Abstract
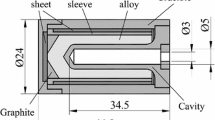
Metal carbon eutectic cells (high-temperature fixed points, HTFPs) (Machin in AIP Conf Proc 1552:305, 2013) are being considered for use as reliable high-temperature references for non-contact thermometry above the copper point (\(1084.62\,^{\circ }\hbox {C}\)). Recent studies have demonstrated the concept of using doped metal carbon eutectic cells as artefacts suitable for temperature scale comparisons (Teixeira et al. in AIP Conf Proc 1552:363, 2013; Teixeira et al. in Int J Thermophys 35:467–474, 2014; Machin et al. in Int J Thermophys 36:327–335, 2015). When using such artefacts, the participating institutes do not know the realization temperature of the doped HTFP cell, because it has been modified by the addition of a selected dopant at a definite concentration. The use of such fixed points can critically evaluate the real measurement capability of the institutes in any comparison. The pyrometry laboratory of Inmetro developed a set of doped Ni–C eutectic cells in 2012 and 2013. This paper describes the long-term stability of a Sn-doped Ni–C cell constructed in 2012, which accumulated more than 220 h above \(1300\,^{\circ }\hbox {C}\) amounting to more than 50 cycles of melts and freezes. The cell remained stable, well within the measurement uncertainty, throughout the evaluation period demonstrating the utility of such cells for scale comparison purposes.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Machin, Twelve years of high temperature fixed point research: a review. AIP Conf. Proc. 1552, 305 (2013)
R. Teixeira, G. Machin, A. Orlando, Towards the development of high temperature comparison artifacts for radiation thermometry. AIP Conf. Proc. 1552, 363 (2013)
R. Teixeira, G. Machin, A. Orlando, Development of high-temperature fixed points of unknown temperature suitable for key comparisons. Int. J. Thermophys. 35, 467–474 (2014)
G. Machin, R. Teixeira, X. Lu, D. Lowe, Bilateral comparison between NPL and INMETRO using a high-temperature fixed point of unknown temperature. Int. J. Thermophys. 36, 327–335 (2015)
M.J. de Groot, E.W.M. van der Ham, R. Monshouwer, CCT-K5: comparison of local realizations of the ITS-90 between the silver point and \(1700\,^{\circ }\text{C}\) using vacuum tungsten strip lamps as transfer standards, in Final ReportCCT-K5, BIPM (Sept 2008)
H.C. McEvoy, G. Machin, et al., Update on progress with the radiation thermometry key comparison CCT-K10, in Abstract Book of Tempmeko 16 (INTiBS, ISBN: 978-83-939559-7-8; 2016), p. 239
L. Kňazovická, D. Lowe, G. Machin, H. Davies, A. Rani, Stability of cobalt–carbon high temperature fixed points doped with iron and platinum. Metrologia 52, 353–359 (2015)
D. Lowe, G. Machin, Development of metal-carbon eutectic blackbody cavities to \(2500\,^{\circ }\text{ C }\) at NPL, in Tempmeko 01, The 8th International Symposium on Temperature and Thermal Measurements in Industry and Science, ed. by B. Fellmuth, J. Seidel, G. Scholz (VDE VERLAG GMBH, Berlin; 2002), pp. 519–524
J. Hartmann, K. Anhalt J. Hollandt, E. Schreiber, Y. Yamada, Improved thermal stability of the linear pyrometer LP3 for high temperature measurements within the EU-project Himert, in Temperatur 2003, vol. 1784 (VDI-Bericht, Berlin; 2003), pp. 135–141
D.H. Lowe, G. Machin, Evaluation of methods for characterising the melting curves of a high temperature cobalt–carbon fixed-point to define and determine its melting temperature. Metrologia 49, 189–199 (2012)
Acknowledgements
R. T. would like to thank the technicians of the pyrometry laboratory of Inmetro for all the support during the measurements and also for the development of the dedicated software in charge of the determination of the point of inflection and calculation of melting temperature.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Selected Papers of the 12th International Symposium on Temperature, Humidity, Moisture and Thermal Measurements in Industry and Science.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Teixeira, R.N., Machin, G. Long-Term Stability Evaluation of a Sn-Doped Ni–C Eutectic Cell Suitable for Radiation Thermometry. Int J Thermophys 38, 80 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-017-2205-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-017-2205-y