Abstract
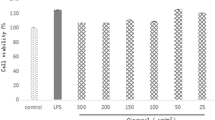
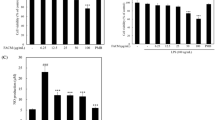
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effects of polydatin (PD) on cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) expressions at protein and transcriptional levels, as well as the production of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) and nitric oxide (NO) in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced macrophage RAW 264.7 cells. To elucidate the underlying mechanism responsible for these symptoms, we investigated the phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway and nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) expression. NO was analyzed with the Griess method. PGE2 was measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). iNOS and COX-2 messenger RNA (mRNA) were identified by qPCR assay. iNOS, COX-2, NF-κB, extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and p38 protein expressions were detected with Western blot. The results revealed that PD effectively inhibited NO and PGE2 production, and it is not surprising that PD reduced iNOS and COX-2 expression at protein and transcriptional levels. Additionally, PD significantly ameliorated the activation of NF-κB and the phosphorylation of MAPKs in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 macrophages. These findings suggested that PD exerted potent anti-inflammatory activity in macrophages.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tao, J.Y., L. Zhao, Z.J. Huang, X.Y. Zhang, S.L. Zhang, Q.G. Zhang, et al. 2008. Anti-inflammatory effects of ethanol extract from Kummerowia striata (Thunb.) Schindl on lps-stimulated RAW 264.7 cell. Inflammation 31: 154–166.
Salvemini, D., H. Ischiropoulos, and S. Cuzzocrea. 2003. Roles of nitric oxide and superoxide in inflammation. Methods in Molecular Biology (Clifton, NJ) 225: 291–303.
Wang, J., Y.T. Liu, L. Xiao, L. Zhu, Q. Wang, T. Yan. 2014. Anti-inflammatory effects of apigenin in lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory in acute lung injury by suppressing COX-2 and NF-kB Pathway. Inflammation. ;37:2085–2090. doi: 10.1007/s10753-014-9942-x.
Mancini, A.D., and J.A. Di Battista. 2011. The cardinal role of the phospholipase A(2)/cyclooxygenase-2/prostaglandin E synthase/prostaglandin E(2) (PCPP) axis in inflammostasis. Inflammation Research: Official Journal of the European Histamine Research Society [Et al.] 60: 1083–1092.
You, R., W. Long, Z. Lai, L. Sha, K. Wu, X. Yu, et al. 2013. Discovery of a potential anti-inflammatory agent: 3-oxo-29-noroleana-1,9(11),12-trien-2,20-dicarbonitrile. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 56: 1984–1995.
Ci, X., R. Ren, K. Xu, H. Li, Q. Yu, Y. Song, et al. 2010. Schisantherin A exhibits anti-inflammatory properties by down-regulating NF-kappaB and MAPK signaling pathways in lipopolysaccharide-treated RAW 264.7 cells. Inflammation 33: 126–136.
Mi Jeong, S., M. Davaatseren, W. Kim, P. Sung Kwang, S.H. Kim, H. Haeng Jeon, et al. 2009. Vitisin A suppresses LPS-induced NO production by inhibiting ERK, p38, and NF-kappaB activation in RAW 264.7 cells. International Immunopharmacology 9: 319–323.
Van Laecke, S., W. Van Biesen, R. Vanholder. 2014. The paradox of bardoxolone methyl: A call for every witness on the stand? Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism. 17:9–14.
Park, K.I., S.R. Kang, H.S. Park, H. do Lee, A. Nagappan, J.A. Kim, et al. 2012. Regulation of proinflammatory mediators via NF-kappaB and p38 MAPK-dependent mechanisms in RAW 264.7 macrophages by polyphenol components isolated from Korea Lonicera japonica THUNB. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine: eCAM 2012: 828521.
Shiyu, S., L. Zhiyu, Y. Mao, B. Lin, W. Lijia, Z. Tianbao, et al. 2011. Polydatin up-regulates Clara cell secretory protein to suppress phospholipase A2 of lung induced by LPS in vivo and in vitro. BMC Cell Biology 12: 31.
Nazimek, K., and K. Bryniarski. 2012. The biological activity of macrophages in health and disease. Postȩpy Higieny i Medycyny Doświadczalnej (Online) 66: 507–520.
Murakami, A., Ohigashi H. Targeting, and NOX. 2007. INOS and COX-2 in inflammatory cells: Chemoprevention using food phytochemicals. International Journal of Cancer Journal International du Cancer 121: 2357–2363.
Xiong, H., Y. Cheng, X. Zhang, and X. Zhang. 2014. Effects of taraxasterol on iNOS and COX-2 expression in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 macrophages. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 155: 753–757.
