information quantum and quantum computation. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2000)
Rabitz, H., Zhu, W.S.: Optimal control of molecular motion: design, implementation, and inversion. Acc. Chem. Res. 33, 572 (2000)
Timoney, N., Elman, V., Glaser, S., Weiss, C., Johanning, M., Neuhauser, W., Wunderlich, C.: Error-resistant single-qubit gates with trapped ions. Phys. Rev. A 77, 052334 (2008)
Singer, K., Poschinger, U., Murphy, M., Ivanov, P., Ziesel, F., Calarco, T., Schmidt-Kaler, F.: Colloquium: trapped ions as quantum bits: essential numerical tools. Rev. Mod. Phys. 82, 2609 (2010)
Poulsen, U., Sklarz, S., Tannor, D., Calarco, T.: Correcting errors in a quantum gate with pushed ions via optimal control. Phys. Rev. A 82, 012339 (2010)
Treutlein, P., Hänsch, T. W., Reichel, J., Negretti, A., Cirone, M.A., Calarco, T.: Microwave potentials and optimal control for robust quantum gates on an atom chip. Phys. Rev. A 74, 022312 (2006)
De Chiara, G., Calarco, T., Anderlini, M., Montangero, S., Lee, P.J., Brown, B.L., Phillips, W.D., Porto, J.V.: Optimal control of atom transport for quantum gates in optical lattices. Phys. Rev. A 77, 052333 (2008)
Chang, D.E., Thompson, J.D., Park, H., Vuletic, V., Zibrov, A.S., Zoller, P., Lukin, M.D.: Trapping and manipulation of isolated atoms using nanoscale plasmonic structures. Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 123004 (2009)
Doerk, H., Idziaszek, Z., Calarco, T.: Atom-ion quantum gate. Phys. Rev. A 81, 012708 (2010)
Goerz, M., Calarco, T., Koch, C.: The quantum speed limit of optimal controlled phasegates for trapped neutral atoms. J. Phys. B, At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 44, 154011 (2011)
Hacker, B., Welte, S., Rempe, G., Ritter, S.: A photon-photon quantum gate based on a single atom in an optical resonator. Nature 536, 193 (2016)
Zhong, H.S., Pan, J.W., et al: Quantum computational advantage using photons. Science 70, 6523 (2020)
Waldherr, G., et al.: Quantum error correction in a solid-state hybrid spin register. Nature 506, 204 (2014)
Zhou, B.B., Baksic, A., Ribeiro, H., Yale, C.G., Heremans, F.J., Jerger, P., Auer, A., Burkard, G., Clerk, A.A., Awschalom, D.D.: Accelerated quantum control using superadiabatic dynamics in a solid-state lambda system. Nat. Phys. 13, 330 (2017)
Wolfe, C.S., Bhallamudi, V.P., Wang, H.L., Du, C.H., Manuilov, S., Teeling-Smith, R.M., Berger, A.J., Adur, R., Yang, F.Y., Hammel, P.C.: Offresonant manipulation of spins in diamond via precessing magnetization of a proximal ferromagnet. Phys. Rev. B 89, 180406 (2014)
Hirose, M., Cappellaro, P.: Coherent feedback control of a single qubit in diamond. Nature 532, 77 (2016)
Bhaskar, M.K., Sukachev, D.D., Sipahigil, A., Evans, R.E., Burek, M.J., Nguyen, C.T., Rogers, L.J., Siyushev, P., Metsch, M.H., Park, H., Jelezko, F., Lončar, M., Lukin, M.D.: Quantum nonlinear optics with a germanium-vacancy color center in a nanoscale diamond waveguide. Phys. Rev. Lett. 118, 223603 (2017)
Lovchinsky, I., et al.: Nuclear magnetic resonance detection and spectroscopy of single proteins using quantum logic. Science 351, 6275 (2016)
DeMille, D.: Quantum computation with trapped polar molecules. Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 067901 (2002)
