Abstract
Primates often consume either bark or cambium (inner bark) as a fallback food to complete their diet during periods of food scarcity. Wild chimpanzees exhibit great behavioral diversity across Africa, as studies of new populations frequently reveal. Since 2014, we have been using a combination of camera traps and indirect signs to study the ecology and behavior of wild chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes verus) in Comoé National Park, Ivory Coast, to document and understand the behavioral adaptations that help them to survive in a savanna–forest mosaic landscape. We found that Comoé chimpanzees peel the bark of the buttresses of kapok tree (Ceiba pentandra) trees to eat the cambium underneath. Individuals of all sex/age classes across at least six neighboring communities peeled the bark, but only during the late rainy season and beginning of the dry season, when cambium may represent an important fallback food. Baboons (Papio anubis) also target the same trees but mainly eat the bark itself. Most of the bark-peeling wounds on Ceiba trees healed completely within 2 years, seemingly without any permanent damage. We recorded chimpanzees visiting trees in early stages of wound recovery but leaving them unpeeled. Only 6% of peeled trees (N = 53) were reexploited after a year, suggesting that chimpanzees waited for the rest of the trees to regrow the bark fully before peeling them again, thus using them sustainably. Many human groups of hunter-gatherers and herders exploited cambium sustainably in the past. The observation that similar sustainable bark-peeling behavior evolved in both chimpanzees and humans suggests that it has an important adaptive value in harsh environments when other food sources become seasonally scarce, by avoiding the depletion of the resource and keeping it available for periods of scarcity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
The consumption of bark or cambium (also called “inner bark,” the living wood immediately below the bark through which the sap flows) has been described in different climates and habitats and for many mammal species, including brown bears (Ursus arctos) in Siberia (Seryodkin et al. 2017), several ungulate species in Europe (Feher et al. 2016), and African elephants (Loxodonta africana) in Uganda and Benin (Kassa et al. 2013; Ssali et al. 2012). In many of these examples, massive extraction of the bark or cambium, all around the trunk, permanently damages the trees and it is more commonly called bark-stripping, an unsustainable practice that often causes the death of the stripped tree.
Primates, including species of Lemuridae, Indridae, Cercopithecidae, Pongidae, and Hominidae, have long been known to peel and consume the bark and cambium of woody plants (Nishida 1976) and, more recently, capuchin monkeys (Cebus capucinus, Sapajus nigritus) were also found to peel bark in Central and South America (Hanson 2007; Mikisch and Liebsch 2014). Guenons (Cercopithecus mitis: Beeson 1987), barbary macaques (Macaca sulvanus:, Camperio-Ciani et al. 2001; Van Lavieren and Wich 2009), and chacma baboons (Papio ursinus: Bigalke and Hensbergen 2010; Katsvanga et al. 2009) unsustainably strip the bark of conifers in forestry plantations and are therefore considered pest species in human-dominated African landscapes. Among the great apes, bark is an important fallback food for both orangutans (Pongo abelli:, Campbell et al. 2011) and gorillas (Gorilla gorilla:, Rogers et al. 1994).
Eastern chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes schweinfurtii) in Gombe (Goodall 1968) and Issa Valley, Ugalla (Russak 2013), both in Tanzania, consume the cambium of Brachystegia bussei and other unidentified species, by cutting the bark with their teeth, then pulling large strips of bark away from the tree with their hands and scraping the bark transversely with their teeth. At Mahale, Tanzania, chimpanzees consume the bark and especially the cambium of 31 different tree species in the late rainy season as a response to fruit scarcity (Nishida 1976; Nishisa and Uehara 1983). In contrast, central chimpanzees (P. t. troglodytes) consume little bark or cambium and, in Loango, Gabon, they consume none, although sympatric gorillas consume cambium (Head et al. 2011). Western chimpanzees (P. t. verus) consume the bark or cambium of at least five woody species in Fongoli and four in Mt. Assirik, both dry savanna–woodland mosaics in Senegal (McGrew et al. 1988; Pruetz 2006), and consume 11 different species in the forest habitat of Bossou, Guinea (Matsuzawa et al. 2011). In the dry savanna–woodland of Bafing, Mali, chimpanzees eat the inner bark of Pterocarpus erinaceus and probably that of three additional species (Duvall 2008). Chimpanzees inhabiting Canthanhez National Park, Guinea Bissau, consume the fruits, flowers, and bark of Ceiba pentandra (Bessa et al. 2015), but the authors do not indicate whether chimpanzees eat the inner or outer bark and did not describe how the chimpanzees stripped the bark. Very recently (November 2019), chimpanzees of Fongoli, Senegal, were observed peeling the bark and eating the cambium of two trees of Ceiba pentandra (J. Pruetz pers. comm.).
The bark-peeling behavior exhibited by great apes could also have been present in fossil members of the Hominidae family. Evidence from microwear traces and isotopes found in the dental calculus of Australopithecus sediba have been interpreted as a sign of a diet that included bark or wood, in a similar proportion to the present chimpanzees inhabiting savanna–woodland mosaics (Henry et al. 2012) although we cannot know the technique this australopithecine used to forage on these hard foods. Traditional human bark-peeling is carried out with specific tools that resemble paleolithic tools made by Neanderthals, leading some authors to speculate that Neanderthals (Homo neanderthalensis) practiced bark-peeling and consumption of cambium of different tree species, identified from paleo-pollen (Sandgathe and Hayden 2003).
Modern human (Homo sapiens) hunter-gatherers, such as the indigenous peoples of North America from the Yukon to New Mexico (e.g., Blackfeet, Carrier, Gitskan, Kootenais, Okanagan-Colville peoples), and traditional herders such as the Saami people in Northern Europe, have peeled conifers, birches, poplars, or elm trees in a sustainable way. These humans peeled only one side of the tree, not cutting the sap flow to the rest, and allowed the bark to regrow fully before reexploiting it. Thus, they avoided killing the trees, to have a reliable source of cambium during famine periods (Niklasson et al. 1994; Ostlund et al. 2009; Prince 2001). This sustainable bark-peeling has been carried out across thousands of years, leaving permanent traces on culturally modified trees, as demonstrated through dendrochronology and archaeobotany (Niklasson et al. 1994; Ostlund et al. 2009; Prince 2001). However, the sustainable harvest of cambium these authors define for humans has not been described for other primates.
Western chimpanzees are the most threatened subspecies of chimpanzee (IUCN: Critically Endangered, A4bcd, Humle et al. 2016). Their populations have declined by 80% overall and by 90% in Ivory Coast (Campbell et al., 2008; Kühl et al. 2017). The wild chimpanzees in Comoé National Park had been censused (Campbell et al., 2008; Hoppe Dominik 1991; Marchesi et al. 1995; WCF 2014, unpubl. report), but not otherwise studied, before we started our project in October 2014. This chimpanzee population inhabits a savanna–forest mosaic habitat in the southwest portion of the park and shows behaviors that have not been described in other populations, such as dipping for water with especially long brush-tipped stick tools (Lapuente et al. 2016). These behaviors could provide the chimpanzees with an adaptive advantage over other animals in using the scarce resources of their dry and harsh environment. They also exhibit a variant of the behavior recently described as accumulative stone throwing (Kühl et al. 2016). Better knowledge of the behaviors Comoé chimpanzees use to overcome the difficult ecological conditions of their environment gives us insight into the behavioral flexibility and adaptability of savanna chimpanzees, similarly to other adaptive behaviors observed in savanna in Kharakhena, Senegal (Boyer Ontl and Pruetz, in press) and Issa, Tanzania (Hernandez and Reitan, in press).
Peeling of Ceiba pentandra bark has been mentioned (Bessa et al. 2015), but not described in detail for humans or apes. In October 2014, when we started our research on Comoé chimpanzees, we found hundreds of long traces (50–150 cm) of bark-peeling on Ceiba pentandra buttresses across our study area in the southwest of the park. The traces suggested that the outer bark was peeled in long stripes and then the inner bark or cambium was scraped from the wounds. Traces appeared to be especially concentrated in areas with abundant footprints, dung, or direct observations of chimpanzees. In addition, elephants (Loxodonta cyclotis), monkeys (Papio anubis, Cercocebus lunulatus, Chlorocebus sabaeus, Cercopithecus lowei, Cercopithecus petaurista, Procolobus verus), and humans were also present in the area and might have been responsible for these traces. We initiated this study of the bark peeling in Comoé National Park with the following questions in mind:
-
Question 1: Given that the bark-peeling traces were concentrated in the activity hot spots of chimpanzees and frequently associated with chimpanzee signs and that chimpanzees are known to strip the bark of other tree species, do chimpanzees peel Ceiba pentandra bark?
