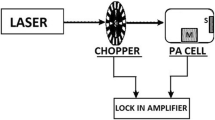
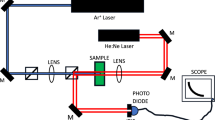
Abstract
Samples of a titanium–aluminum–vanadium alloy (Ti6Al4V) having different values of roughness are studied by photothermal radiometry. Among the numerous studies carried out on the influence of surface roughness on the photothermal signal, those that relate the air/substrate interfacial volume to an apparent homogeneous layer with effective thermal properties are considered. For such a system, a one-dimensional heat transfer model can successfully be used to describe the response to harmonic excitation up to high frequencies where the thermal diffusion length is of the order of magnitude as the roughness. The breakdown of the effective layer model at high frequencies has prompted some authors to develop more sophisticated methods to describe the complex phenomena encountered. In this study, it is proposed to keep the simple, effective layer model, but also to modify it by including an effective optical absorption coefficient and a reflection coefficient closely related to the surface characteristics. The effective layer becomes semitransparent to the excitation as it turns thermally thick (thickness/thermal diffusion length >1). The apparent thickness of the layer is shown to be directly related to the average difference between the maximum peak and the minimum trough of the surface profile and linearly correlated with the average roughness. This model can be used over a wide range of roughnesses.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Chirtoc, in Thermal Wave Physics and Related Photothermal Techniques: Basic Principles and Recent Developments, ed. by E. Martin (Transworld Research Network, Trivandrum, Kerala, 2009), chap. 2, pp. 29–63
Bein B., Krueger S., Pelzl J.: Can. J. Phys 64, 1208 (1986)
Garcia J.A., Mandelis A., Farahbakhsh B., Lebowitz C., Harris I.: Int. J. Thermophys. 20, 1587 (1999)
Walther H.G.: J. Appl. Phys. 89, 2939 (2001)
Walther H.G., Larciprete M.C., Mayr P., Paoloni S., Schmitz B.: Anal. Sci. 17, 428 (2001)
Walther H.G.: Appl. Surf. Sci. 193, 156 (2002)
Garcia J.A., Nicolaides L., Park P., Mandelis A., Farahkbahsh B.: Anal. Sci. 17, 89 (2001)
Nicolaides L., Mandelis A.: J. Appl. Phys. 90, 1255 (2001)
Nicolaides L., Mandelis A., Beingessner C.J.: Anal. Sci. 17, 383 (2001)
Drevet R., Velard F., Potiron S., Laurent-Maquin D., Benhayoune H.: J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 22, 753 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Antoniow, J.S., Chirtoc, M., Drevet, R. et al. A Simple Method to Assess Surface Roughness by Photothermal Investigation (PTR) Using an Effective Semitransparent Layer. Int J Thermophys 33, 1960–1965 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-012-1287-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-012-1287-9