Suzuki, S., Mishima, K., Yamashita, K.: Ab initial study of optimal control of ammonia molecular vibrational wavepackets: towards molecular quantum computin. Chem. Phys. Lett. 410, 358 (2005)
Bomble, L., Lauvergnat, D., Remacle, F., Desouter-Lecomte, M.: Vibrational computing: Simulation of a full adder by optimal control. J. Chem. Phys. 128, 064110 (2008)
Bomble, L., Lauvergnat, D., Remacle, F., Desouter-Lecomte, M.: Controlled full adder or subtractor by vibrational quantum computing. Phys. Rev. A 80, 022332 (2009)
Bomble, L., Lauvergnat, D., Remacle, F., Desouter-Lecomte, M.: Controlled full adder-subtractor by vibrational computing. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 12, 15628 (2010)
Li, S., Shen, P., Chen, T., Xue, Z. -Y.: Noncyclic nonadiabatic holonomic quantum gates via shortcuts to adiabaticity. Fron. Phys. 16(5), 51502 (2021)
Liu, W.W., Zhang, C.L., Zhang, L.: Fast and robust implementation of quantum gates by transitionless quantum driving. Quantum Inf. Pro. 20, 118 (2021)
Zhao, T.H., Wang, M.H., Zhou, B.: Optimal quantum state transformations based onmachine learning. Quant. Inf. Pro. 20, 212 (2021)
Cimini, V., Gherardini, S., Barbieri, M., Gianani, I., Sbroscia, M., Buffoni, L., Paternostro, M., Caruso, F.: Experimental characterization of the energetics of quantum logic gates. npj Quant. Inf. 6, 96 (2020)
Li, X, Wu, Y., Steel, D., Gammon, D., Stievater, T.H, Katzer, D.S., Park, D., Piermarocchi, C., Sham, L.J.: An all-optical quantum gate in a semiconductor quantum dot. Nature 301, 809 (2003)
Geng, J., Wu, Y., Wang, X., Xu, K., Shi, F., Xie, Y., Rong, X., Du, J.: Experimental time-Optimal universal control of spin qubits in solids. Phys. Rev. Lett. 117, 170501 (2016)
Xu, Y., Cai, W., Ma, Y., Mu, X., Hu, L., Chen, T., Wang, H., Song, Y.P., Xue, Z.-Y., Yin, Z.-Q., Sun, L.: Single-loop Realization of arbitrary nonadiabatic holonomic single-qubit quantum gates in a superconducting circuit. Phys. Rev. Lett. 121, 110501 (2018)
Ebadi, S., Wang, T.T., Levine, H., Keesling, A., Semeghini, G., Omran, A., Lukin, M.D.: Quantum phases of matter on a 256-atom programmable quantum simulator. Nature 595(7866), 227–232 (2021)
Tesch, C.M., de Vivie-Riedle, R.: Vibrational molecular quantum computing: Basis set independence and theoretical realization of the DeutschCJozsa algorithm. J. Chem. Phys. 121, 12158 (2004)
Zhao, M., Babikov, D.: Phase control in the vibrational qubit. J. Chem. Phys. 125, 024105 (2006)
Zhu, J., Kais, S., Wei, Q., Herschbach, D., Friedrich, B.: Implementation of quantum logic gates using polar molecules in pendular states. J. Chem. Phys. 138, 024104 (2013)
Ho, T. -S., Rabitz, H.: Why do effective quantum controls appear easy to find?. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 180, 226–240 (2006)
Ho, T. -S., Dominy, J., Rabitz, H.: Landscape of unitary transformations in controlled quantum dynamics. Phys. Rev. A 79, 013422 (2009)
Shu, C. -C., Ho, T. -S., Xing, X., Rabitz, H.: Frequency domain quantum optimal control under multiple constraints. Phys. Rev. A 93, 033417 (2016)
Shu, C.-C., Ho, T.-S., Rabitz, H.: Monotonic convergent quantum optimal control method with exact equality constraints on the optimized control fields. Phys. Rev. A 93, 053418 (2016)
Nanduri, A., Ho, T. -S., Rabitz, H.: Quantum-control-landscape structure viewed along straight paths through the space of control fields. Phys. Rev. A 93, 023427 (2016)