-
Question 2: Given that the bark-peeling wounds were marked with cuts and scratches that had the aspect of teeth and nail marks, but sometimes looked like they were made with tools, is the bark removed to eat the cambium using teeth, hands or tools?
-
Question 3: Considering that we found many bark-peeling traces on medium sized Ceiba pentandra trees after the rainy season of our first year of study, is the bark peeled selectively on trees of a limited range of sizes, of a preferred species and during a particular season?
-
Question 4: Assuming that chimpanzees produce the bark peeling traces and considering that these animals are social and all sex/age classes forage on the same types of food resources, do individuals of all sex/age classes peel the bark of Ceiba pentandra?
-
Question 5: Considering that the bark-peeling traces consistently appeared in distant areas occupied by different chimpanzee communities, is the behavior widespread and not limited to a particular community?
-
Question 6: Assuming that the Ceiba pentandra tree can heal after bark-peeling, that the tree growth is not reduced or its health affected, and that the animals wait for the wounds to regrow completely before peeling the bark again, is the repeated reexploitation of the resource sustainable?
Methods
Study Site
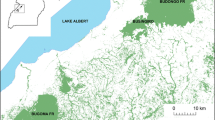
At more than 11,400 km2, Comoé National Park is the largest protected area in Ivory Coast and one of the biggest in West Africa (Fig. 1). It is characterized by savanna–woodland mosaic habitat, with 9% forest habitats that are more concentrated in the southern half of the park (Mühlenberg et al.1990). It is classified as a very open and dry landscape for chimpanzees, overall (van Leeuwen et al. 2020). The chimpanzees mainly use gallery forest, along the rivers, and forest islands, not linked to watercourses but growing on plateaus along the interfluvia (Lapuente et al. 2016; Mühlenberg et al.1990). The Comoé River crosses the park from north to south and gives its name to the park. The climate is dry and warm with a mean annual temperature of 27°C and precipitation ca. 1090 mm (Hennenberg, 2005) although in our study site, in the southwestern corner of the park, a mean of 1010 mm was measured from 1993 to 2000 (Fischer et al. 2002) and 1014 mm during our study, from October 2014 to December 2017. The dry season lasts from the end of October to the end of April, with some scattered rainstorms, while the rainy season lasts from May to October, with the highest precipitation in May and September (Fig. 2). Our study area of 900 km2 in the southwestern corner of the park is the driest portion of the park and has the highest percentage of forest cover (22%).
Forested habitats used by chimpanzees in our study area can be divided into five main types: two types of gallery forests (semideciduous, dominated by Cynometra megalophylla, and deciduous) and three types of forest island (deciduous, semideciduous, and liana-dominated). Ceiba pentandra grows in all of them (Hennenberg 2005; Mühlenberg et al. 1990).
Ceiba pentandra (kapok tree, cotton tree, or ceiba) is a tree in the family Malvaceae, subfamily Bombacoideae. It is native to South and Central America and tropical West and Central Africa, where it has grown since the Pleistocene (Dick et al. 2007; Maley and Livingstone, 1983). It can reach >70 m tall (Dick et al. 2007) and >3 m in diameter with fast growth of up to 2 cm in diameter per year (Lapuente and Linsenmair, pers. obs.). The tree is usually sustained by big tabular roots or buttresses that can be >5 m high and wide (Lapuente and Linsenmair, pers. obs.). Young trees are protected by big conical thorns and upper branches are always protected by abundant thorns.
Ceiba pentandra is common in Ivory Coast, where it is found across all forested habitats, from rainforest to savanna–woodland (Lauginie 2007). In Comoé, it is the biggest tree, emerging from the canopy of both forest-islands and gallery forest. In this region of Northern Ivory Coast, humans traditionally used the wood of medium sized Ceiba pentandra trees to make canoes, but never cut older trees, which were formerly revered, and presented with offerings of pottery or votive stone axes, since they were thought to contain spirits (local elders, pers. comm.). People used the cotton that surrounds the seeds to fill mattresses and pillows and the ash from the wood to make soap. People still cook and eat the leaves (local elders, pers. comm.). They occasionally harvest bark for medicinal purposes, like in other parts of West Africa and abroad, since it is locally believed to be effective as an antidiabetic, antidiarrheic, antibiotic, and analgesic, and to treat other ailments (Djomeni et al. 2006; Ueda et al. 2002).
Chimpanzees consume different parts of Ceiba pentandra trees across West Africa, including flowers and unripe fruits in Fongoli, Senegal (Lindshield 2014; Pruetz 2006); leaves, fruits, and seeds in Mt. Assirik, Senegal (Luchterhand et al. 1982; McGrew et al. 1988); young leaves and flowers in Bossou, Guinea (Matsuzawa et al. 2011); and fruits and flowers in Tenkere, Sierra Leone (Alp 1997). Although Ceiba species is available, chimpanzees in Mahale, Tanzania have not been observed to consume any of its parts in 50 years of research (Nakamura et al. 2015). West African chimpanzees use tools to aid foraging on Ceiba pentandra. Chimpanzees in Tenkere, Sierra Leone, use sticks to protect their feet or as seats while eating fruits and flowers on the spiny branches of Ceiba pentandra trees (Alp 1997). Adult male chimpanzees in Bossou, Guinea, crack Ceiba pentandra branches and strip them of the spiny bark to make hook-shaped tools that they use to reach fruits from a fig tree (Sugiyama and Koman 1979).
Data Collection
We sampled the home ranges of four chimpanzee communities in our study area (Odissey, Aeneid, Achean, and Trojan; Lapuente et al. 2016) monthly, from October 2014 to December 2017, completing a minimum of 40 km of transects and reconnaissance surveys across a different chimpanzee home range every week. We studied the Aeneid, Achean, and Trojan home ranges in collaboration with the Pan African Programme: The Cultured Chimpanzee, of the Primatology Department of Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology, MPI-EVA (Vaidyanathan 2011) from October 2015 to May 2017. We also sampled two more home ranges less intensely in the northern and western extremes of our 900 km2 study area, which we visited once in February 2015 and four times during the dry season of 2016–17. Along the transects and reconnaissance surveys we recorded all direct and indirect observations of chimpanzees, such as bark-peeling traces, nests, feeding signs, footprints, tool use sites, vocalizations, and dung. For each observation, we recorded the date, time, habitat type, and GPS coordinates. For all bark-peeling traces detected on Ceiba pentandra along these surveys, we recorded the diameter of the tree trunk above the buttresses, the percentage of the canopy covered by leaves, flowers, or fruits, the number of peeling traces or cuts and their relative age. Since we did not know the real age of the traces when we started our study, we classified them into four categories: stage 1, when they appeared fresh or very recent done, with a wet wound and no signs of bark regrowth; stage 2, when the wound was completely dry and the surrounding bark had started to grow and cover it; stage 3, when the bark regrowth had completely sealed the wound but the bark was still young, green and thin and wound edges were still visible and sharp; and stage 4, when the wound was covered in old thick grey bark and the wound edges were also old and covered by bark regrowth (Fig. 3). From January 2015 to December 2017, we recorded both peeled and intact C. pentandra trees along transects and reconnaissance surveys and measured the above-buttress diameter of intact trees. For trees that were impossible to measure directly due to gigantic buttresses that we could not climb, we took photos with a measuring tape as a reference to estimate the diameter of the bole above the buttresses.
Stages of recovery of the bark after bark-peeling on Ceiba pentandra buttresses in Come National Park, Ivory Coast. 1, Freshly peeled buttress, wet with sap and unoxidized, with long strips of hanging bark. 2, Traces already dry with edges of new bark forming. 3, New bark has almost completely covered the wound, but it is not yet sealed and the bark is still green and thin in places. 4, Thick, old bark completely sealing the wound and of the same color as the rest of the buttresses but with the characteristic appearance of several parallel protruding deformations of the spine.
