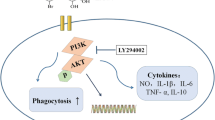
Abstract
Gingerol was the main functional substance of Zingiberaceous plant which has been known as traditional medicine for thousands of years. The purpose of this experiment was to explore anti-inflammatory effects of gingerol and study the possible mechanism in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated RAW246.7 cells. The cells were treated with 10 μg/mL LPS and 300, 200, 100, and 50 μg/mL gingerol for 24 h. The cytotoxicity of gingerol was determined by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetra-zoliumbromide (MTT) method. Nitric oxide (NO) production was observed using Griess assays. Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) and pro-inflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin (IL)-1β, and IL-6 have been analyzed by ELISA. Real-time PCR was used to detect the mRNA expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), IL-6, and IL-1β in LPS-induced RAW246.7 cells. Nuclear transcription factor kappa-B (NF-κB) signaling pathway-related proteins have been assessed by western blot assays. The determination of MTT showed that cell viability was not significantly affected by up to 300 μg/mL gingerol. Compared with LPS group, 50, 100, 200, and 300 μg/mL gingerol can inhibit the production of NO and the inhibitory rate was 10.4, 29.1, 58.9, and 62.4%, respectively. The results indicated gingerol existed anti-inflammatory effect. In addition, gingerol also observably inhibited LPS-induced TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and PGE2 (p < 0.01) expression and secretion in a dose-dependent manner. At the genetic level, after the intervention of gingerol, mRNA transcriptions of iNOS, COX-2, IL-6, and IL-1β were all decreased. The protein expressions of iNOS, NF-κB, p-p65, and p-IκB were significantly increased in LPS-induced cells, while these changes were reversed by the treatment with gingerol. This study suggested that gingerol exerts its anti-inflammatory activities in LPS-induced macrophages which can inhibit the production of inflammatory cytokines by targeting the NF-κB signaling pathway.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhai, X.-T., J.-Q. Chen, C.-H. Jiang, J. Song, D.-Y. Li, H. Zhang, X.-B. Jia, W. Tan, S.-X. Wang, Y. Yang, and F.-X. Zhu. 2016. Corydalis bungeana Turcz. attenuates LPS-induced inflammatory responses via the suppression of NF-κB signaling pathway in vitro and in vivo. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 194: 153–161.
Ahn, C.-B., Y.-S. Cho, and J.-Y. Je. 2015. Purification and anti-inflammatory action of tripeptide from salmon pectoral fin byproduct protein hydrolysate. Food Chemistry. 168: 151–156.
Baldwin, G.S. 2000. Do NSAIDs contribute to acute fatty liver of pregnancy? Medical Hypotheses 54 (5): 846.
Stuart, M.J., S.J. Gross, H. Elrad, et al. 1982. Effects of acetylsalicylic acid ingestion on maternal and neonatal hemostatic. The New England Journal of Medicine 307: 909.
Guo, J.-B., Y. Fan, W.-J. Zhang, H. Wu, L.-M. Du, and Y.-X. Chang. 2017. Extraction of gingerols and shogaols from ginger ( Zingiber officinale Roscoe) through microwave technique using ionic liquids. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis 62: 35–42.
Young, H.-Y., Y.-L. Luo, H.-Y. Cheng, W.-C. Hsieh, J.-C. Liao, and W.-H. Peng. 2005. Analgesic and anti-inflammatory activities of [6]-gingerol. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 96 (1–2): 207–210.
Zhang, F., K. Thakur, F. Hu, J.-G. Zhang, and Z.-J. Wei. 2017. Cross-talk between 10-gingerol and its anti-cancerous potential: A recent update. Food Function 8:2635–2649.
Brahma Naidu, P., V.V. Uddandrao, R. Ravindar Naik, P. Suresh, B. Meriga, M.S. Begum, R. Pandiyan, and G. Saravanan. 2016. Ameliorative potential of gingerol: Promising modulation of inflammatory factors and lipid marker enzymes expressions in HFD induced obesity in rats. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology 419: 139–147.
Li, Y., B. Xu, M. Xu, D. Chen, Y. Xiong, M. Lian, Y. Sun, Z. Tang, L. Wang, C. Jiang, and Y. Lin. 2017. 6-Gingerol protects intestinal barrier from ischemia/reperfusion-induced damage via inhibition of p38 MAPK to NF-kappaB signalling. Pharmacological Research 119: 137–148.
Gibon, E., L.Y. Lu, K. Nathan, and S.B. Goodman. 2017. Inflammation, ageing, and bone regeneration. Journal of Orthopaedic Translation 10: 28–35.
Chen, L.Z., W.W. Sun, L. Bo, J.Q. Wang, C. Xiu, W.J. Tang, J.B. Shi, H.P. Zhou, and X.H. Liu. 2017. New arylpyrazoline-coumarins: Synthesis and anti-inflammatory activity. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 138: 170–181.
Gu, Q., H. Yang, and Q. Shi. 2017. Macrophages and bone inflammation. Journal of Orthopaedic Translation 10: 86–93.
Dong, L., L. Yin, Y. Zhang, X. Fu, and J. Lu. 2017. Anti-inflammatory effects of ononin on lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells. Molecular Immunology 83: 46–51.
Wu, J., M. Li, L. Liu, Q. An, J. Zhang, J. Zhang, M. Li, W. Duan, D. Liu, Z. Li, and C. Luo. 2013. Nitric oxide and interleukins are involved in cell proliferation of RAW264.7 macrophages activated by viili exopolysaccharides. Inflammation 36 (4): 954–961.
