Abstract
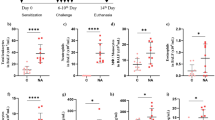
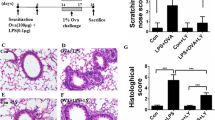
Piperine, one of the active components of black pepper, has been reported to have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. However, the effects of piperine on lipolysaccharide (LPS)-induced acute lung injury (ALI) have not been reported. Thus, the protective effects of piperine against LPS-induced ALI were investigated in this study. LPS-induced lung injury was assessed by histological study, myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity, and inflammatory cytokine production. Our results demonstrated that piperine attenuated LPS-induced MPO activity, lung edema, and inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β production. Histological studies showed that piperine obviously attenuated LPS-induced lung injury. In addition, piperine significantly inhibited LPS-induced NF-κB activation. In conclusion, our results demonstrated that piperine had a protective effect on LPS-induced ALI. The anti-inflammatory mechanism of piperine is through inhibition of NF-κB activation. Piperine may be a potential therapeutic agent for ALI.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hughes, M., I.S. Grant, and F.N. MacKirdy. 2000. Incidence and mortality after acute respiratory failure and acute respiratory distress syndrome in Sweden, Denmark, and Iceland. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 162: 332–332.
Ware, L.B. 2006. Pathophysiology of acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome. Seminars in Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 27: 337–349.
Goodman, R.B., J. Pugin, J.S. Lee, and M.A. Matthay. 2003. Cytokine-mediated inflammation in acute lung injury. Cytokine & Growth Factor Reviews 14: 523–535.
Joh, E.H., W. Gu, and D.H. Kim. 2012. Echinocystic acid ameliorates lung inflammation in mice and alveolar macrophages by inhibiting the binding of LPS to TLR4 in NF-kappa B and MAPK pathways. Biochemical Pharmacology 84: 331–340.
Wu, J., Y.Y. Zhang, L. Guo, H. Li, and D.F. Chen. 2013. Bupleurum polysaccharides attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation via modulating toll-like receptor 4 signaling. PLoS ONE 8: e78051.
Chandrasekar, B., J.B. Smith, and G.L. Freeman. 2001. Ischemia-reperfusion of rat myocardium activates nuclear factor-KappaB and induces neutrophil infiltration via lipopolysaccharide-induced CXC chemokine. Circulation 103: 2296–2302.
Bhatia, M., and S. Moochhala. 2004. Role of inflammatory mediators in the pathophysiology of acute respiratory distress syndrome. Journal of Pathology 202: 145–156.
Ruffini, E., A. Parola, E. Papalia, P.L. Filosso, M. Mancuso, A. Oliaro, G. Actis-Dato, and G. Maggi. 2001. Frequency and mortality of acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome after pulmonary resection for bronchogenic carcinoma. European Journal of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery 20: 30–37.
Vijayakumar, R.S., D. Surya, and N. Nalini. 2004. Antioxidant efficacy of black pepper (Piper nigrum L.) and piperine in rats with high fat diet induced oxidative stress. Redox Report 9: 105–110.
Rauscher, F.M., R.A. Sanders, and J.B. Watkins. 2000. Effects of piperine on antioxidant pathways in tissues from normal and streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Journal of Biochemical and Molecular Toxicology 14: 329–334.
Ying, X.Z., K.H. Yu, X.W. Chen, H. Chen, J.J. Hong, S.W. Cheng, and L. Peng. 2013. Piperine inhibits LPS induced expression of inflammatory mediators in RAW 264.7 cells. Cellular Immunology 285: 49–54.
Bae, G.S., J.J. Kim, K.C. Park, B.S. Koo, I.J. Jo, S.B. Choi, C.H. Lee, W.S. Jung, J.H. Cho, S.H. Hong, et al. 2012. Piperine inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced maturation of bone-marrow-derived dendritic cells through inhibition of ERK and JNK activation. Phytotherapy Research 26: 1893–1897.
Bae, G.S., M.S. Kim, J. Jeong, H.Y. Lee, K.C. Park, B.S. Koo, B.J. Kim, T.H. Kim, S.H. Lee, S.Y. Hwang, et al. 2011. Piperine ameliorates the severity of cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis by inhibiting the activation of mitogen activated protein kinases. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 410: 382–388.
