Abstract
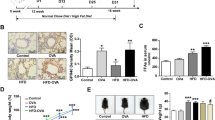
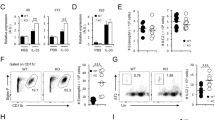
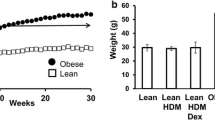
Although natural killer T cells (NKT cells) are altered in obese asthmatic mice, their function remains completely unclear. To further explore the potential mechanism of NKT cells in airway inflammation of obesity-associated asthma, we examined the effects of α-galactosylceramide (KRN7000) on airway inflammation in obese asthmatic mice. Male C57BL/6J mice were divided into five groups: (1) control; (2) asthma; (3) A + KRN, asthma with KRN7000; (4) obese asthma; and (5) OA + KRN, obese asthma with KRN7000. Cytometric bead array (CBA) was used to detect interleukin-4 (IL-4), IL-10, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and interferon-γ (IFN-γ) in the serum. Flow cytometry was used to detect NKT cells and CD69+ NKT cells. Airway inflammation was observed in pathological sections, and calmodulin (CaM) expression was observed by immunohistochemistry in lung tissues. Airway inflammation in the obese asthma group was more severe than that of the asthma group. Airway inflammation of the OA + KRN group was reduced more than that of the A + KRN group. CD69+ NKT cells were only significantly reduced in the OA + KRN group. The levels of serum IFN-γ and TNF-α increased more in the OA + KRN group than in the A + KRN group. CaM is widely expressed in the cytoplasm of the lung tissues and was sharply decreased in the OA + KRN group. KRN7000 can significantly reduce airway inflammation in obesity-associated asthma by regulating NKT cell cytokine secretion and intracellular calcium. These results may contribute to the development of novel therapeutic approaches.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Oliveira, M.J., M. Vieira, D. Coutinho, I. Ladeira, I. Pascoal, J. Ferreira, J.M. Da Silva, A. Carvalho, And R. Lima. 2019. Severe asthma in obese patients: improvement of lung function after treatment with omalizumab. Pulmonology 25: 15-20.
Kleniewska, P., and R. Pawliczak. 2019. The influence of apocynin, lipoic acid and probiotics on antioxidant enzyme levels in the pulmonary tissues of obese asthmatic mice. Life Sciences 234: 116780.
Forno, E., and J.C. Celedón. 2017. The effect of obesity, weight gain, and weight loss on asthma inception and control. Current Opinion in Allergy and Clinical Immunology 17: 123–130.
Marko, M., and R. Pawliczak. 2018. Obesity and asthma: risk, control and treatment. PostȩPy Dermatologii I Alergologii 35: 563–571.
Chen, Y.P., J.H. Zhang, C.Q. Li, Q.X. Sun, and X.H. Jiang. 2015. Obesity enhances Th2 inflammatory response via natural killer T cells in a murine model of allergic asthma. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine 8: 15403–15412.
Chen, Y.P., B.Q. Xiao, J.H. Zhang, W.W. Liu, Y.Q. Xiao, and C.Q. Li. 2018. New method of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease mouse models and mechanism about immune cells. Chinese Pharmacological Bulletin 34 (6): 882–886.
Zhang, J.H., Y.P. Chen, X. Yang, and C.Q. Li. 2017. Vitamin D3 levels and Nlrp3 expression in murine models of obese asthma: association with asthma outcomes. Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research = Revista Brasileira De Pesquisas Médicas E Biológicas 51: E6841.
Mercer, J.C., M.J. Ragin, and A. August. 2005. Natural killer T cells: rapid responders controlling immunity and disease. The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology 37: 1337–1343.
Karmakar, S., J. Paul, and T. De. 2011. Leishmania Donovani Glycosphingolipid Facilitates antigen presentation by inducing relocation of Cd1d into lipid rafts in infected macrophages. European Journal of Immunology 41: 1376–1387.
