Abstract
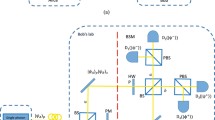
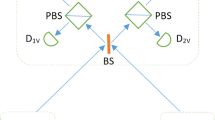
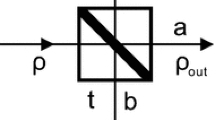
Quantum key agreement (QKA) is an important primitive of quantum cryptography and has attracted continuous attention. However, in practical QKA, the imperfections of the honest participant’s detectors can be exploited by the dishonest participant to compromise the security of QKA. To remove all the detector-side-channels, we report the first detector-device-independent (DDI) QKA(DDI-QKA) protocol based on single-photon Bell-state measurement. Only the time-bin and path encoding are needed. Complete Bell-state measurement can be achieved based on the time-bin and path encoding. It is shown that the proposed protocol satisfies three conditions of a secure QKA protocol in theory, i.e., correctness, fairness, and security. Furthermore, it is implemented with linear optical elements only and thus it is feasible with current technology.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennett, C. H., and Brassard, G.: Quantum cryptography: public key distribution and coin tossing. Proceed IEEE Int Conf Comput, Syst Signal Process, 175–179. IEEE, New York (1984)
Gisin, N., Ribordy, G., Tittel, W., Zbinden, H.: Quantum cryptography. Rev. Mod. Phys. 74, 145–195 (2002)
Diffie, W., Hellman, M.: New directions in cryptography. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory. 22, 644–654 (1976)
Zhou, N., Zeng, G., Xiong, J.: Quantum key agreement protocol. Electron. Lett. 40, 1149 (2004)
Naresh, V.S., Reddi, S.: Multiparty quantum key agreement with strong fairness property. Comput Syst Sci Eng. 35(6), 457–465 (2020)
Naresh, V.S., Nasralla, M.M., Reddi, S., García-Magariño, I.: Quantum Diffie-Hellman extended to dynamic quantum group key agreement for e-Healthcare multi-agent systems in smart cities. Sensors. 20(14), 3940 (2020)
Tsai, C., Hwang, T.: On Quantum Key Agreement Protocol. Technical Report, C-S-I-E, NCKU, Taiwan (2009)
Chong, S.K., Hwang, T.: Quantum key agreement protocol based on BB84. Opt. Commun. 283, 1192–1195 (2010)
He, Y.F., Ma, W.P.: Quantum key agreement protocols with four-qubit cluster states. Quantum Inf. Process. 14, 3483–3498 (2015)
He, Y.F., Ma, W.P.: Two-party quantum key agreement with five-particle entangled states. Int. J. Quantum Inf. 15(03), 1750018 (2017)
Zhu, H.F., Wang, C.N., Li, Z.X.: Semi-honest three-party mutual authentication quantum key agreement protocol based on GHZ-like state. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 60, 293–303 (2021)
Zhu, H.F., Liu, T.H., Wang, C.N.: A one-round quantum mutual authenticated key agreement protocol with semi-honest server using three-particle entangled states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 60, 929–943 (2021)
Huang, X., Zhang, S.-B., Chang, Y., Qiu, C., Liu, D.-M., Hou, M.: Quantum key agreement protocol based on quantum search algorithm. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 60, 838–847 (2021)
Shi, R.H., Zhong, H.: Multi-party quantum key agreement with bell states and bell measurements. Quantum Inf. Process. 12, 921–932 (2013)
Liu, B., Gao, F., Huang, W., Wen, Q.Y.: Multiparty quantum key agreement with single particles. Quantum Inf. Process. 12, 1797–1805 (2013)
Sun, Z., Huang, J., Wang, P.: Efficient multiparty quantum key agreement protocol based on commutative encryption. Quantum Inf. Process. 15(5), 2101–2111 (2016)
Mohajer, R., Eslami, Z.: Cryptanalysis of a multiparty quantum key agreement protocol based on commutative encryption. Quantum Inf. Process. 16(8), 197 (2017)
Wang, P., Sun, Z., Sun, X.: Multi-party quantum key agreement protocol Secure Against Collusion Attacks. Quantum Inf. Process. 16, 170 (2017)
Yang, Y.G., Li, B.R., Kang, S.Y., et al.: New quantum key agreement protocols based on cluster states. Quantum Inf. Process. 18, 77 (2019)
Zhou, N.-R., Zhu, K.-N., Wang, Y.-Q.: Three-party semi-quantum key agreement protocol. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 59, 663–676 (2020)
Tang, J., Shi, L., Wei, J.H.: Controlled quantum key agreement based on maximally three-qubit entangled states. Modern Phys Lett B. 34(18), 2050201 (2020)