Botting, R., and S.S. Ayoub. 2005. COX-3 and the mechanism of action of paracetamol/acetaminophen. Prostaglandins, Leukotrienes, and Essential Fatty Acids 72: 85–87.
Chan, M.M., and A.R. Moore. 2010. Resolution of inflammation in murine autoimmune arthritis is disrupted by cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition and restored by prostaglandin E2-mediated lipoxin A4 production. Journal of Immunology (Baltimore, Md: 1950) 184: 6418–6426.
Forstermann, U., I. Gath, P. Schwarz, E.I. Closs, and H. Kleinert. 1995. Isoforms of nitric oxide synthase. Properties, cellular distribution and expressional control. Biochemical Pharmacology 50: 1321–1332.
Ignarro, L.J., G.M. Buga, K.S. Wood, R.E. Byrns, and G. Chaudhuri. 1987. Endothelium-derived relaxing factor produced and released from artery and vein is nitric oxide. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 84: 9265–9269.
Bogdan, C. 2001. Nitric oxide and the immune response. Nature Immunology 2: 907–916.
Asano, K., C.B. Chee, B. Gaston, C.M. Lilly, C. Gerard, J.M. Drazen, et al. 1994. Constitutive and inducible nitric oxide synthase gene expression, regulation, and activity in human lung epithelial cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 91: 10089–10093.
Chen, N., Q. Wu, G. Chi, L.W. Soromou, J. Hou, Y. Deng, et al. 2013. Prime-O-glucosylcimifugin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice. International Immunopharmacology 16: 139–147.
Chen, C.Y., W.H. Peng, K.D. Tsai, and S.L. Hsu. 2007. Luteolin suppresses inflammation-associated gene expression by blocking NF-kappaB and AP-1 activation pathway in mouse alveolar macrophages. Life Sciences 81: 1602–1614.
Romano, M., M. Sironi, C. Toniatti, N. Polentarutti, P. Fruscella, P. Ghezzi, et al. 1997. Role of IL-6 and its soluble receptor in induction of chemokines and leukocyte recruitment. Immunity 6: 315–325.
Geiser, T., K. Atabai, P.H. Jarreau, L.B. Ware, J. Pugin, and M.A. Matthay. 2001. Pulmonary edema fluid from patients with acute lung injury augments in vitro alveolar epithelial repair by an IL-1beta-dependent mechanism. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 163: 1384–1388.
Cheng, B.C., X.Q. Ma, H.Y. Kwan, K.W. Tse, H.H. Cao, T. Su, et al. 2014. A herbal formula consisting of Rosae Multiflorae Fructus and Lonicerae Japonicae Flos inhibits inflammatory mediators in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 153: 922–927.
Miggin, S.M., E. Palsson-McDermott, A. Dunne, C. Jefferies, E. Pinteaux, K. Banahan, et al. 2007. NF-kappaB activation by the Toll-IL-1 receptor domain protein MyD88 adapter-like is regulated by caspase-1. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 104: 3372–3377.
Guha, M., and N. Mackman. 2001. LPS induction of gene expression in human monocytes. Cellular Signalling 13: 85–94.
Choi, C.Y., K.R. Park, J.H. Lee, Y.J. Jeon, K.H. Liu, S. Oh, et al. 2007. Isoeugenol suppression of inducible nitric oxide synthase expression is mediated by down-regulation of NF-kappaB, ERK1/2, and p38 kinase. European Journal of Pharmacology 576: 151–159.
Wu, D., S. Zheng, W. Li, L. Yang, Y. Liu, X. Zheng, et al. 2013. Novel biphasic role of resolvin D1 on expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated lung fibroblasts is partly through PI3K/AKT and ERK2 pathways. Mediators of Inflammation 2013: 964012.
Thalhamer, T., M.A. McGrath, and M.M. Harnett. 2008. MAPKs and their relevance to arthritis and inflammation. Rheumatology (Oxford, England) 47: 409–414.
Lee, Y.S., H.T. Lan Tran, and Q. Van Ta. 2009. Regulation of expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 by JNK in Raw 264.7 cells: Presence of inhibitory factor(s) suppressing MMP-9 induction in serum and conditioned media. Experimental & Molecular Medicine 41: 259–268.
Yun, K.J., J.Y. Kim, J.B. Kim, K.W. Lee, S.Y. Jeong, H.J. Park, et al. 2008. Inhibition of LPS-induced NO and PGE2 production by asiatic acid via NF-kappa B inactivation in RAW 264.7 macrophages: Possible involvement of the IKK and MAPK pathways. International Immunopharmacology 8: 431–441.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lou, T., Jiang, W., Xu, D. et al. Inhibitory Effects of Polydatin on Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated RAW 264.7 Cells. Inflammation 38, 1213–1220 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-014-0087-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-014-0087-8