Shu, C.-C., Dong, D.Y., etersen, I.R.P., Henriksen, N.E.: Complete elimination of nonlinear light-matter interactions with broadband ultrafast laser pulses. Phys. Rev. A 95, 033809 (2017)
Guo, Y., Dong, D.Y., Shu, C.-C.: Optimal and robust control of quantum state transfer by shaping the spectral phase of ultrafast laser pulses. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 20, 9498 (2018)
D’Alessandro, D., Dahled, M.: Optimal control of two-level quantum systems. IEEE Trans. Automat. Control. 46, 866 (2001)
Dong, D.Y., Wu, C.Z., Chen, C.L., Qi, B., Petersen, I.R., Nori, F.: Learning robust pulses for generating universal quantum gates. Sci. Rep. 6, 36090 (2016)
Li, J.F.: Remote preparation of an arbitrary two-qubit state and optimal control of quantum logical gates. Ph. D. Dissertation (Shanghai : East China Normal University) (2019)
Koch, C.P., Boscain, U., Calarco, T., Dirr, G., Filipp, S., Glaser, S.J., Kosloff, R., Montangero, S., Schulte-Herbrüggen, T., Sugny, D., Wilhelm, F.K.: Quantum optimal control in quantum technologies. Strategic report on current status, visions and goals for research in Europe. EPJ Quant. Technol. 9, 19 (2022)
Glaser, S.J., Boscain, U., Calarco, T., Koch, C.P., Köckenberger, W., Kosloff, R., Kuprov, I., Luy, B., Schirmer, S., Schulte-Herbrüggen, T., Sugny, D., Wilhelm, F.K.: Training schrödinger’s cat: quantum optimal control. Strategic report on current status, visions and goals for research in Europe. Eur. Phys. J. D. 69, 279 (2015)
Dupont, N., Chatelain, G., Gabardos, L., Arnal, M., Billy, J., Peaudecerf, B., Sugny, D., Guéry-Odelin, D.: Quantum state control of a bose-einstein condensate in an optical lattice. PRX Quant. 2, 040303 (2021)
Li, J.F., Hu, J.R., Wan, F., He, D.S.: Optimization two-qubit quantum gate by two optical control methods in molecular pendular states. Sci. Rep. 12, 14918 (2022)
Cerfontaine, P., Botzem, T., Ritzmann, J., Humpohl, S.S., Ludwig, A., Schuh, D., Bougeard, D., Wieck, A.D., Bluhm, H.: Closed-loop control of a gaas-based singlet-triplet spin qubit with 99.5 gate fidelity and low leakage. Nat. Commun. 11, 4144 (2020)
Homida, A.H., Sakrb, M.R., Mohamedc, A. -B. A., Abdel-Atyd, M., Obadae, A.-S.F.: Rashba control to minimize circuit cost of quantum fourier algorithm in ballistic nanowire. Phys. Lett. A 383, 1247 (2019)
Probst, S., Ranjan, V., Ansel, Q., Heeres, R., Albanese, B., Albertinale, E., Vion, D., Esteve, D., Glaser, S.J., Sugny, D., Bertet, P.: Shaped pulses for transient compensation in quantum-limited electron spin resonance spectroscopy. J Magn. Reson. 303, 42–47 (2019)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province under Grant No. 2021JQ-813 and the fund of Xianyang Normal University under Grant No. XSYK20010.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.L. and D.H. analyzed the theoretical framework. Z.X. and J.H. performed the numerical simulations under the supervision of J.L. All authors discussed the results and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, JF., Xin, ZX., Hu, JR. et al. Quantum Optimal Control for Pauli Operators Based on Spin-1/2 System. Int J Theor Phys 61, 268 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-022-05246-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-022-05246-z