To obtain the density and basal area of the trees in the area, we placed 405 square habitat plots of 400 m2 along regular transects across forest patches in the home ranges of chimpanzees living both sides of the Comoé River, 205 plots west and 200 east of the river. Within the plots, we counted and identified all trees above 10 cm in diameter at breast height (DBH), obtaining the corresponding densities per species. We calculated basal area was in m2/ha applying the formula
(Arandjelovic et al. 2011).
In parallel to the reconnaissance survey and transect sampling, we systematically placed camera traps across our study area in forest habitats using a grid with 1 km2 cells as sampling units within which we selected chimpanzee activity hot-spots (Lapuente et al. 2016; Vaidyanathan 2011). From October 2014 to October 2015, we used 20 Bushnell HD trophy cams (model 119437). From October 2015 to May 2017, we added 60 cameras Bushnell HD Aggressor. From May 2017 to December 2017, we continued our study with 30 cameras, of which 12 were Browning SPEC-OPS and the rest were Bushnell HD trophy cams. We programmed all cameras to record 1-minute videos. Cameras were motion triggered with a passive infrared (PIR) sensor. When the light was insufficient to record color videos, cameras recorded infrared black-and-white videos. We used the cameras to record chimpanzee behavior, tool use, and habitat use, and to identify individuals. To confirm the identification, we used double blind recognition: two trained biologists (JL and P. C. Köster) independently identified 86 chimpanzees from six different communities from 2090 videos, by observing individual characteristics such as face and body features, scars, missing ears, and balding patterns. We tested the reliability of identifications with Cohen’s κ coefficient to measure the percentage of coincidence between independent identification by the two trained biologists (Head et al. 2011; Lapuente et al. 2016). We determined community structure and the limits of home ranges by observing consistent associations between individuals and their ranging patterns with camera traps distributed across the study area. Once we knew the forest patches that each community occupied, we used the minimum convex polygon method to estimate the minimum home range for each community (Head et al. 2011; Lapuente et al. 2016).
From November 15, 2014, we detected bark-peeling traces close to chimpanzee traces such as nests, footprints, and dung. To determine the species producing the traces and the techniques used, we monitored affected trees with camera traps. From November 2014 to December 2017, we monitored 65 different bark-peeling sites with camera traps, of which we monitored three trees for the entire sampling period, 12 for two full consecutive bark-peeling seasons and the remaining 40 trees for one of the three seasons. We measured or estimated the diameter above the buttresses of 1469 of these trees (708 with bark-peeling traces and 761 untouched) to compare the mean diameter between these three classes.
When we recorded videos of bark-peeling activity, we measured the length, width, and depth of traces and the direction of the cuts with respect to the buttress spine.
To test if the bark-peeling effects hampered the growth of Ceiba pentandra trees, we selected 20 trees with recent bark-peeling traces and 20 untouched trees of similar initial diameters (60–110 cm). We measured the bole above the buttresses in October 2015 and again in October 2017.
To test if bark thickness increased with the age of the trees, we cut 2 cm × 2 cm of bark from the spine of unpeeled buttresses from 31 trees of different sizes and measured the bark thickness in mm with a gauge. We also measured the thickness of the regrown bark over 10 bark-peeling traces of stage 3 wounds, using the same method, to test whether the regrown bark was thicker or thinner than the uncut bark.
To determine how long the tree bark took to attain stage 4 of recovery, we selected a small buttress with traces of repeated peeling, including stage 4 traces and cut it transversely to take a sample that included the whole bark-peeling history of the buttress. After polishing it, we counted the annual growth rings (Niklasson et al. 1994; Ostlund et al. 2009; Prince 2001). Dendrochronology has been successfully applied to savanna trees (Daniellia olivieri) and forest trees (Anogeissus leiocarpus, Diospyros abyssinica) in Comoé National Park (Schongart et al. 2006), but not to Ceiba pentandra. However, other authors have used growth rings in a very close Neotropical species, Ceiba speciosa, for dendrochronology and dendroclimatology (Vasconcellosa et al. 2019) and Ceiba pentandra growth rings are prominent (Duvall 2011). Nevertheless, our method should be validated by further studies in Comoé.
Video Recordings of Bark-Peeling Behavior
In videos that recorded animals peeling Ceiba pentandra bark, we defined a bark-peeling event as the period in which a single individual animal continuously peeled bark and ate it at the same location and on the same day. If the same individual left the location and returned the next day to peel the same tree, we counted it as a new bark-peeling event. If several individuals were peeling bark at the same time and location, we recorded each of them individually, as separate events, to compare the technique and time invested among different species and age/sex classes.
For each individual bark-peeling event, we noted the species peeling the bark and its age/sex class, distinguishing infants, juveniles, adolescents, and adults (Goodall 1968) and the duration of the event in seconds. We also counted the number of cuts made on the bark with the teeth, whether the animals pulled the bark off with their teeth or hands, whether the animals consumed the bark itself or the cambium, the number of scrapes made on the cambium, whether the scrapes were made with teeth or fingernails, and whether the scrapes were made perpendicular or longitudinal with respect to the spine of the buttress. We estimated the length of cuts from the videos and measured most of them afterwards if no later cut had been made on the same spot.
Data Analysis
We used R-studio software (R Core Team 2018) for all statistical analysis. We tested for significant differences between means using Wilcoxon–Mann–Whitney U-test because our data had a nonparametric distribution. Specifically, we tested for interspecific or intraspecific differences in the duration of bark-peeling events, number of cuts, cut length, number of times per event that chimpanzees and baboons used their hands or teeth to pull out bark from the cut, number of times per event that each species scraped the cambium longitudinally or transversely from the cut with their teeth, and number of times that chimpanzees used their nails to scrape cambium per event. We also used U-test for interspecific (chimpanzee–baboon) differences for the technique used, if they used hands or teeth to pull the bark and if they made longitudinal or transversal scraping with teeth or fingernails. We applied Pearson’s correlation to test the relationship between the thickness of the bark on the spine of the buttress of Ceiba pentandra trees and the diameter of the bole above the buttresses. We analyzed geographic and GPS data in Quantum GIS.
Ethical Note
We used noninvasive techniques for this study, including camera traps and indirect signs, to avoid causing any unnecessary stress or harm to the wild chimpanzees. We took hygienic and security measures to avoid putting animals at risk (Arandjelovic et al. 2011) and all undertook data collection under the supervision of park managers, respecting the rules of the park, the laws of Ivory Coast, and international laws on endangered species. We obtained all necessary research permits. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are not publicly available due to the conservation measures for the protection of this critically endangered population of Western chimpanzees but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Results
Ceiba pentandra Density and Basal Area
We found that Ceiba pentandra grows in our study area at a mean density of 178.4 ± 33.2 trees/km2, with a mean basal area of 3 ± 0.3 m2/ha.
Animal Species Recorded in Videos
Between October 2014 and December 2017, we recorded 8112 camera days, while monitoring Ceiba pentandra bark-peeling sites (with one camera day being 24 h of continuous monitoring by one camera). We recorded 12,234 videos in which 44 species of mammals were present, including 8 species of primates (Pan troglodytes verus, Papio anubis, Cercocebus lunulatus, Chlorocebus sabaeus, Cercopithecus lowei, Cercopithecus petaurista, Procolobus verus, Galago senegalensis); 7 species of rodents (Histrix cristata, Atherurus africanus, Thrionomys swinderianus, Cricetomys gambianus, Funisciurus pyrropus, Heliosciurus rufobrachium, Protoxerus stangeri); 12 species of bovids (Syncerus caffer, Tragelaphus euryceros, T. scriptus, Cephalophus sylvicultor, C. niger, C. dorsalis, C. rufilatus, Philantomba maxwelli, Kobus ellipsiprymnus, K. kob, Hippotragus equinus, Alcelaphus bulselaphus); 10 species of small and medium-sized carnivores (Crossarchus obscurus, Ichneumia albicauda, Atilax paludinosus, Herpestes ichneumon, Genetta genetta, G. thyerri, Mellivora capensis, Profelis aurata, Civettictis civetta, Canis adustus); 2 species of big carnivores (Panthera pardus, Crocuta crocuta), pangolins (Manis tricuspis, M. tetradactyla), ardvaarks (Orycteropus afer), hippopotamuses (Hippopotamus amphibius), and elephants (Loxodonta cyclotis); and 3 species of hogs (Hilochoerus meinertzeghani, Potamochoerus porcus, and Phacochoerus africanus).
