Abstract
There has been considerable interest in Blended learning (BL) and how it is transforming teaching and learning in higher education institutions. Research in this area is focused on course level issues in relation to how students and faculty members interact and adopt blended learning, with very limited focus on institutional adoption. There is the need for more institutional adoption research to guide how higher education institutions shape policies as they transition from the traditional face to face delivery model to fully blended universities. This study adopts a grounded theory methodology to investigate institutional BL adoption initiatives. A public university in Ghana, which is in its early/adoption implementation stage, is selected as a case study and analysed using the constant comparative analytical technique. The university management took a decision in 2013 to transition from face to face delivery to a fully adopted blended learning approach. The university subsequently adopted a BL policy which, among other things, directed faculty members to teach courses via a mix of face to face and online using a Moodle Learning Management System (LMS). Findings from this study present the identified factors that influence and impact the adoption of BL program in institutions. Findings from this study suggest that institutional decision to adopt or reject BL is influenced by the level of the institutional desire to adopt blended learning and the level of the institution’s intention to adopt blended. The outcome of the findings is developed into an institutional adoption model to guide managers of institutions intending to transition to BL delivery model.

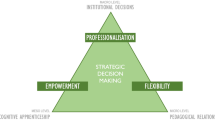
Source: Antwi-Boampong and Bokolo (2021)
Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Material
Not applicable.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
Adebayo, O., Iwu-James, J., Olawoyin, O., Fagbohun, O., Esse, U., Yusuf, F., Owolabi, S. (2019). Blended learning in higher education: implication and strategies for academic library support. In INTED2019 Proceedings, 1(March), (pp. 7210–7217). https://doi.org/10.21125/inted.2019.1746
Adekola, J., Dale, V. H. M., & Gardiner, K. (2017a). Development of an institutional framework to guide transitions into enhanced blended learning in higher education. Research in Learning Technology. https://doi.org/10.25304/rlt.v25.1973
Adekola, J., Dale, V. H. M., Gardiner, K., Murray, J.-A., & Fischbacher-Smith, M. (2017). Institutional and student transitions to into blended learning. In 3rd International Enhancement in Higher Education Conference, (pp 1–10) Glasgow, UK.
Adekola J., Dale, V., & Powell, K. (2017). Student transitions to blended learning – challenges and solutions
Ansong, E., Boateng, R., Boateng, S. L., & Anderson, A. B. (2017). The nature of e-learning adoption by stakeholders of a university in Africa. E-Learning and Digital Media, 14(4), 226–243. https://doi.org/10.1177/2042753017731235
Apandi, A. M., & Raman, A. (2020). Factors affecting successful implementation of blended learning at higher education. International Journal of Instruction, Technology, and Social Sciences, 1(1), 13–23.
Asabere, N., Togo, G., Acakpovi, A., Torby, W., & Ampadu, K. (2017). AIDS: An ICT model for integrating teaching, learning and research in technical university education in Ghana. International Journal of Education and Development Using Information and Communication Technology, 13(3), 162–183.
Asampana, I., Akanferi, A. A., & Ami-Narh, J. (2017). Reasons for poor acceptance of web-based learning using an LMS and VLE in Ghana. Interdisciplinary Journal of Information, Knowledge, and Management. https://doi.org/10.28945/3742
Asante, J. N. (2014). The State of ICT integration in the early years in ghana schools. Literacy Information and Computer Education Journal, Special, 3(1), 1750–1757.
Asunka, S. (2008). October – 2008 online learning in higher education in Sub-Saharan Africa : Ghanaian university students experiences and perceptions. The International Review of Research in Open and Distributed Learning, 9(3), 1–23.
Asunka, S. (2013). Overcoming barriers to instructor adoption of a learning management system. Cases on Educational Technology Implementation for Facilitating Learning. https://doi.org/10.4018/978-1-4666-3676-7.ch014
Atuahene, F., & Owusu-Ansah, A. (2013). A descriptive assessment of higher education access, participation, equity, and disparity in Ghana. SAGE Open, 3(3), 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1177/2158244013497725
Awidi, I. T. (2013). E-learning Implementation Strategies for an ICT-Challenged Environment : Case of the University of Ghana, Legon. Retrieved from https://ro.ecu.edu.au/theses/573
Bervell, B., & Umar, I. N. (2020). Blended learning or face-to-face? does tutor anxiety prevent the adoption of learning management systems for distance education in Ghana? Open Learning, 35(2), 159–177. https://doi.org/10.1080/02680513.2018.1548964
Blankson, H. (2015). The impact of e-learning on teaching and learning in Cape Coast polytechnic. African Journal of Applied Research (AJAR), 1(1), 262–272. https://doi.org/10.1525/aeq.1992.23.1.05x1104l
Blieck, Y., Zhu, C., Schildkamp, K., Struyven, K., Pynoo, B., & Cindy, L. (2020). A conceptual model for effective quality management of online and blended learning. Electronic Journal of E-Learning, 18(2), 189–204.