Godfrey, D.I., S. Stankovic, and A.G. Baxter. 2009. Developing Nkt cells need their calcium. Nature Immunology 10: 231–233.
Kawano, T., J. Cui, Y. Koezuka, I. Toura, Y. Kaneko, K. Motoki, H. Ueno, R. Nakagawa, H. Sato, E. Kondo, H. Koseki, and M. Taniguchi. 1997. Cd1d-restricted and Tcr-mediated activation of Valpha14 Nkt cells by glycosylceramides. Science 278: 1626–1629.
Van Kaer, L., and L. Wu. 2018. Therapeutic potential of invariant natural killer T cells in autoimmunity. Frontiers in Immunology 9: 519.
Parekh, V.V., S. Lalani, S. Kim, R. Halder, M. Azuma, H. Yagita, V. Kumar, L. Wu, and L.V. Kaer. 2009. Pd-1/Pd-L Blockade prevents anergy induction and enhances the anti-tumor activities of glycolipid-activated invariant Nkt cells. The Journal of Immunology: Official Journal of the American Association of Immunologists 182: 2816–2826.
Engin, A. 2017. Human protein kinases and obesity. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology 960: 111–134.
Novosad, S., S. Khan, B. Wolfe, and A. Khan. 2013. Role of obesity in asthma control, The Obesity-Asthma Phenotype. The Journal of Allergy 2013: 538642.
Holguin, F., S.A. Comhair, S.L. Hazen, R.W. Powers, S.S. Khatri, E.R. Bleecker, W.W. Busse, W.J. Calhoun, M. Castro, A.M. Fitzpatrick, B. Gaston, E. Israel, N.N. Jarjour, W.C. Moore, S.P. Peters, W.G. Teague, K.F. Chung, S.C. Erzurum, and S.E. Wenzel. 2013. An association between l-arginine/asymmetric dimethyl arginine balance, obesity, and the age of asthma onset phenotype. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 187: 153–159.
Gibeon, D., K. Batuwita, M. Osmond, L.G. Heaney, C.E. Brightling, R. Niven, A. Mansur, R. Chaudhuri, C.E. Bucknall, A. Rowe, Y. Guo, P.K. Bhavsar, K.F. Chung, and A. Menzies-Gow. 2013. Obesity-associated severe asthma represents a distinct clinical phenotype: analysis of the British Thoracic Society Difficult Asthma Registry Patient Cohort According To Bmi. Chest 143: 406–414.
Wenzel, S.E. 2012. Asthma phenotypes: the evolution from clinical to molecular approaches. Nature Medicine 18: 716–725.
Potaczek, D.P., H. Harb, S. Michel, B.A. Alhamwe, H. Renz, and J. Tost. 2017. Epigenetics and allergy: from basic mechanisms to clinical applications. Epigenomics 9: 539–571.
Dixon, A.E., F. Holguin, A. Sood, C.M. Salome, R.E. Pratley, D.A. Beuther, J.C. Celedón, and S.A. Shore. 2010. An official American Thoracic Society Workshop Report: obesity and asthma. Proceedings of the American Thoracic Society 7: 325–335.
Peters, U., A.E. Dixon, and E. Forno. 2018. Obesity and asthma. The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 141: 1169–1179.
Bendelac, A., P.B. Savage, and L. Teyton. 2007. The Biology Of Nkt Cells. Annual Review of Immunology 25: 297–336.
Godfrey, D.I., S. Stankovic, and A.G. Baxter. 2010. Raising the Nkt cell family. Nature Immunology 11: 197–206.
Iwamura, C., and T. Nakayama. 2018. Role of cd1d- and mr1-restricted t cells in asthma. Frontiers in Immunology 9: 1942.
Imai, A., E. Fujimoto, K. Tamura, M. Utsuyama, and K. Sato. 2019. A maternal high-fat diet may accelerate adipo-immunologic aging in offspring. Life Sciences 219: 100–108.
