Abstract
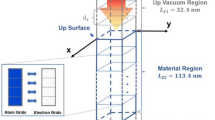
The interaction between the laser and material is commonly described by the macroscale method, two-temperature model (TTM), and the microscale method, molecular dynamics. In the present paper, the melting and resolidification of ultrashort laser interaction with thin gold film is investigated in terms of a meso-scale method. The lattice Boltzmann method (LBM) including the electron–phonon collision term is established. A fixed grid approach is applied in the phonon subsystem to describe the phase change. The transition zone between solid and liquid is treated as the porous medium. The results predicted by the LBM coincide with the experiment data quite well. In addition, the detailed comparisons between the TTM with interfacial tracking method and the LBM are conducted. The influences of the laser fluences and pulse widths on the transition phase are also investigated.










Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- a :
-
Thermal diffusion coefficient (m2·s−1)
- C :
-
Heat capacity (J·m−3·K−1)
- F :
-
External force (N)
- F l :
-
Liquid fraction
- G :
-
Electron–lattice coupling factor (W·m−3·K−1)
- h m :
-
Latent heat of melting (J·kg−1)
- J :
-
Heat source fluence of laser (J·m−2)
- k :
-
Electron wave vector (m−1)
- k B :
-
Boltzmann constant (J·K−1)
- L :
-
Thickness of gold film (m)
- M k, k′ :
-
Electron–phonon matrix element
- m :
-
Mass (kg)
- N :
-
Number density of atom (m−3)
- q :
-
Phonon wave vector (m−1)
- R :
-
Reflectivity of gold film
- R g :
-
Gas constant for gold (J·kg−1·K−1)
- S :
-
Heat source of unit volume (W·m−3)
- s :
-
Interfacial location (m)
- T :
-
Temperature (K)
- T l,I :
-
Interfacial temperature for lattices (K)
- t :
-
Time (s)
- t p :
-
Full width at half maximum (FWHM) pulse width (s)
- U :
-
Potential energy coefficient
- V :
-
Phase space
- v :
-
Velocity (m·s−1)
- w :
-
Weighting factor
- x :
-
Coordinate (m)
- δ :
-
Optical penetration depth (m)
- δ b :
-
Ballistic range (m)
- Δl :
-
Length of the transition zone (m)
- ɛ :
-
Energy (J)
- λ :
-
Thermal conductivity (W·m−1·K−1)
- ℏ:
-
Planck constant (J·s)
- ξ :
-
Radius of phase transition zone (K)
- ρ :
-
Density (kg·m−3)
- Γ :
-
Relaxation time for the collision between different particles (s)
- τ :
-
Relaxation time for the collision in the homogeneous particles (s)
- ω :
-
Frequency (s−1)
- Ω:
-
Collision term
- D:
-
Debye
- e:
-
Electron
- eq:
-
Thermal equilibrium state
- F:
-
Fermi
- i:
-
Initial
- I:
-
Interfacial
- l:
-
Lattice
- ph:
-
Phonon
- s:
-
Sound
References
P. Hannaford, Femtosecond Laser Spectroscopy (Springer, Berlin, 2005)
D. Bourell, M. Wohlert, N. Harlan, S. Das, J. Beaman, Adv. Eng. Mater. 4, 666 (2002)
W.N. Su, P. Erasenthiran, P.M. Dickens, P.I. Mech, Eng. C-J. Mec. 217, 127 (2003)
J. Huang, Y. Zhang, J.K. Chen, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 52, 3091 (2009)
A.K. Upadhyay, H.M. Urbassek, J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 40, 3518 (2007)
S.L. Anisimov, B.L. Kapeliovich, T.L. Perel’ man, Sov. Phys. JETP 39, 375 (1974)
T.Q. Qiu, C.L. Tien, ASME J. Heat Transf. 115, 835 (1993)