Animal Species That Peel Ceiba pentandra Bark
After more than 3 years monitoring the trees, the only species we recorded peeling bark on Ceiba pentandra were chimpanzees and baboons. Both chimpanzees and baboons peeled long stripes of bark of Ceiba pentandra, but while the baboons consumed mainly the bark itself (N = 29 bark only consumption, 6 = cambium consumption), the chimpanzees always left the bark aside to consume the exposed cambium (N = 38). Of all the remaining species of mammals, only two more primates and two rodent species showed interest in C. pentandra bark. Guenons (Cercopithecus lowei and C. petaurista), giant pouched rats (Cricetomys gambianus), and squirrels (Funisciurus pyrropus) bit small round portions of bark (<4 cm in diameter) from the thinner parts previously peeled by chimpanzees or baboons, at stages 2 and 3 of healing.
We recorded 54 videos of baboons and 130 videos of chimpanzees peeling the Ceiba pentandra bark between August and November 2016, representing 35 events for the baboons and 38 for the chimpanzees. We recorded these videos at 14 different sites across the home-ranges of four communities of chimpanzees (Lapuente et al. 2016). Both baboons and chimpanzees peeled the bark of the same tree at only 2 of the 14 sites and at different times during the same season, with baboons always peeling the bark first and chimpanzees doing so 2 and 3 weeks later. Of the remaining 12 bark-peeling sites, 4 were used exclusively by baboons and 8 exclusively by chimpanzees. We recorded chimpanzees of all age/sex classes peeling the bark. We never recorded adult female baboons peeling bark but adolescent and juvenile females and male baboons of all ages did peel bark (Table I).
For infants, we did not consider the length of the cut because they always used the cuts previously made by the adults. We found no significant interspecific or intraspecific differences for the duration of the event (Mann–Whitney U, P > 0.05, Electronic Supplementary Material [ESM] Table SI), except for juvenile baboons, which is much shorter than for adult chimpanzee males (W = 131.5, P = 0.025) and adult chimpanzee females (W = 192.5, P = 0.031). When comparing number of cuts, we found no significant interspecific or intraspecific differences (Mann-Whitney U, P > 0.05, ESM Table SII), while for cut length, we found significant differences only when comparing adult chimpanzee males, which made significantly longer cuts than juvenile chimpanzees (W = 18, P = 0.035) and juvenile baboons (W = 51, P = 0.004) (ESM Table SIII). However, the mean duration of bark-peeling events in adult chimpanzees was twice that in adult baboons, and the mean length of the cuts was also greater in chimpanzees than in baboons (Table I).
Technique Used to Peel Bark
To start the cut, both species used their canines, but while baboons bit small portions of bark from different parts of the buttress spine, chimpanzees always made a transverse first cut of several centimeters in the upper part and pulled to tear a long stripe of bark using their hands or teeth, exposing the cambium underneath (Table II). After this initial cut, chimpanzees continued pulling pieces of bark either with their hands (22 of 38 events) or their teeth (16 of 38 events). The chimpanzees used their hands to pull the bark significantly more often than baboons did (W = 462.5, P = 0.003). The chimpanzees were the only ones that used their fingernails to scrape the cambium exposed, and while there was no significant difference between the use of fingernails and the transversal teeth scraping (W = 654, P = 0.05271), they scraped significantly more longitudinally with teeth than with fingernails (W = 1265, P = 1.623e-05). Chimpanzees scraped the cambium with teeth significantly more longitudinally than transversely (W = 1427.5, P = 2.034e-10). On the other hand, baboons scraped significantly more transversely than longitudinally (W = 169, P = 3.252e-09) (ESM Table SIV, videos 1 and 2).
Once the cut was open, the baboons left the bark torn into small pieces around the buttress, while the chimpanzees left long strips rolled at the base of the buttress or lying around the tree (Figs. 4 and 5). The two species consumed the exposed cambium in different ways. While the baboons scraped exclusively with their teeth, the chimpanzees always used both their fingernails and teeth. Most of the scraping made by baboons was transverse to the spine of the buttress (93.2%, N = 689), while the chimpanzees scraped mostly longitudinally (95.1%, N = 656) and only made transverse scrapes at the bottom of the cut when it was too close to the ground to scrape longitudinally with their teeth (5%, N = 32) (Fig. 6, Table II).
Chimpanzees stripping bark from Ceiba pentandra trees in Comoé National Park, Ivory Coast, November 2016. Left: Adult male Aeneas, adult female Dido, and juvenile female Juno, from the Aeneid community, pull long stripes of bark from a buttress that has previously been peeled multiple times. Right: Adult male Priamo, from the Trojan community, scrapes the cambium longitudinally from an open cut with his fingernails, a technique used exclusively by chimpanzees.
Baboons peeling bark from Ceiba pentandra trees in Comoe National Park, Ivory Coast, September and October 2016. Left: An adult male baboon in the home range of the Achean chimpanzee community bites pieces of bark transversely from a buttress. Right: A young male baboon scrapes an open cut transversely with his teeth from in the home range of the Odissey chimpanzee community.
Characteristic traces produced by chimpanzees (left) and baboons (right) peeling bark from Ceiba pentandra trees in Comoé National Park, Ivory Coast, (November 2014– December 2017). Chimpanzees made longitudinal, long scrape marks with their fingernails and front teeth and left long stripes of bark at the bottom of the buttress. Baboons bit a piece of bark (top, right) and scraped the cambium transversely with their teeth, leaving horizontal traces and pieces of bitten bark on the ground (bottom, right).
The total number of scrapes per event was similar between the two species (Table II), but since chimpanzees made much longer longitudinal scrapes, the quantity of cambium obtained was probably higher.
We found stone tools beside 85 of the peeled trees. However, these tools were probably used for stone throwing, since we found stone throwing traces in most of the 85 trees associated with stones and we did not record any tool use in relation to the bark peeling at any of the sites.
Bark-Peeling Seasonality
In 2016, we recorded 73 events of bark-peeling by chimpanzees with our camera-traps, the first on August 5, 2016 and the last on November 26, 2016. Counting Ceiba pentandra trees that had stage 1 traces of bark-peeling along transects and reconnaissance surveys, we found the earliest signs at the end of the month of June (data from 2 years) and the latest in mid-December (data from 4 years). We found the highest number of freshly peeled trees in October and November, over three consecutive years. We never found freshly peeled trees between January and May (dry season). Thus, we found that this behavior is displayed only during the rainy season and the beginning of the dry season, peaking at the end of the rainy season, when the trees are still full of leaves, and ceasing completely when the trees start producing flowers in mid-December.
Bark Peeling Behavior in Other Chimpanzee Communities over Time
Chimpanzees of all age and sex classes peeled bark (Tables I and II). We recorded videos in four known chimpanzee communities (Odissey, Achean, Trojan, and Aeneid), with most of the individuals already identified (Lapuente et al. 2016). We also found traces of bark peeling on Ceiba pentandra trees across neighboring areas to the north and west, where at least two more communities live (communities A, K, Fig. 7). We found new bark-peeling traces in each of these home ranges in 2015, 2016, and 2017.
The distribution of bark-peeling traces on Ceiba pentandra trees (red dots) and untouched Ceiba pentandra trees (green dots) across the study area of 900 km2 in Comoé National Park, Ivory Coast (October 2014–December 2017). Colored areas represent the home ranges of six different chimpanzee communities where we found traces of the behavior. Home ranges are based on data from camera traps and concentrated signs of chimpanzee presence (nests, tools, dung, footprints, feeding signs, and direct observations).
Tree Species Selection
From October 2014 to May 2015 we found 958 trees that had evidence of debarking by animals, of which 857 were Ceiba pentandra (89.5%). Trees of other species were debarked mainly by elephants based on tusk marks, footprints, and other traces or by unknown animal species (Table III).