Van Kaer, L., V.V. Parekh, and L. Wu. 2011. Invariant natural killer t cells: bridging innate and adaptive immunity. Cell and Tissue Research 343: 43–55.
Guo, R.J., X.J. Huang, Z.D. Liang, Y.Y. Zeng. 2008. The preliminary study of ultrastructure of mouse nkt cells Journal of Jinan University (Natural Science & Medicine Edition) 29: 311-314.
Zhang, X., J. Zheng, L. Zhang, Y. Liu, G.P. Chen, H.P. Zhang, L. Wang, D.Y. Kang, L.G. Wood, and G. Wang. 2017. Systemic inflammation mediates the detrimental effects of obesity on asthma control. Allergy and Asthma Proceedings.
Su, X., Y. Ren, M. Li, X. Zhao, L. Kong, and J. Kang. 2018. Association between lipid profile and the prevalence of asthma: a meta-analysis and systemic review. Current Medical Research and Opinion 34: 423–433.
Jha, A., M.H. Ryu, O. Oo, H.J. Bews, J.C. Carlson, J. Schwartz, S. Basu, C.S. Wong, and A.J. Halayko. 2018. Prophylactic benefits of systemically delivered simvastatin treatment in a house dust mite challenged murine model of allergic asthma. British Journal of Pharmacology 175: 1004–1016.
Cowan, D.C., J.O. Cowan, R. Palmay, A. Williamson, and D.R. Taylor. 2010. simvastatin in the treatment of asthma: lack of steroid-sparing effect. Thorax 65: 891–896.
Torina, A., G. Guggino, M.P. La Manna, and G. Sireci. 2018. The janus face of nkt cell function in autoimmunity and infectious diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19.
Marcelo, K.L., A.R. Means, and B. York. 2016. The Ca(2+)/calmodulin/Camkk2 axis: nature’s metabolic camshaft. Trends in Endocrinology and Metabolism: TEM 27: 706–718.
Spinelli, A.M., Y. Liu, L.Y. Sun, J.C. González-Cobos, J. Backs, M. Trebak, and H.A. Singer. 2015. Smooth muscle camkiiδ promotes allergen-induced airway hyperresponsiveness and inflammation. PflüGers Archiv : European Journal Of Physiology 467: 2541–2554.
Wen, J., X. Meng, B. Xuan, T. Zhou, H. Gao, H. Dong, and Y. Wang. 2018. Na+/Ca2+ Exchanger 1 In airway smooth muscle of allergic inflammation mouse model. Frontiers in Pharmacology 9: 1471.
Kan, J., C. Zhao, S. Lu, G. Shen, J. Yang, P. Tong, L. Xi, R. Zhang, X. Liang, D. Su, D. Li, and Y. Liu. 2019. S100a16, A novel lipogenesis promoting factor in livers of mice and hepatocytes in vitro. Journal of Cellular Physiology 234: 21395–21406.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the technical assistance of Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Drug Non-Clinical Evaluation and Research.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Funding
This research received funding from the Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi Province (Grant number: 2020JJA140130), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant number: 81860005), Guangxi University Young and Middle-aged Teachers Basic Ability Improvement Project (Grant number:2017KY0106), Key Program “New Drug Creation” of Guangdong Key Research and Development Plan (Grant number: 2019B020202001)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
In this work, Yiping Chen, and Jinghong Zhang designed study; Yiping Zhu, Geng Su, and Yanying Zhao performed research and analyzed data; Wei Yang contributed new methods or models; Yiping Chen and Weiwei Lu wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All animal care and experimental protocols were approved by the Ethical Principles in Animal Research adopted by the Guangxi Medical University for Animal Experimentation, and followed the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals.
Consent for publication
All authors consent the publication of this manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Zhu, Y., Su, G. et al. KRN7000 Reduces Airway Inflammation via Natural Killer T Cells in Obese Asthmatic Mice. Inflammation 44, 1982–1992 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-021-01475-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-021-01475-2