Abstract
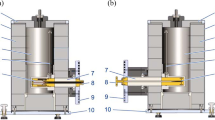
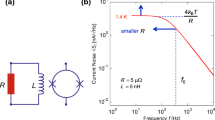
Technical advances and new results in noise thermometry at temperatures near the tin freezing point and the zinc freezing point using a quantized voltage noise source (QVNS) are reported. The temperatures are derived by comparing the power spectral density of QVNS synthesized noise with that of Johnson noise from a known resistance at both 505 K and 693 K. Reference noise is digitally synthesized so that the average power spectra of the QVNS match those of the thermal noise, resulting in ratios of power spectra close to unity in the low-frequency limit. Three-parameter models are used to account for differences in impedance-related time constants in the spectra. Direct comparison of noise temperatures to the International Temperature Scale of 1990 (ITS-90) is achieved in a comparison furnace with standard platinum resistance thermometers. The observed noise temperatures determined by operating the noise thermometer in both absolute and relative modes, and related statistics together with estimated uncertainties are reported. The relative noise thermometry results are combined with results from other thermodynamic determinations at temperatures near the tin freezing point to calculate a value of T − T 90 = +4(18) mK for temperatures near the zinc freezing point. These latest results achieve a lower uncertainty than that of our earlier efforts. The present value of T − T 90 is compared to other published determinations from noise thermometry and other methods.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benz S.P., Qu J.F., Rogalla H., White D.R., Dresselhaus P.D., Tew W.L., Nam S.W.: IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 58, 884 (2009)
Tew W.L., Labenski J.R., Nam S.W., Benz S.P., Dresselhaus P.D., Burroughs C.J.: Int. J. Thermophys. 28, 629 (2007)
Labenski J.R., Tew W.L., Benz S.P., Nam S.W., Dresselhaus P.: Int. J. Thermophys. 29, 1 (2008)
Benz S.P., Martinis J.M., Dresselhaus P.D., Nam S.W.: IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 52, 545 (2003)
Benz S.P., White D.R., Qu J.F., Rogalla H., Tew W.L.: C.R. Phys. 10, 849 (2009)
White D.R., Benz S.P., Labenski J.R., Nam S.W., Qu J.F., Rogalla H., Tew W.L.: Metrologia 45, 395 (2008)
S.P. Benz, J.M. Martinis, S.W. Nam, W.L. Tew, D.R. White, in Proceedings of TEMPMEKO 2001, 8th International Symposium on Temperature and Thermal Measurements in Industry and Science, ed. by B. Fellmuth, J. Seidel, G. Scholz (VDE Verlag, Berlin, 2002), pp. 37–44
White D.R., Benz S.P.: Metrologia 45, 93 (2008)
Labenski J.R., Tew W.L., Nam S.W., Benz S.P., Dresselhaus P.D., Burroughs C.J.: IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 56, 481 (2007)
White D.R., Zimmermann E.: Metrologia 37, 11 (2000)
S.W. Nam, S.P. Benz, J.M. Martinis, P. Dresselhaus, W.L. Tew, D.R. White, in Temperature: Its Measurement and Control in Science and Industry, vol. 7, ed. by D.C. Ripple (AIP, Chicago, 2003), pp. 37–42
B.W Mangum, G.T. Furukawa, Guidelines for Realizing the International Temperature Scale of 1990 (ITS-90) (U.S. Department of Commerce, National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg, 1990)
Benz S.P., Hamilton C.A.: Appl. Phys. Lett. 68, 3171 (1996)
Qu J.F., Benz S.P., Rogalla H., White D.R.: Metrologia 46, 512 (2009)
Nam S.W., Benz S.P., Dresselhaus P.D., Tew W.L., White D.R., Martinis J.M.: IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 52, 550 (2003)
G.F. Strouse, D.R. Defibaugh, M.R. Moldover, and D.C. Ripple, in Temperature: Its Measurement and Control in Science and Industry, vol. 7, ed. by D.C. Ripple (AIP, Chicago, 2003), pp. 31–36
Mohr P.J., Taylor B.N., Newell D.B.: Rev. Mod. Phys. 80, 633 (2008)
D.R. Taubert, J. Hartmann, J. Hollandt, J. Fischer, in Temperature: Its Measurement and Control in Science and Industry, vol. 7, ed. by D.C. Ripple (AIP, Chicago, 2003), pp. 7–12
Noulkow N., Taubert R., Meindl P., Hollandt J.: Int. J. Thermophys. 30, 131 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tew, W.L., Benz, S.P., Dresselhaus, P.D. et al. Progress in Noise Thermometry at 505 K and 693 K Using Quantized Voltage Noise Ratio Spectra. Int J Thermophys 31, 1719–1738 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-010-0830-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-010-0830-9