Vaibhav, K., P. Shrivastava, H. Javed, A. Khan, M.E. Ahmed, R. Tabassum, M.M. Khan, G. Khuwaja, F. Islam, M.S. Siddiqui, et al. 2012. Piperine suppresses cerebral ischemia-reperfusion-induced inflammation through the repression of COX-2, NOS-2, and NF-kappa B in middle cerebral artery occlusion rat model. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry 367: 73–84.
Lv, H., C. Zhu, Y. Liao, Y. Gao, G. Lu, W. Zhong, Y. Zheng, W. Chen, and X. Ci. 2015. Tenuigenin ameliorates acute lung injury by inhibiting NF-kappaB and MAPK signalling pathways. Respiratory Physiology & Neurobiology 216: 43–51.
Fu, K., T. Piao, M. Wang, J. Zhang, J. Jiang, X. Wang, and H. Liu. 2014. Protective effect of catalpol on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice. International Immunopharmacology 23: 400–406.
Sato, K., M.B. Kadiiska, A.J. Ghio, J. Corbett, Y.C. Fann, S.M. Holland, R.G. Thurman, and R.P. Mason. 2002. In vivo lipid-derived free radical formation by NADPH oxidase in acute lung injury induced by lipopolysaccharide: a model for ARDS. FASEB Journal 16: 1713–1720.
Gong, J.H., J.P. Gong, J.Z. Li, K. He, P.Z. Li, and X.W. Jiang. 2013. Glycogen synthase kinase 3 inhibitor attenuates endotoxin-induced liver injury. Journal of Surgical Research 184: 1035–1044.
Matsuo, Y., H. Onodera, Y. Shiga, M. Nakamura, M. Ninomiya, T. Kihara, and K. Kogure. 1994. Correlation between myeloperoxidase-quantified neutrophil accumulation and ischemic brain injury in the rat. Effects of neutrophil depletion. Stroke 25: 1469–1475.
Ran, X., S. Chao, Z. Jun-Gang, H. Yun, C. Kuan-Bing, and S. Wen-Jun. 2014. Protective effect of veratric acid on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice. European Journal of Pharmacology 740: 227–232.
Tianzhu, Z., Y. Shihai, and D. Juan. 2014. The effects of morin on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by suppressing the lung NLRP3 inflammasome. Inflammation 37: 1976–1983.
Halbertsma, F.J.J., M. Vaneker, G.J. Scheffer, and J.G. van der Hoeven. 2005. Cytokines and biotrauma in ventilator-induced lung injury: a critical review of the literature. Netherlands Journal of Medicine 63: 382–392.
Feng, J., Xiao, B., Chen, W., Ding, T., Chen, L., Yu, P., Xu, F., Zhang, H., Liu, Z., Liang, G. 2015. Synthesis and anti-inflammatory evaluation of novel C66 analogs for the treatment of LPS-induced acute lung injury. Chem Biol Drug Des.
Sun, Y., Y. Zhao, J. Yao, L. Zhao, Z. Wu, Y. Wang, D. Pan, H. Miao, Q. Guo, and N. Lu. 2015. Wogonoside protects against dextran sulfate sodium-induced experimental colitis in mice by inhibiting NF-kappaB and NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Biochemical Pharmacology 94: 142–154.
Zhao, Z., X. Tang, X. Zhao, M. Zhang, W. Zhang, S. Hou, W. Yuan, H. Zhang, L. Shi, H. Jia, et al. 2014. Tylvalosin exhibits anti-inflammatory property and attenuates acute lung injury in different models possibly through suppression of NF-kappaB activation. Biochemical Pharmacology 90: 73–87.
Wang, L.L., Y. Xu, Q. Yu, Q. Sun, Y. Xu, Q. Gu, and X. Xu. 2014. H-RN, a novel antiangiogenic peptide derived from hepatocyte growth factor inhibits inflammation in vitro and in vivo through PI3K/AKT/IKK/NF-kappa B signal pathway. Biochemical Pharmacology 89: 255–265.
Yang, P., Y. Han, L. Gui, J. Sun, Y.L. Chen, R. Song, J.Z. Guo, Y.N. Xie, D. Lu, and L. Sun. 2013. Gastrodin attenuation of the inflammatory response in H9c2 cardiomyocytes involves inhibition of NF-kappaB and MAPKs activation via the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling. Biochemical Pharmacology 85: 1124–1133.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, Y., Liu, J., Li, H. et al. Piperine Ameliorates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury via Modulating NF-κB Signaling Pathways. Inflammation 39, 303–308 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-015-0250-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-015-0250-x