Bohle Carbonell, K., Dailey-Hebert, A., & Gijselaers, W. (2013). Unleashing the creative potential of faculty to create blended learning. Internet and Higher Education. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iheduc.2012.10.004
Bokolo, A., Kamaludin, A., Romli, A., Mat Raffei, A. F., A/L Eh Phon, D. N., Abdullah, A., Baba, S. (2020). A managerial perspective on institutions’ administration readiness to diffuse blended learning in higher education: Concept and evidence. Journal of Research on Technology in Education, 52(1), 37–64. https://doi.org/10.1080/15391523.2019.1675203
Buchanan, T., Sainter, P., & Saunders, G. (2013). Factors affecting faculty use of learning technologies: implications for models of technology adoption. Journal of Computing in Higher Education. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12528-013-9066-6
Casanovas, I. (2010). Exploring the current theoretical background about adoption through institutionalization of online education in Universities: needs for further research. Electronic Journal of E-Learning, 8(2), 73–84.
Charbonneau-gowdy, P., Frenzel, M., & Bello, U. A. (2016). Converting from ‘ Doubter ’ to Promoter of Blended Learning Approaches in Higher Education.
Charmaz, K. (2015). Grounded theory: Methodology and theory construction. In International Encyclopedia of the Social & Behavioral Sciences: Second Edition (Second Edi, Vol. 10). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-097086-8.44029-8
Dziuban, C., Graham, C. R., Moskal, P. D., Norberg, A., & Sicilia, N. (2018). Blended learning: the new normal and emerging technologies. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education, 15(1), 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-017-0087-5
Garrison, D. R., & Kanuka, H. (2004). Blended learning: Uncovering its transformative potential in higher education. Internet and Higher Education. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iheduc.2004.02.001
Garrison, D. R., & Vaughan, N. D. (2013). Institutional change and leadership associated with blended learning innovation: Two case studies. Internet and Higher Education. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iheduc.2012.09.001
Gautreau, C. (2011). Motivational factors affecting the integration of a learning management system by faculty. Journal of Educators Online. https://doi.org/10.9743/JEO.2011.1.2
Gautreau, C. (2016). Motivational factors affecting the integration of a learning management system by faculty. The Journal of Educators Online. https://doi.org/10.9743/jeo.2011.1.2
Georgieva, S., & Allan, G. (2008). Best practices in project management through a grounded theory lens. Electronic Journal of Business Research Methods, 6(1), 43–52.
Glaser, B. G. (2002). Conceptualization: On theory and theorizing using grounded theory. International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 1(2), 23–38. https://doi.org/10.1177/160940690200100203
Graham, C. R., Woodfield, W., & Harrison, J. B. (2013). A framework for institutional adoption and implementation of blended learning in higher education. Internet and Higher Education, 18, 4–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iheduc.2012.09.003
Güzer, B., & Caner, H. (2014). The past, present and future of blended learning: an in depth analysis of literature. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 116, 4596–4603. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2014.01.992
Khan, B. H. (2002). A framework for E-learning. Educational Technology, 42(1), 59–60.
Kituyi, G., & Tusubira, I. (2013). A framework for the integration of e-learning in higher education institutions in developing countries Geoffrey Kituyi and Irene Tusubira Makerere university business school, Uganda. International Journal of Education and Development Using Information and Communication Technology (IJEDICT), 9(2), 19–36.
Koehler, M. J., Mishra, P., & Cain, W. (2009). What is technological pedagogical content knowledge (TPACK)? Contemporary Issues in Technology and Teacher Education, 9(1), 60–70. https://doi.org/10.1177/002205741319300303
Korpelainen, E. (2011). Theories of ICT system implementation and adoption - a critical review. Aalto University, 57.
Kotoua, S., Ilkan, M., & Kilic, H. (2015). The growing of online education in Sub Saharan Africa: Case study Ghana. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 191, 2406–2411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2015.04.670
Kumi-Yeboah, A., Young, W., & Boadu, K. (2013). 21st century distance learning in Sub-Saharan Africa: distance and blended learning in Ghana. In Advancing Technology and Educational Development through Blended Learning in Emerging Economies, (September), (p 142). https://doi.org/10.4018/978-1-4666-4574-5.ch008
Licqurish, S., & Seibold, C. (2011). Applying a contemporary grounded theory methodology. Nurse Researcher, 18(4), 11–16. https://doi.org/10.7748/nr2011.07.18.4.11.c8630
Liu, Q., Geertshuis, S., & Grainger, R. (2020). Understanding academics adoption of learning technologies: A systematic review. Computers and Education, 151(February), 103857. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2020.103857
Lysek, M. H. T. (2018). A grounded theory on obtaining congruence in decision making. The Grounded Theory Review, 17(1), 70.
