Abstract
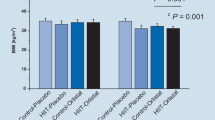
Physical activity has been shown to lower levels of inflammatory markers. However, results are inconsistent, indicating different modes of exercise may have different effects on inflammatory cytokines. We aimed to investigate the effects of 12 weeks of moderate-intensity aerobic, resistance, or combination exercise on TNF-α and IL-6 compared to no exercise in overweight and obese individuals. TNF-α levels were significantly decreased at week 12 compared to baseline by 20.8 % in the Aerobic group (p = 0.011), 26.9 % in the Resistance group (p = 0.0001), and 32.6 % in the Combination group (p = 0.003). Levels of TNF-α were significantly lower in the Combination compared to the Control group after 12 weeks of exercise training (−22.6 %, p = 0.025) when adjusting for baseline levels. Twelve weeks of moderate-intensity aerobic, resistance, but mainly combination exercise training decreased TNF-α in overweight and obese individuals compared to no exercise. Therefore, combination exercise training may be physiologically relevant in decreasing the risk of developing chronic diseases.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bruunsgaard, H. 2005. Physical activity and modulation of systemic low-level inflammation. Journal of Leukocyte Biology 78: 819–835.
Haffner SM. 2007. Abdominal adiposity and cardiometabolic risk: do we have all the answers? The American Journal of Medicine 120(9A): S10–17.
Kern, P.A., S. Ranganathan, C. Li, L. Wood, and G. Ranganathan. 2001. Adipose tissue tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-6 expression in human obesity and insulin resistance. American Journal of Physiology, Endocrinology and Metabolism 280: 745–751.
Nicklas, B.J., W. Ambrosius, S.P. Messier, G.D. Miller, B.W.J.H. Penninx, R.F. Loeser, S. Palla, E. Bleecker, and M. Pahor. 2004. Diet-induced weight loss, exercise, and chronic inflammation in older, obese adults: a randomized controlled clinical trial. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 79: 544–551.
Olson, T.P., D.R. Dengel, A.S. Leon, and K.H. Schmitz. 2007. Changes in inflammatory biomarkers following one-year of moderate resistance training in overweight women. International Journal of Obesity 31: 996–1003.
Niebauer, J. 2008. Effects of exercise training on inflammatory markers in patients with heart failure. Heart Failure Reviews 13(1): 39–49.
Straczkowski, M., I. Kowalska, S. Dzienis-Straczkowska, A. Stepien, E. Skibiriska, M. Szelachowska, and I. Kinalska. 2001. Changes in tumor necrosis factor-α system and insulin sensitivity during an exercise training program in obese women with normal and impaired glucose tolerance. European Journal of Endocrinology 145: 273–290.
Ziccardi, P., F. Nappo, G. Giugliano, K. Esposito, R. Marfella, M. Cioffi, F. D'Andrea, A.M. Molinari, and D. Giugliano. 2002. Reduction of inflammatory cytokine concentrations and improvement of endothelial functions in obese women after weight loss over one year. Circulation 105: 804–809.
Benson, S., O.E. Janssen, S. Hahn, S. Tan, T. Dietz, K. Mann, K. Pleger, M. Schedlowski, P.C. Arck, and S. Elsenbruch. 2008. Obesity, depression, and chronic low-grade inflammation in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Brain, Behavior, and Immunity 22: 177–184.
Cartier, A., I. Lemieux, N. Alméras, A. Tremblay, J. Bergeron, and J.-P. Després. 2008. Visceral obesity and plasma glucose-insulin homeostasis: contributions of interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α in men. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 93: 1931–1938.
Peterson, A.M.W., and B.K. Pederson. 2006. The role of IL-6 in mediating the anti-inflammatory effects of exercise. Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology 57(Suppl 10): 43–51.
Fontana, L., J.C. Eagon, M.E. Trujillo, P. Scherer, and S. Klein. 2007. Visceral fat adipokine secretion is associated with systemic inflammation in obese humans. Diabetes 56: 1010–1013.