Additional Uses of Ceiba pentandra by Chimpanzees in Comoé National Park
We observed Comoé chimpanzees consuming the fruits, flowers, and young leaves as well as the cambium of Ceiba pentandra. All the observations of fruit, flowers, and leaves consumption were during the period in which they do not peel bark. Bark peeling stopped in December, once Ceiba pentandra trees started flowering, but when they had not yet produced leaves and fruit. By the beginning of the bark-peeling season, the end of June, no more flowers, fruits, and few young leaves of Ceiba pentandra were available. We also found chimpanzee nests in Ceiba pentandra trees four times during the dry season.
Selection of Ceiba pentandra Trees for Bark Peeling
We checked 1834 Ceiba pentandra trees in our 900 km2 study area during the study (October 2014–December 2017). Nine hundred and eight of these had traces of bark peeling and 926 had no signs of peeling.
Trees with recent peeling traces (stages 1 and 2) had significantly smaller diameters above the buttresses than those with only older traces (stages 3 and 4) (W = 35,197, P < 0.001) and untouched trees (W = 114660, P < 0.001) (Table IV).
Effect of Bark Thickness on the Selection of Ceiba pentandra Trees to Peel
We found a significant and strong positive correlation between diameter above the buttresses and bark thickness in 31 Ceiba pentandra trees (r = 0.742, df = 29, P < 0.001) (Fig. 8).
We found that 87% (N = 45) of the previously bark-peeled trees that were revisited by chimpanzees had regrown bark in stage 3 of recovery. We measured 10 samples of this green thinner bark from stage 3 traces and we found that it was a mean of 4.5 ± SD 0.97 mm thick.
Is Bark Peeling of Ceiba pentandra: Sustainable or Damaging?
Of 908 trees with bark-peeling traces over 3 years, only 2 fell down during strong windstorms, while 6 of 926 unpeeled Ceiba pentandra trees fell after storms.
Of the 53 Ceiba pentandra trees with stage 1 traces in 2014 and 2015, 4 had stage 3 traces (completely sealed the wounds with bark) 1 year later and 41 had reached stage 3 traces 2 years later. Twelve trees took 3 years to become stage 3, due to very large wounds, >20 cm wide. Only 3 of these 53 trees were revisited and peeled again by chimpanzees in the next year while 14 were revisited and peeled again 2 years after the initial peeling, once the bark had regrown and covered most of the wound. In all cases of bark-peeled trees, only the spines of the buttresses were peeled, which represented <5% of the surface of bark at that level, leaving the rest of the bark around the tree intact.
When we counted the growth rings in the section we cut from a repeatedly peeled buttress, with completely sealed wounds (Fig. 9), we found that the buttress had been peeled three times in the past 16 years and that ≥8 years had passed since the last peeling. We conducted experimental cuts in four buttresses of four different trees that we checked after 3 years, finding that a visible growth ring forms every dry season on the buttresses of Ceiba pentandra in the conditions at Comoé National Park, Ivory Coast.
Regrowth of bark over bark-peeling traces made by chimpanzees on Ceiba pentandra buttresses in Comoé National Park, Ivory Coast. A, Stage 1, trace photographed in February 2015. B, The same trace 1 year later. C, Heavily peeled tree in October 2015; this tree was also peeled in October 2014. D, The same tree in October 2017; all the wounds have been completely sealed by regrown bark.
We found no significant differences in growth in the 20 peeled and 20 unpeeled trees we monitored between October 2015 and October 2017 (W = 202.5, P = 0.955) (Table V).
Sustainable Exploitation of Ceiba pentandra Trees by Chimpanzees
We found 45 Ceiba pentandra trees that were peeled repeatedly during the study period, 40 of which were peeled twice and 5 were peeled three times, once per year. Of the 40 trees peeled twice, 11 (28%) were peeled 1 year after the first peeling, 19 (48%) after 2 years and 10 (25%) after 3 years. In 39 of the 45 revisits (87%) the chimpanzees peeled over previously peeled stage 3 traces, provoking the progressive deformation of the buttress’ spine, with several parallel protruding deformations of the spine (Fig. 3). Moreover, of the 908 Ceiba pentandra trees we monitored, 712 (78.4 %) had traces of at least two different recovery stages, indicating that they had been peeled twice. Of these, 485 (53.4%) had traces of at least three different stages (Fig. 10).
We recorded three videos of three different adult females and one adult male inspecting the buttresses of four different Ceiba pentandra trees and then looking up toward the canopy and leaving the spot without peeling. We also recorded four adult females and one male in four different videos checking the buttress and the canopy and then starting to peel bark. Moreover, we recorded two sequences of videos of the same group of chimpanzees checking the buttresses of a specific Ceiba pentandra tree and leaving afterwards, but the same group returned exactly 1 year later to the same tree and peeled the bark (Fig. 11, ESM video 3). In all cases, the only part of the tree peeled was the spine of the buttress, which represented on average <5% of the total surface of the bark at that level of the tree such that most of the sap would continue to flow without interruption.
Discussion
With this study, we confirmed that both chimpanzees and baboons peeled long strips of bark from the spine of the buttresses of Ceiba pentandra to consume the cambium underneath. Furthermore, we found that this harvesting activity was sustainable, since the peeling wounds healed, usually in 2 years, and with no obvious decrease in survival or growth. Finally, we observed that chimpanzees waited for the bark to regrow before reexploiting the trees. The high availability of the resource (i.e., the high density of Ceiba pentandra in the chimpanzee communities’ home ranges), helped the sustainability of the reexploitation. Although we recorded guenons and rodents creating small round holes in the bark, we only recorded baboons and chimpanzees peeling the bark of Ceiba pentandra in >3 years of study.
During the study, including three complete rainy and dry seasons, we found that all the fresh traces were made during the late rainy season and beginning of the dry season on Ceiba pentandra trees with a mean diameter of 104 cm. Ceiba pentandra represented 89.46% of bark-peeled trees, suggesting that the cambium of this species is more important for Comoé chimpanzees than the other tree species available. Ceiba pentandra trees <60 cm in diameter are usually covered by big thorns and have poorly developed buttresses, making bark-peeling much more difficult. Ceiba pentandra trees >120 cm in diameter usually have bark thicker than 1 cm, making it more difficult to cut the bark with teeth. All these data suggest that chimpanzees prefer to peel thinner bark.
The videos confirmed that both chimpanzees and baboons use their teeth and hands to pull bark strips from the cuts. Both species scraped the cambium with their teeth to eat it, but only baboons ate portions of bark and only chimpanzees used their fingernails to scrape the cambium and eat it. However, we never recorded the use of tools to cut the bark or scrape the cambium. We also found that all chimpanzee age/sex classes and studied communities in Comoé perform the behavior.
Multiple species of mammals strip the bark from different species of trees to feed on either the bark itself or the cambium underneath (Feher et al. 2016; Seryodkin et al. 2017; Ssali et al. 2012). In most cases, these mammals cause serious damage to the trees, known in forestry as bark-stripping, which often kills the tree. Most of these animals are considered pests that destroy forestry plantations or natural forest stands. This is also the case for most African primates that strip bark; for instance, Barbary macaques in Morocco and Algeria are threatening the last wild Cedrus atlantica forests by bark-stripping during dry periods. It has been hypothesized that the main driver of this destructive behavior is to obtain moisture for the bark, as the macaques lack access to good water sources during the bark-peeling periods (Camperio-Ciani et al. 2001; Van Lavieren and Wich, 2009). The destructive bark-stripping caused on pine plantations by blue monkeys (Cercopithecus mitis) in Malawi and chacma baboons in Zimbawe and South Africa is also considered a pest behavior by some authors (Beeson 1987; Bigalke and Hensbergen 2010; Katsvanga et al. 2009). In these cases, the reduction of natural habitats and food resources and the intrusion of anthropic landscapes such as the exotic pine plantations has been cited as the main cause for the destructive behavior in periods of food scarcity.