J.K. Chen, J.E. Beraun, Numer. Heat Transf. A 40, 1 (2001)
D.Y. Tzou, J. Heat Transf. 117, 8 (1995)
J.K. Chen, D.Y. Tzou, J.E. Beraun, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 49, 307 (2006)
I.H. Chowdhury, X. Xu, Numer. Heat Transf. A 44, 219 (2003)
C. Konrad, Y.W. Zhang, Y. Shi, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 50, 2236 (2007)
Y.W. Zhang, J.K. Chen, J. Appl. Phys. 104, 054910 (2008)
Y.W. Zhang, J.K. Chen, ASME J. Heat Transf. 130, 062401 (2008)
Y. Ren, J.K. Chen, Y. Zhang, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 55, 1620 (2012)
J. Huang, Y. Zhang, J.K. Chen, Appl. Phys. A 95, 643 (2009)
J. Huang, Y.W. Zhang, J.K. Chen, M. Yang, Front. Energy 6, 1 (2012)
Y. Ren, C.W. Cheng, J.K. Chen, Y. Zhang, D.Y. Tzou, Int. J. Therm. Sci. 70, 32 (2013)
Q. Peng, Y. Zhang, Y. He, Y. Mao, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 61, 675 (2013)
L. Zhou, L. Li, Appl. Phys. A 116, 2157 (2014)
Y. Yamashita, T. Yokomine, S. Ebara, A. Shimizu, Int. J. Thermophys. 27, 627 (2006)
L. Yang, Y. Gan, Y. Zhang, J.K. Chen, Appl. Phys. A 106, 725 (2012)
P. Ji, Y. Zhang, J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 46, 495108 (2013)
A.A. Mohamad, Lattice Boltzmann Method, Fundamentals and Engineering Applications with Computer Codes (Springer, London, 2011)
G. de Fabritiis, A. Mancini, D. Mansutti, S. Succi, Int. J. Mod. Phys. C Comput. Phys. Phys. Comput. 9, 1405 (1998)
W. Miller, J. Cryst. Growth 230, 263 (2001)
A.D. Brent, V.R. Voller, K.J. Reid, Numer. Heat Transf. 13, 297 (1988)
W. Miller, S. Succi, D. Mansutti, Phys. Rev. Lett. 86, 3578 (2001)
D. Chatterjee, S. Chakraborty, Phys. Lett. A 341, 320 (2005)
D. Chatterjee, S. Chakraborty, Phys. Lett. A 351, 359 (2006)
S.C. Mishra, N.C. Behera, A.K. Garg, A. Mishra, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 51, 4447 (2008)
C. Körner, E. Attar, P. Heinl, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 211, 978 (2011)
J. Zhao, P. Cheng, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 110, 94 (2017)
S.I. Anisimov, Proc. SPIE 2793, 192 (1997)
P.B. Allen, Phys. Rev. Lett. 59, 1460 (1987)
J.M. Ziman, Electrons and Phonons (Oxford Univ. Press, London, 1960)
M.I. Kaganov, I.M. Lifshitz, L.V. Tanatarov, Sov. Phys. JETP 4, 173 (1957)
J.K. Chen, W.P. Latham, J.E. Beraun, J. Laser Appl. 17, 63 (2005)
E.A. Semma, M.E. Ganaoui, R. Bennacer, C. R. Mecanique 335, 295 (2007)
S.D. Brorson, J.G. Fujimoto, E.P. Ippen, Phys. Rev. Lett. 59, 1962 (1987)
T. Juhasz, H.E. Elsayed-Ali, X.H. Hu, W.E. Bron, Phys. Rev. B 45, 13819 (1992)
B.C. Stuart, M.D. Feit, S. Herman, A.M. Rubenchik, B.W. Shore, M.D. Perry, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 13, 459 (1996)
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 51476102.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, L., Wu, M. & Zhou, L. Lattice Boltzmann Simulations for Melting and Resolidification of Ultrashort Laser Interaction with Thin Gold Film. Int J Thermophys 39, 88 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-018-2409-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-018-2409-9