Suzuki, K., J. Peake, K. Nosaka, M. Okutsu, C.R. Abbiss, R. Surriano, D. Bishop, M.J. Quod, H. Lee, D.T. Martin, et al. 2006. Changes in markers of muscle damage, inflammation and HSP70 after an Ironman Triathlon race. European Journal of Applied Physiology 8(6): 525–534.
Panagiotakos, D.B., C. Pitsavos, C. Chrysohoou, S. Kavouras, and C. Stefanadis. 2005. The associations between leisure-time physical activity and inflammatory and coagulation markers related to cardiovascular disease: the ATTICA Study. Preventive Medicine 40: 432–437.
Kondo, T., I. Kobayashi, and M. Murakami. 2006. Effect of exercise on circulating adipokine levels in obese young women. Endocrine Journal 53(2): 189–195.
Dekker, M.J., S. Lee, R. Hudson, K. Kilpatrick, T.E. Graham, R. Ross, and L.E. Robinson. 2007. An exercise intervention without weight loss decreases circulating interleukin-6 in lean and obese men with and without type 2 diabetes mellitus. Metabolism 56: 332–338.
Polak, J., E. Klimcakova, C. Moro, N. Viguerie, M. Berlan, J. Hejnova, B. Richterova, I. Kraus, D. Langin, and V. Stich. 2006. Effect of aerobic training on plasma levels and subcutaneous abdominal adipose tissue gene expression of adiponectin, leptin, interleukin 6, and tumor necrosis factor α in obese women. Metabolism 55: 1375–1381.
Marcell, T.J., K.A. McAuley, T. Traustadóttir, and P.D. Reaven. 2005. Exercise training is not associated with improved levels of C-reactive protein or adiponectin. Metabolism 54: 533–541.
Stensvold, D., S.A. Slørdahl, and U. Wisløff. 2012. Effect of exercise training on inflammation status among people with metabolic syndrome. Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders 10(4): 267–272.
Stewart, L.K., M.G. Flynn, W.W. Campbell, B.A. Craig, J. Robinson, K.L. Timmerman, B.K. McFarlin, P.M. Coen, and E. Talbert. 2007. The influence of exercise training on inflammatory cytokines and C-reactive protein. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise 39(10): 1714–1719.
Oberbach, A., A. Tönjas, N. Klöting, M. Fasshauer, J. Kratzsch, M.W. Busse, R. Paschke, M. Stumvoll, and M. Blüher. 2006. Effect of a 4 week physical training program on plasma concentrations of inflammatory markers in patients with abnormal glucose tolerance. European Journal of Endocrinology 154: 577–585.
Balducci, S., S. Zanuso, A. Nicolucci, F. Fernando, S. Cavallo, P. Cardelli, S. Fallucca, E. Alessi, C. Letizia, A. Jimenez, et al. 2010. Anti-inflammatory effect of exercise training in subjects with type 2 diabetes and the metabolic syndrome is dependent on exercise modalities and independent of weight loss. Nutrition, Metabolism, and Cardiovascular Diseases 20: 608–617.
Ho, S.S., S.S. Dhaliwal, A.P. Hills, and S. Pal. 2012. The effect of 12 weeks of aerobic, resistance or combination exercise training on cardiovascular risk factors in the overweight and obese in a randomized trial. BMC Public Health 12(1): 704. doi:10.1186/1471-2458-12-704.
Ho SS, Radavelli-Bagatini S, Dhaliwal SS, Hills AP, Pal S. 2012. Resistance, aerobic, and combination training on vascular function in overweight and obese adults. The Journal of Clinical Hypertension (Greenwich) 14(12): 848–854. doi:10.1111/j.1751-7176.2012.00700.x.
Karvonen, M.J., E. Kentale, and O. Mustala. 1957. The effects of training on heart rate: a longitudinal study. Annales Medicinae Experimentalis et Biologiae Fenniae 35(3): 307–315.