Scarcity of alternative food sources has been interpreted as the most probable reason why great apes rely on bark or cambium as a fallback food, especially during the rainy season, as in the case of orangutans (Campbell et al. 2011), gorillas (Rogers et al. 1994), and chimpanzees (Goodall 1968; Nishida 1976; Nishida and Uehara 1983; Pruetz 2006). In the case of humans, the use of inner bark in extreme climates, such as areas close to the Arctic Circle, is also interpreted as an emergency food in times of scarcity, such as early spring (Niklasson et al. 1994; Ostlund et al. 2009; Prince 2001). However, while most mammals, including monkeys and great apes, cause serious damage and even death to the trees with bark-stripping, human hunter-gatherers and herders harvested the cambium of trees in a consciously sustainable way, by peeling only a section of the trunk that never completely severs the flow of sap through the xylem (Niklasson et al. 1994; Ostlund et al. 2009; Prince 2001). The chimpanzees of Comoé National Park also appear to peel the bark during periods of food scarcity (Lapuente et al. unpubl. data), but they only peel the bark of the spine of buttresses of Ceiba pentandra, leaving the rest of the tree intact. Ceiba pentandra trees usually have very large buttresses or tabular roots, with a surface of several square meters of bark each side of the buttress (Lapuente and Linsenmair, pers. obs.). The strips that Comoé chimpanzees peeled rarely reached the bole of the trunk and they never peeled the space between buttresses. This selective peeling of a nonvital part of the bark allows sap to continue to flow uninterrupted and thus the trees do not show any sign of deterioration, suggesting that the bark peeling of the buttresses’ spines did not hamper the growth of the trees. We cannot say if the chimpanzees are conscious of the importance of peeling only a small proportion of the bark for the survival of the tree. It is probable that they only peel the spine because it is more accessible, both to perform the initial cut with their teeth and to scrape the cambium with their teeth. Nevertheless, the technique they use allows the tree to easily recover.
On nine occasions, we recorded chimpanzees inspecting the buttresses, leaving them unpeeled on four occasions and proceeding to peel in five other occasions. This suggests that the chimpanzees may be able to tell when the buttress is ripe to peel and that they do not peel the buttress until the wounds of previous peelings are at least stage 3 of recovery, with a thin green new bark covering them almost completely (ESM video 3). Because of this behavior, trees can be peeled repeatedly (at least 16 years; Fig. 10), as we confirmed by counting that 53% of trees had been previously peeled on at least three different occasions. These data suggest that the chimpanzees in Comoé regularly peel Ceiba pentandra trees more than once and that they can keep peeling them for many years.
Left: Transverse section of a Ceiba pentandra buttress. The appearance of the bark over the stage 4 bark-peeling traces is the same as on the rest of the tree, gray and fully regrown. Right: Appearance of the transverse cut after polishing with the traces of three separate bark-peeling events marked with red numbers from 1 to 3. The growth rings over the last wounds are still clearly visible and correspond to a minimum of 8 years, marked with green numbers.
Chimpanzees in Comoé National Park, Ivory Coast, checking and peeling the bark of Ceiba pentandra trees. Left: Adult female Dido from the Aeneid community checks the buttresses of a Ceiba pentandra tree in November 2015. This tree had been peeled in November 2014 and the traces are stage 2 of recovery in the left image. Dido left after inspecting the tree for 42 seconds. Right: Dido returned exactly 1 year later to the same tree and peeled all the buttresses. The bark-peeling traces of 2014 had become stage 3 by November 2016, 2 years later (video still-shots).
The great abundance of Ceiba pentandra trees in the home ranges of Comoé chimpanzees and the very small proportion of dead trees with bark-peeling traces, similar to the proportion of dead untouched trees, suggests that the damage caused by bark peeling does not produce any extra mortality in the trees. We questioned J. Pruetz. about the mortality caused by chimpanzees peeling the bark of Pterocarpus erinaceus and Ceiba pentandra in Fongoli. She explained that the branches of Pterocarpus peeled by chimpanzees died, although, as far as she knew, the chimpanzees hardly ever ate the bark on the trunk to the point that it killed the entire Pterocarpus erinaceus tree (J. Pruetz pers. comm.). Pruetz said that Fongoli chimpanzees were eating the bark of the lower part of the trunk of young Ceiba pentandra trees, which might kill the tree, depending on how it reacted, but they had not circled the whole trunk of the two trees found in November 2019 (J. Pruetz pers. comm.). The appearance of the bark-peeling traces and the technique used to scrape the cambium was the same as in Comoé and show traces of repeated peeling (Fig. 12); thus we can assume that the type of bark peeling and the consequences for the trees are similar, and that it could also be a case of sustainable bark peeling but the number of observations (2) precludes detailed comparison. Baboons have not been observed peeling the bark of Ceiba pentandra in Fongoli yet, and Ceiba pentandra is relatively rare in Fongoli, although we have no data on density or basal area (J. Pruetz pers. comm.).
Back in Comoé, monitoring 20 peeled and 20 untouched trees for 2 years showed no significant difference in the diameter growth rate. We found no reference to mortality caused to bark-peeled trees by chimpanzees in the literature, but smaller tree species can die if the bark is stripped all around the bole by monkeys, bears, or elephants (Beeson 1987; Bigalke and Hensbergen 2010; Camperio-Ciani et al. 2001; Feher et al. 2016; Katsvanga et al. 2009; Seryodkin et al. 2017; Ssali et al. 2012; Van Lavieren and Wich 2009). All these data suggest that the trees recover totally after the peeling and that bark peeling is a sustainable exploitation of this very valuable resource that can probably be carried out for generations, answering our sixth question.
Very old trees, with diameters of >2 m above the buttresses, had very old traces of bark peeling in many cases, suggesting that the behavior has been going on for several decades, but testing this would require destructive sampling. We found traces of all recovery stages in hundreds of trees across the home ranges of at least six different chimpanzee communities, in an area of 900 km2, suggesting that the behavior is widespread and established in the area. The videos show chimpanzees of all age/sex classes bark-peeling, often with juveniles and infants doing or trying to do it beside their mothers, suggesting that the behavior could be customary (Whiten et al. 1999), passed from one generation to the next, and may be an important part of the culture of Comoé chimpanzees. Cultural behaviors in other study sites have been found to provide solutions to the challenges of living in very hot and dry savannas (Boyer Ontl and Pruetz,, this issue; Lindshield et al., in press; Wessling et al., in press).
The fact that sustainable bark peeling was also an important form of obtaining fallback food for human hunter-gatherers in recent prehistory (Niklasson et al. 1994; Ostlund et al. 2009; Prince 2001) and the possibility that bark peeling was also important for Neanderthals (Sandgathe and Hayden 2003) and Australopithecus (Henry et al. 2012) suggests that this behavior of Comoé chimpanzees could be a good model for the sustainable exploitation of alternative resources and fallback foods by human ancestors. Early hominins could have lived in savanna–forest mosaics similar to those of Comoé, suffering similar environmental stresses and food shortages, which could have triggered similar solutions, including sustainable bark peeling (Henry et al. 2012; McGrew et al. 1988; Wessling et al. 2018).
The density of Ceiba pentandra trees in Comoé, with a mean of 178 trees/km2, and a mean basal area of 3.05 m2/ha, is much higher than the density and basal area in similar habitats in Benin, with 9–57 trees/km2 and 0.038–0.115 m2/ha respectively (Sokpon et al. 2011). This relatively high abundance provides a potential fallback food that is probably very important (Lapuente et al. unpubl. data) for the survival of these chimpanzees in the harsh and unpredictable environment of the park. Ceiba pentandra is common all across West and Central Africa, but chimpanzees have only been found to peel the bark of this species in Cantanhez National Park, Guinea Bissau (Bessa et al. 2015), Fongoli, Senegal (J. Pruetz pers. comm.) and Comoé. In Comoé this behavior could be an adaptive response to the ecology of the park, where the savanna–woodland mosaic contains a significant percentage of forest (9–13%) where Ceiba pentandra can thrive. In Fongoli, where the same kind of bark peeling that we found in Comoé has been observed very recently (November 2019), Ceiba pentandra is relatively rare, so this behavior could not produce an important fallback food for chimpanzees, although the abundant Pterocarpus erinaceus, which they peel seasonally every year could (J. Pruetz pers. comm.). Comoé chimpanzees’ ability to exploit this resource has probably helped them to occupy habitats that would be otherwise marginal. Savanna chimpanzees are presented with special challenges by their demanding habitat, with seasonal extremes and great fluctuations in food availability (Lapuente et al. unpubl. data). Ceiba pentandra bark peeling appears to be one of the survival strategies developed by the savanna chimpanzees of Comoé.