Maloney, S., Nicklen, P., Rivers, G., Foo, J., Ooi, Y. Y., Comm, M., & Ilic, D. (2015). A cost-effectiveness analysis of blended versus face-to-face delivery of evidence-based medicine to medical students. Journal of Medical Internet Research, 17(7), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.2196/jmir.4346
Marfo, J. S., & Okine, R. K. (2016). Implementation of e-Learning in Ghanaian Tertiary Institutions (A case study of KNUST ). E-Learning, 3(9), 29–41.
Mirata, V., Hirt, F., Bergamin, P., & van der Westhuizen, C. (2020). Challenges and contexts in establishing adaptive learning in higher education: Findings from a Delphi Study. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-020-00209-y
Moser, F. Z. (2007). Faculty adoption of educational technology: Educational technology support plays a critical role in helping faculty add technology to their teaching. Educause Quarterly, 30(1), 66–69.
Norberg, A., Dziuban, C. D., & Moskal, P. D. (2011). A time-based blended learning model. On the Horizon, 19(3), 207–216. https://doi.org/10.1108/10748121111163913
Nunes, J. M. B., Martins, J. T., Zhou, L., Alajamy, M., & Al-Mamari, S. (2010). Contextual sensitivity in grounded theory: The role of pilot studies. The Electronic Journal of Business Research Methods, 8(2), 73–84.
Ocak, M. A. (2011). Why are faculty members not teaching blended courses? Insights from faculty members. Computers & Education, 56(3), 689–699.
Owston, R., York, D., & Malhotra, T. (2019). Blended learning in large enrolment courses: student perceptions across four different instructional models. Australasian Journal of Educational Technology, 35(5), 29–45.
Pereira, I., & Figueiredo, A. D. (2010). Promoting motivation and participation in higher education: A b-learning experience. In Proceedings - Frontiers in Education Conference, FIE, (pp. 1–6). https://doi.org/10.1109/FIE.2010.5673204
Previtali, P., & Scarozza, D. (2019). Blended learning adoption: A case study of one of the oldest universities in Europe. International Journal of Educational Management, 33(5), 990–998. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJEM-07-2018-0197
Rasheed, R. A., Kamsin, A., & Abdullah, N. A. (2020). Challenges in the online component of blended learning: A Systematic Review. Computers and Education, 144(March 2019), 103701. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2019.103701
Rowley, J. (2012). Conducting research interviews. Management Reserach Review, 35(3/4), 260–271.
Samarawickrema, G., & Stacey, E. (2007). Adopting web-based learning and teaching: A case study in higher education. Distance Education. https://doi.org/10.1080/01587910701611344
Siddiquee, T. A. R., Abdullah, F. B., Sanusi, A., & Hasan, M. K. (2019). The Blended Learning (B-Learning): present status and future prospects. Researchgate.Net, (November). Retrieved from https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Tahir_Abdul_Rahman_Siddiquee/publication/337415296_The_Blended_Learning_B-Learning_Present_Status_and_Future_Prospects/links/5dd6609c458515cd48b08b8b/The-Blended-Learning-B-Learning-Present-Status-and-Future-Prospects.
Stein, J., & Graham, C. R. (2020). Essentials for blended learning. Essentials for Blended Learning. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781351043991
Tamanja, E., & Pajibo, E. (2019). Ghana’S free senior high school policy: evidence and insight from data. In: EDULEARN19 Proceedings, 1(May), (pp 7837–7846). https://doi.org/10.21125/edulearn.2019.1906
Taplin, R. H., Kerr, R., & Brown, A. M. (2013). Who pays for blended learning? a cost–benefit analysis. Internet and Higher Education. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iheduc.2012.09.002
Tawiah, R., Lamptey, R. B., Okyere, G. A., Oduro, W., & Thompson, M. O. (2019). Review of e-Learning environment at the Kwame Nkrumah university of science and technology, Ghana. Library Philosophy and Practice (e-journal). 2337
Taylor, J. A., & Newton, D. (2013). Beyond blended learning: a case study of institutional change at an Australian regional university. Internet and Higher Education. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iheduc.2012.10.003
Tshabalala, M., Ndeya-Ndereya, C., & Van Der Merwe, T. (2014). Implementing blended learning at a developing university: Obstacles in the way. The Electronic Journal of E-Learning, 12(1), 101–110.
Yeou, M. (2016). An investigation of student’s acceptance of moodle in a blended learning setting using technology acceptance model. Journal of Educational Technology Systems, 44(3), 300–318.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix 1
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Antwi-Boampong, A., Bokolo, A.J. Towards an Institutional Blended Learning Adoption Model for Higher Education Institutions. Tech Know Learn 27, 765–784 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10758-021-09507-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10758-021-09507-4