Abstract
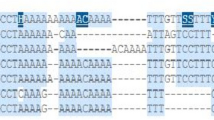
Chronic inflammation triggers DNA damage and oncogenic mutations and causes tumor formation and tumor progression. One of the important components of the inflammatory response is Toll-like receptor (TLR) family. The objective of our study is to determine the relationship between rs4986790(+896A/G) and rs4986791(+1196C/T) gene polymorphisms and lung cancer risk. PCR-RFLP technique was carried out to identify the genotypes in 100 control individuals and 160 lung cancer patients. DNA extracted from peripheral blood samples were amplified and digested with NcoI and HinfI then visualized. We did not find any difference between genotype frequencies between controls and patients (p > 0.05) in rs4986790. But a significant difference between control group and patients with lung cancer as for genotype frequencies (χ 2 = 4.19, p = 0.041) in rs4986791 variants was found. Our data indicate that any correlation was not found between rs4986790 polymorphism and lung cancer, while a correlation between rs4986791 and lung cancer has been determined and found to be associated with lung cancer risk.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bosch, F., Cancer Etiology, in Manual of Clinical Oncology. 1994, Springer. p. 56–90.
Lu, Z., A. Murday, and C. Bennett, Cancer Screening and Prevention. Prevention Practice in Primary Care, 2013: p. 93.
Stewart, B.W., P. Kleihues, and I.A.f.R.o. Cancer. 2003. World cancer report. Vol. 57. Lyon: IARC press.
Takahashi, H., et al. 2010. Tobacco smoke promotes lung tumorigenesis by triggering IKKβ-and JNK1-dependent inflammation. Cancer Cell 17(1): 89–97.
Kratz, A., et al. 1996. Chronic inflammation caused by lymphotoxin is lymphoid neogenesis. The Journal of Experimental Medicine 183(4): 1461–1472.
Hofseth, L.J., and M.J. Wargovich. 2007. Inflammation, cancer, and targets of ginseng. The Journal of Nutrition 137(1): 183S–185S.
Aggarwal, B.B., et al. 2006. Inflammation and cancer: how hot is the link? Biochemical Pharmacology 72(11): 1605–1621.
Becker, C.E. and L.A. O’Neill. Inflammasomes in inflammatory disorders: the role of TLRs and their interactions with NLRs. in Seminars in immunopathology. 2007. Springer.
Lafferty, E.I., S.T. Qureshi, and M. Schnare. 2010. The role of toll-like receptors in acute and chronic lung inflammation. J Inflamm (Lond) 7: 57.
Oberholzer, A., C. Oberholzer, and L.L. Moldawer. 2001. Sepsis syndromes: understanding the role of innate and acquired immunity. Shock 16(2): 83–96.
Hayashi, F., et al. 2001. The innate immune response to bacterial flagellin is mediated by Toll-like receptor 5. Nature 410(6832): 1099–1103.
He, W., et al. 2007. TLR4 signaling promotes immune escape of human lung cancer cells by inducing immunosuppressive cytokines and apoptosis resistance. Molecular Immunology 44(11): 2850–2859.
Wang, E., et al. 2010. High expression of Toll-like receptor 4/myeloid differentiation factor 88 signals correlates with poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. British Journal of Cancer 102(5): 908–915.
Szajnik, M., et al. 2009. TLR4 signaling induced by lipopolysaccharide or paclitaxel regulates tumor survival and chemoresistance in ovarian cancer. Oncogene 28(49): 4353–4363.
Kutikhin, A.G. 2011. Impact of Toll-like receptor 4 polymorphisms on risk of cancer. Human Immunology 72(2): 193–206.
Achyut, B., et al. 2007. Association of Toll-like receptor–4 (Asp299Gly and Thr399Ileu) gene polymorphisms with gastritis and precancerous lesions. Human Immunology 68(11): 901–907.
Rigoli, L., et al. 2010. TLR4 and NOD2/CARD15 genetic polymorphisms and their possible role in gastric carcinogenesis. Anticancer Research 30(2): 513–517.
Srivastava, K., et al. 2010. Significant association between toll‐like receptor gene polymorphisms and gallbladder cancer. Liver International 30(7): 1067–1072.
Chen, Y.-C., et al. 2005. Sequence variants of Toll-like receptor 4 and susceptibility to prostate cancer. Cancer Research 65(24): 11771–11778.
Tsilidis, K.K., et al. 2009. Association of common polymorphisms in IL10, and in other genes related to inflammatory response and obesity with colorectal cancer. Cancer Causes & Control 20(9): 1739–1751.
Ak, G., et al. 2007. Lung cancer in individuals less than 50 years of age. Lung 185(5): 279–286.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Research Foundation of Eskisehir Osmangazi University, grant number 201311D08. We thank all consultants, staff, general practitioners, and interviewees who participated in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kurt, H., Ozbayer, C., Bayramoglu, A. et al. Determination of the Relationship Between rs4986790 and rs4986791 Variants of TLR4 Gene and Lung Cancer. Inflammation 39, 166–171 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-015-0235-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-015-0235-9