Further research is needed to fully understand the exploitation of bark by Comoé chimpanzees. For example, phytochemical changes in the contents of sap and bark, either defensive or nutritional, may influence the timing and extent of bark peeling. Knowledge of this behavior and its ecological and cultural importance is of key importance to understand the nutritional and ecological needs of this population and to plan adequate conservation measures to preserve the integrity and quality of the habitats of these Critically Endangered Western chimpanzee, especially in the face of the increasing threat posed by climatic change.
References
Alp, R. (1997). “Stepping-sticks” and “seat-sticks”: New types of tools used by wild chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes) in Sierra Leone. American Journal of Primatology, 41(1), 45–52.
Arandjelovic, M., Boesch, C., Campbell, G., Hoffman, G., Junker, J. et al. (2011). Guidelines for research and data collection for the cultured chimpanzee Pan African programme–field protocol. http://panafrican.eva.mpg.de/english/approaches_and_methods.php
Beeson, M. (1987). The origins of bark-stripping by blue monkeys (Cercopithecus mitis): Implications for management. Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society, 91, 265–291.
Bessa, J., Sousa, C., & Hockings, K. J. (2015). Feeding ecology of chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes verus) inhabiting a forest-mangrove-savanna-agricultural-matrix at Caiquene-Cadique, Cantanhez National Park, Guinea-Bissau. American Journal of Primatology, 77, 651–665.
Bigalke, R. C., & Hensbergen, H. J. (2010). Baboon damage in plantation forestry in South Africa. South African Forestry Journal, 152, 26–33.
Boyer Ontl, K., & Pruetz, J. D. (in press). Mothers prefer caves: Lactation affects chimpanzee (Pan troglodytes verus) cave use in southeastern Senegal. International Journal of Primatology.
Campbell, G., et al. (2008). Alarming decline of West African chimpanzees in Cote d’Ivoire. Current Biology, Vol 18 No 19
Campbell-Smith, G., Campbell-Smith, M., Singleton, I., & Linkie, M. (2011). Raiders of the lost bark: Orangutan foraging strategies in a degraded landscape. PLoS ONE, 6(6), e20962. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0020962.
Camperio-Ciani, A., Martinoli, L., Capiluppi, C., Arahou, M., & Mouna, M. (2001). Effects of water availability and habitat quality on bark-stripping behavior in barbary macaques. Conservation Biology, 15(1), 259–265.
R Core Team (2018). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed June 25, 2018).
Dick, C. W., Bermingham, E., Lemes, M. R., & Gribel, R. (2007). Extreme long-distance dispersal of the lowland tropical rainforest tree Ceiba pentandra L. (Malvaceae) in Africa and the Neotropics. Molecular Ecology, 16, 3039–3049.
Djomeni, P. D. D., Tédong, L., Asongalem, E. A., Dimo, T., Sokeng, S. D., & Kamtchouing, P. (2006). Hypoglycaemic and antidiabetic effect of root extracts of Ceiba pentandra in normal and diabetic rats. African Journal of Traditional, Complementary, and Alternative Medicines, 3(1), 129–136.
Duvall, C. S. (2008). Chimpanzee diet in the Bafing area, Mali. African Journal of Ecology, 46, 679–683.
Duvall, C. S. (2011). Ceiba pentandra (L.) Gaertn. Record from PROTA4U. In M. Brink & E. G. Achigan-Dako (Eds.), PROTA (Plant Resources of Tropical Africa / Ressources végétales de l’Afrique tropicale) Wageningen, Netherlands. http://www.prota4u.org/search.asp (accessed November 11, 2019).
Feher, A., Szemethy, L., & Katona, K. (2016). Selective debarking by ungulates in temperate deciduous forests: Preference towards tree species and stem girth. European Journal of Forest Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10342-016-1000-9.
Fischer, F., Gross, M., & Linsenmair, K. E. (2002). Updated list of the larger mammals of the Comoé National Park, Ivory Coast. Mammalia, 66, 83–92.
Goodall, J. (1968). The behaviour of free-living chimpanzees in the Gombe Stream Reserve. Animal Behaviour Monographs, 1, 161–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0066-1856(68)80003-2.
Hanson, T. (2007). Consumption of Carapa guianensis bark by Cebus capucinus in La Reserva Biológica Indo-Maíz, Nicaragua. Neotropical Primates, 14(2), 85–87. https://doi.org/10.1896/044.014.0210.
Head, J. S., Boesch, C., Makaga, L., & Robbins, M. (2011). Sympatric chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes troglodytes) and gorillas (Gorilla gorilla gorilla) in Loango National Park, Gabon: Dietary composition, seasonality and intersite comparisons. International Journal of Primatology, 32, 755–775. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10764-011-9499-6.
Hennenberg, K. J. (2005). Vegetation ecology of forest-savanna ecotones in the Comoé National Park (Ivory Coast): Border and ecotone detection, core-area analysis, and ecotone dynamics. Dissertation thesis, Rostock, Germany.
Henry, A. G., Ungar, P. S., Passey, B. H., Sponheimer, M., Rossouw, L. et al (2012). The diet of Australopithecus sediba. Nature, 487, 90–93.
Hernandez Aguilar, R. A., & Reitan, T. (in press). Deciding where to sleep: Spatial levels of nesting selection in savanna chimpanzees at Issa. International Journal of Primatology: Tanzania.
Hoppe-Dominik, B. (1991) Distribution and status of chimpanzee (Pan troglodytes verus) on the Ivory Coast. Primates 31: 45–75
Humle, T., Boesch, C., Campbell, G., Junker, J., Koops, K., Kuehl, H., & Sop, T. (2016). Pan troglodytes ssp. verus. (errata version published in 2016). The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016: e.T15935A102327574
Kassa, B. D., Fandohan, B., Azihou, A. F., & Kaka, R. G. (2013). Survey of Loxodonta africana (Elephantidae)-caused bark injury on Adansonia digitata (Malavaceae) within Pendjari Biosphere Reserve, Benin. African Journal of Ecology, 52, 385–394.
Katsvanga, C. A. T., Jimu, L., Zinner, D., & Mupangwa, J. F. (2009). Diet of pine plantation and non-plantation ranging baboon (Papio ursinus) groups with reference to bark consumption in the eastern highlands of Zimbabwe. Journal of Horticulture and Forestry, 1(9), 168–175.
Kühl, H. S., Kalan, A. K., Arandjelovic, M., Aubert, F., D''Auvergne, L. et al (2016). Chimpanzee accumulative stone throwing. Science Reports, 6, 22219. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep22219.
Kühl, H. S., Sop, T., Williamson, E. A., Mundry, R., Brugière, D. et al. (2017). The Critically Endangered western chimpanzee declines by 80%. American Journal of Primatology, 79, e22681, https://doi.org/10.1002/ajp.22681
Lapuente, J., Hicks, C., & Linsenmair, E. (2016). Fluid dipping technology of chimpanzees in Comoe National Park, Ivory Coast. American Journal of Primatology, 79(5). https://doi.org/10.1002/ajp.22628.
Lauginie, F. (2007). Conservation de la nature et aires protégées en Côte d'Ivoire. Abidjan: NEI/Hachette & Afrique Nature.
Lindshield, S., Ndiaye, P. I., Walters, A., Gueye, M., & Bogart, S. L. (in press). Facultative nocturnality in savanna chimpanzees at risk of carnivore depredation in Niokolo-Koba National Park. International Journal of Primatology: Senegal.
Lindshield, Stacy M. (2014). Multilevel analysis of the foraging decisions of western chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes verus) and resource scarcity in a savanna environment at Fongoli, Senegal. Graduate Theses and Dissertations. 14235. https://lib.dr.iastate.edu/etd/14235
Luchterhand, K., McGrew, W. C., Sharman, M. J., Baldwin, P. J., Tutin, C. E. G., et al (1982). On early hominid plant-food niches. Current Anthropology, 23(2), 211–218.