Li, L., Li, Z.: A verifiable multiparty quantum key agreement based on bivariate polynomial. Inf. Sci. 521, 343–349 (2020)
Lin, S., Zhang, X., Guo, G.-D., Wang, L.-L., Liu, X.-F.: Multiparty quantum key agreement. Phys. Rev. A. 104, 042421 (2021)
Kwiat, P.G., Berglund, A.J., Altepeter, J.B., et al.: Science (New York, N.Y.). 290(5491), 498–501 (2000)
Huang, W., Wen, Q.Y., Liu, B., Gao, F., Sun, Y.: Quantum key agreement with EPR pairs and single particle measurements. Quantum Inf. Process. 13, 649–663 (2014)
Huang, W., Su, Q., Wu, X., Li, Y.B., Sun, Y.: Quantum key agreement against collective decoherence. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 53, 2891–2901 (2014)
He, Y.F., Ma, W.P.: Two robust quantum key agreement protocols based on logical GHz states. Mod. Phys. Lett. B31(3), 1750015 (2017)
Gao, H., Chen, X.G., Qian, S.R.: Two-party quantum key agreement protocols under collective noise channel. Quantum Inf. Process. 17, 140 (2018)
Wang, S.-S., Jiang, D.-H., Xu, G.-B., Zhang, Y.-H., Liang, X.-Q.: Quantum key agreement with Bell states and Cluster states under collective noise channels. Quantum Inf. Process. 18, 190 (2019)
Makarov, V.: Controlling passively quenched single photon detectors by bright light. New J. Phys. 11, 065003 (2009)
Lydersen, L., Wiechers, C., Wittmann, C., et al.: Hacking commercial quantum cryptography by tailored bright illumination. Nature Photon. 4(10), 686–689 (2010)
Lydersen, L., Wiechers, C., Wittmann, C., et al.: Thermal blinding of gated detectors in quantum cryptography. Opt. Exp. 18(26), 27938–27954 (2010)
Gerhardt, I., Liu, Q., Lamas-Linares, A., et al. Full-field implementation of a perfect eavesdropper on a quantum cryptography system. Nat. Commun. 2(1), 349(2011)
Qin, H., Kumar, R., Makarov, V., et al. Homodyne-detector-blinding attack in continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 98(1), 012312(2018)
Mayers, D., Yao, A.-C.: in Proceedings of the 39th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science (FOCS98) (IEEE Computer Society, Washington, DC, 1998) (1998)
Acín, A., Brunner, N., Gisin, N., Massar, S., Pironio, S., Scarani, V.: Device-independent security of quantum cryptography against collective attacks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 230501 (2007)
Lo, H.-K., Curty, M., Qi, B.: Measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 130503 (2012)
Liang, W.Y., Li, M., Yin, Z.Q., et al.: A simple implementation of quantum key distribution based on single-photon Bell-state measurement. Phys. Rev. A 92, 012319 (2015)
Qi, B.: Trustworthiness of detectors in quantum key distribution with untrusted detectors. Phys. Rev. A. 91, 020303(R) (2015)
Aharonov, D., Ta-Shma, A., Vazirani, U. V., and Yao, A. C.: Quantum bit escrow. Proceedings of the thirty-second annual ACM symposium on Theory of computing (ACM, 2000), pp.705–714
Zhao, L., Yin, Z., Wang, S., Chen, W., Chen, H., Guo, G., Han, Z.: Measurement-device-independent quantum coin flipping. Phys. Rev. A. 92, 062327 (2015)
Cabello, A.: Quantum key distribution in the Holevo limit. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 5635(2000)
Huang, W., Wen, Q.Y., Liu, B., Su, Q., Gao, F.: Cryptanalysis of a multi-party quantum key agreement protocol with single particles. Quantum Inf. Process. 13, 1651–1657 (2014)
Acknowledgments
We declare that we have no financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that can inappropriately influence our work, there is no professional or other personal interest of any nature or kind in any product, service and/or company that could be construed as influencing the position presented in, or the review of, the manuscript.
This work was supported by the Open Fund of Advanced Cryptography and System Security Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province (Grant No. SKLACSS-202104); the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 62071015, 62171264).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, YG., Lv, XL., Gao, S. et al. Detector-Device-Independent Quantum Key Agreement Based on Single-Photon Bell State Measurement. Int J Theor Phys 61, 50 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-022-05052-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-022-05052-7