Jeon, H.J., H.J. Kang, H.J. Jung, Y.S. Kang, C.J. Lim, Y.M. Kim, and E.H. Park. 2008. Anti-inflammatory activity of Taraxacum officinale. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 115 (1): 82–88.
Zhang, L.B., Z.T. Man, W. Li, W. Zhang, X.Q. Wang, and S. Sun. 2017. Calcitonin protects chondrocytes from lipopolysaccharide-induced apoptosis and inflammatory response through MAPK/Wnt/NF-kappaB pathways. Molecular Immunology 87: 249–257.
Olbert, M., J. Gdula-Argasinska, G. Nowak, and T. Librowski. 2017. Beneficial effect of nanoparticles over standard form of zinc oxide in enhancing the anti-inflammatory activity of ketoprofen in rats. Pharmacological Reports 69 (4): 679–682.
Sheeba, M.S., and V.V. Asha. 2009. Cardiospermum halicacabum ethanol extract inhibits LPS induced COX-2, TNF-alpha and iNOS expression, which is mediated by NF-kappaB regulation, in RAW264.7 cells. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 124 (1): 39–44.
Bockerstett, K.A., and R.J. DiPaolo. 2017. Regulation of gastric carcinogenesis by inflammatory cytokines. Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology. 4 (1): 47–53.
Chu, C.Q. 2016. Molecular probing of TNF: From identification of therapeutic target to guidance of therapy in inflammatory diseases. Cytokine 101: 64–69.
Hu, P., G.M. Jiang, Y. Wu, B.Y. Huang, S.Y. Liu, D.D. Zhang, Y. Xu, Y.F. Wu, X. Xia, W. Wei, and B. Hu. 2017. TNF-alpha is superior to conventional inflammatory mediators in forecasting IVIG nonresponse and coronary arteritis in Chinese children with Kawasaki disease. Clinica chimica acta. International Journal of Clinical Chemistry 471: 76–80.
Parameswaran, N., and S. Patial. 2010. Tumor necrosis factor-α signaling in macrophages. Critical Reviews™ in. Eukaryotic Gene Expression 20: 87–103.
Szot, P., A. Franklin, D.P. Figlewicz, T.P. Beuca, K. Bullock, K. Hansen, W.A. Banks, M.A. Raskind, and E.R. Peskind. 2017. Multiple lipopolysaccharide (LPS) injections alter interleukin 6 (IL-6), IL-7, IL-10 and IL-6 and IL-7 receptor mRNA in CNS and spleen. Neuroscience 355: 9–21.
Seppola, M., A.N. Larsen, K. Steiro, B. Robertsen, and I. Jensen. 2008. Characterisation and expression analysis of the interleukin genes, IL-1beta, IL-8 and IL-10, in Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.). Molecular Immunology 45 (4): 887–897.
Yang, Q., Q. Chu, X. Zhao, and T. Xu. 2017. Characterization of IL-1beta and two types of IL-1 receptors in miiuy croaker and evolution analysis of IL-1 family. Fish Shellfish Immunology 63: 165–172.
Zhou, L., and D.Y. Zhu. 2009. Neuronal nitric oxide synthase: Structure, subcellular localization, regulation, and clinical implications. Nitric Oxide-Biology and Chemistry 20 (4): 223–230.
Bredt, D.S. 2009. Endogenous nitric oxide synthesis: Biological functions and pathophysiology. Free Radical Research 31 (6): 577–596.
Manferdini, C., F. Paolella, E. Gabusi, L. Gambari, A. Piacentini, G. Filardo, S. Fleury-Cappellesso, A. Barbero, M. Murphy, and G. Lisignoli. 2017. Adipose stromal cells mediated switching of the pro-inflammatory profile of M1-like macrophages is facilitated by PGE2: In vitro evaluation. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage 25 (7): 1161–1171.
Liu, N., Y. Zhuang, Z. Zhou, J. Zhao, Q. Chen, and J. Zheng. 2017. NF-kappaB dependent up-regulation of TRPC6 by Abeta in BV-2 microglia cells increases COX-2 expression and contributes to hippocampus neuron damage. Neuroscience Letters 651: 1–8.
Katanić, J., T. Boroja, V. Mihailović, S. Nikles, S.-P. Pan, G. Rosić, D. Selaković, J. Joksimović, S. Mitrović, and R. Bauer. 2016. In vitro and in vivo assessment of meadowsweet (Filipendula ulmaria) as anti-inflammatory agent. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 193: 627–636.
Perkins, N.D. 1997. Achieving transcriptional specificity with NF-ĸB. Int J Biochem Cell B 29: 1433–1448.
Oeckinghaus, A., and S. Ghosh. 2009. The NF-kappaB family of transcription factors and its regulation. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology 1 (4): a000034.
Gong, J., Q. Chen, Y. Yan, and G. Pang. 2014. Effect of casein glycomacropeptide on subunit p65 of nuclear transcription factor-κB in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated human colorectal tumor HT-29 cells. Food Science and Human Wellness 3 (2): 51–55.
Oh, Y.C., Y.H. Jeong, J.H. Ha, et al. 2014. Oryeongsan inhibits LPS-induced production of inflammatory mediators via blockade of the NF-kappaB, MAPK pathways and leads to HO-1 induction in macrophage cells[J]. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine 14: 242.
Gugasyan, R., R. Grumont, M. Grossmann, et al. 2000. Rel/NF-kappaB transcription factors: Key mediators of B-cell activation[J]. Immunological Reviews 176: 134–140.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the agricultural technology system innovation team of Hebei, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 36 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, N., Sang, Y., Liu, W. et al. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Gingerol on Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated RAW 264.7 Cells by Inhibiting NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Inflammation 41, 835–845 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-018-0737-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-018-0737-3