Maley, J., & Livingstone, D. A. (1983). Late Pleistocene and early Holocene extension of a mountain element in Southern Ghana (West Africa): Preliminary pollen data. Comptes Rendus de L’Academie des Sciences Serie II, 296, 1287–1292.
Marchesi, P., Marchesi, N., Fruth, B., & Boesch, C. (1995) Census and distribution of chimpanzes in Ivory Coast. Primates, 36(4) 591–607.
Matsuzawa, T., Humle, T., & Sugiyama, Y. (Eds.) (2011). The chimpanzees of Bossou and Nimba. Tokyo: Springer.
McGrew, W. C., Baldwin, P. J., & Tutin, C. E. G. (1988). Diet of wild chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes verus) at Mt. Assirik, Senegal: I. Composition. American Journal of Primatology, 16, 213–226. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajp.1350160304.
Mikich, S. B., & Liebsch, D. (2014). Damage to forest plantations by tufted capuchins (Sapajus nigritus): Too many monkeys or not enough fruits? Forest Ecology and Management, 314, 9–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2013.11.026.
Mühlenberg, M., Galat-Luong, A., Poilecot, P., Steinhauer-Burkart, B., & Kühn, I. (1990). L'importance des ilôts forestiers de savane humide pour la conservation de la faune de forêt dense en Côte d’Ivoire. Revue.Ecologie (Terre Vie), 45, 197–214.
Nakamura, M., Hosaka, K., Itoh, N., & Zamma, K. (Eds.) (2015). Mahale chimpanzees: 50 years of research. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Niklasson, M., Zaekrisson, M. O., & Ostlund, L. (1994). A dendroecological reconstruction of use by Saami of Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) inner bark over the last 350 years at Sidvajaure, N. Sweden. Vegetation History and Archaeobotany, 3, 183–190.
Nishida, T. (1976). The bark eating habits in primates, with special reference to their status in the diet of wild chimpanzees. Folia Primatologica, 25, 277–287.
Nishida, T., & Uehara, S. (1983). Natural diet of chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes schweinfurthii): longterm record from the Mahale Mountains, Tanzania. African Study Monographs, 3, 109–130
Ostlund, L., Ahlberg, L., Zackrisson, O., Bergman, I., & Arno, S. (2009). Bark-peeling, food stress and tree spirits – The use of pine inner bark for food in Scandinavia and North America. Journal of Ethnobiology, 29(1), 94–112.
Prince, O. (2001). Dating and interpreting pine cambium collection scars from two parts of the Nechako river drainage, British Columbia. Journal of Archaeological Science, 28, 253–263.
Pruetz, J. D. (2006). Feeding ecology of savanna chimpanzees at Fongoli, Senegal. In G. Hohmann, M. M. Robbins, & C. Boesch (Eds.), Feeding ecology in apes and other primates: Ecological, physical and behavioral aspects (pp. 161–182).. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Rogers, M. E., Tutin, C. E. G., Williamson, E. A., Parnell, R. J. Voysey, B. C., & Fernandez, M. (1994). Seasonal feeding on bark by gorillas: An unexpected keystone food? In B. Thierry, J. R. Anderson, J. J. Roeder, & N. Herrenschmidt (pp. 37–43), Current primatology, Vol. I: Ecology and evolution. Strasbourg: Université Louis Pasteur.
Russak, S. (2013). Ecological role of dry-habitat chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes schweinfurthii) at Issa, Ugalla, Tanzania. PhD thesis. Arizona State University.https://repository.asu.edu/items/18012
Sandgathe, D., & Hayden, B. (2003). Did Neanderthals eat inner bark? Antiquity, 77(298), 709–718. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0003598X00061652
Schöngart, J., Orthmann, B., Hennenberg, K. J., & Worbes, M. (2006). Climate-growth relationship of tropical tree species in West Africa and their potential for climate reconstruction. Global Change Biology, 12(7), 1139–1150. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2486.2006.01154.x.
Seryodkin, I. V., Zakharenko, A. M., Dmitrenok, P. S., & Golokhvast, K. S. (2017). Biochemical content of cambium of Abies nephrolepis eaten by bears on the Far East of Russia. Biochemistry Research International, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3020571
Sokpon, N., Dotonhoué, F., & Ouinsavi, C. (2011). Patterns of ecological structure and spatial distribution of Kapok tree (Ceiba pentandra) populations in Benin. Annales de Université de Parakou, Sér, 2, 5–26.
Ssali, F., Sheil, D., & Nkurunungi, N. B. (2012). How selective are elephants as agents of forest tree damage in Bwindi Impenetrable National Park, Uganda? African Journal of Ecology. https://doi.org/10.1111/aje.12006.
Sugiyama, Y., & Koman, J. (1979). Tool-using and making behavior in wild chimpanzees at Bossou, Guinea. Primates, 20, 513–524.
Ueda, H., Kaneda, N., Kawanishi, K., Alves, S. M., & Moriyasu, M. (2002). A new isoflavone glycoside from Ceiba pentandra (L.). Gaertner. Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 50(3), 403–404.
Vaidyanathan, G. (2011). Apes in Africa: The cultured chimpanzees. Nature News, 476, 266–269.
van Lavieren, E., & Wich, S. (2009). Decline of the Barbary macaque Macaca sylvanus in the cedar forest of the Middle Atlas Mountains, Morocco. Oryx, 0(0), 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0030605309990172
Van Leeuwen, K., Hill, R., Korstjens, A. (2020). Quantifying chimpanzee (Pan troglodytes) landscapes: An environmental approach to classifying forest and savanna chimpanzees. International Journal of Primatology (in press).
Vasconcellosa, T. J., Tomazello-Filhob, M., & Callado, C. (2019). Dendrochronology and dendroclimatology of Ceiba speciosa (A. St.-Hil.) Ravenna (Malvaceae) exposed to urban pollution in Rio de Janeiro city, Brazil. Dendrochronologia, 53, 104–113.
Wessling, E. G., Kühl, H. S., Mundry, R., Deschner, T., & Pruetz, J. D. (2018). The costs of living at the edge: Seasonal stress in wild savanna-dwelling chimpanzees. Journal of Human Evolution, xxx 1e11.
Wessling, E. G., Dieguez, P., Llana, M., Pacheco, L., Pruetz, J. D., & Kühl, H. S. (in press). Chimpanzee (Pan troglodytes verus) density and environmental gradients at their biogeographical range edge. International Journal of Primatology.
Wild Chimpanzee Foundation (WCF) (2014). Etat des ressources naturelles du Parc National de La Comoé et de sa zone peripherique. Rapport de l'inventaire faunique par survol du 17 au 24 avril 2014. 40 pp
Whiten, A., Goodall, J., McGrew, W. C., Nishida, T., Reynolds, V., et al (1999). Nature, 399, 682–685.
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by the Comoé Research Station, the Barcelona Zoo Foundation, Arcus Foundation, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, and Max Planck Society Innovation Fund and Heinz L. Krekeler Foundation. We want to acknowledge for their support and collaboration all the personnel of the Office Ivoirienne de Parcs et Reserves (OIPR) and especially to the Directeur de Zone (DZ) and Directeur General (DG) . We also want to thank Pamela C. Köster for her help with the chimpanzee identification. Thank you to all the personnel of the Comoé Research Station too and to all the assistants and students who have participated in the Comoé Chimpanzee Conservation Project (CCCP), making this study possible. We also acknowledge the reviewers and editors for their help in the revision of the manuscript.
Funding
Open Access funding provided by Projekt DEAL.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JL conceived the research and did the fieldwork, data analysis, and writing of the manuscript, MA, HK, PD, and CB helped with the conception, data analysis, and writing, KEL supervised the whole work and helped in the conception, analysis, and writing.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling Editor: Stacy Lindshield
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Lapuente, J., Arandjelovic, M., Kühl, H. et al. Sustainable Peeling of Kapok Tree (Ceiba pentandra) Bark by the Chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes verus) of Comoé National Park, Ivory Coast. Int J Primatol 41, 962–988 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10764-020-00152-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10764-020-00152-9