Ho, S.S., S.S. Dhaliwal, A. Hills, and S. Pal. 2011. Acute exercise improves postprandial cardiovascular risk factors in overweight and obese individuals. Atherosclerosis 214(1): 178–184.
Pal, S., A. Khossousi, C. Binns, S. Dhaliwal, and V. Ellis. 2011. The effect of a fibre supplement compared to a healthy diet on body composition, lipids, glucose, insulin and other metabolic syndrome risk factors in overweight and obese individuals. British Journal of Nutrition 105: 90–100.
O'Leary, V.B., C.M. Marchetti, R.K. Krishnan, B.P. Stetzer, F. Gonzalez, and J.P. Kirwan. 2006. Exercise-induced reversal of insulin resistance in obese elderly is associated with reduced visceral fat. Journal of Applied Physiology 100: 1584–1589.
Pedersen, B.K., H. Bruunsgaard, M. Klokker, N. Kappel, D.A. MacLean, H.B. Nielsen, T. Rohde, H. Ullum, and M. Zacho. 1997. Exercise-induced immunomodulation—possible roles of neuroendocrine and metabolic factors. International Journal of Sports Medicine 18(Suppl 1): S2–7.
Monzillo, L.U., O. Handy, E.S. Horton, S. Ledbury, C. Mullooly, C. Jarema, S. Porter, K. Ovalle, A. Moussa, and C.S. Mantzpros. 2003. Effect of lifestyle modification on adipokine levels in obese subjects with insulin resistance. Obesity Research 11: 1048–1054.
Fisher, G., T.C. Hyatt, G.R. Hunter, R.A. Oster, R.A. Desmond, and B.A. Gower. 2011. Effect of diet with and without exercise training on markers of inflammation and fat distribution in overweight women. Obesity 19(6): 1131–1136.
Adamopoulos, S., J. Parissis, C. Kroupis, M. Georgiadis, D. Karatzas, G. Karavolias, K. Koniavitou, A.J.S. Coats, and D.T. Kremastinos. 2001. Physical training reduces peripheral markers of inflammation in patients with chronic heart failure. European Heart Journal 22: 791–797.
Larsen, A.I., P. Aukrust, T. Aarsland, and K. Dickstein. 2001. Effect of aerobic exercise training on plasma levels of tumor necrosis factor alpha in patients with heart failure. The American Journal of Cardiology 88: 805–808.
Conraads, V.M., P. Beckers, J. Bosmans, L.S. De Clerck, W.J. Stevens, C.J. Vrints, and D.L. Brutsaert. 2002. Combined endurance/resistance training reduces plasma TNF-α receptor levels in patients with chronic heart failure and coronary artery disease. European Heart Journal 23: 1854–1860.
Goldhammer, E., A. Tanchilevitch, I. Maor, Y. Beniamini, U. Rosenschein, and M. Sagiv. 2005. Exercise training modulates cytokines activity in coronary heart disease patients. International Journal of Cardiology 100: 93–99.
Nindl, B.C., D.E. Scofield, C.A. Strohbach, A.J. Centi, R.K. Evans, R. Yanovich, and D.S. Moran. 2012. IGF-I, IGFBPs, and inflammatory cytokine responses during gender-integrated Israeli army basic combat training. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research 26(7): S73–S81.
Carey, A.L., and M.A. Febbraio. 2004. Interleukin-6 and insulin sensitivity: friend or foe? Diabetologia 47: 1135–1142.
Acknowledgments and Contributions
SH coordinated the trial, conducted data collection, and had input into the manuscript. APH had input into the writing of the manuscript and SSD provided statistical oversight. SSD developed the statistical analysis protocol and performed statistical analysis in conjunction with SH. SP conceived and designed the study, supervised the study and the statistical analysis, and mentored SH. The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest. This trial was partially funded by Curtin DRG grant and ATN Centre for Metabolic Fitness.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ho, S.S., Dhaliwal, S.S., Hills, A.P. et al. Effects of Chronic Exercise Training on Inflammatory Markers in Australian Overweight and Obese Individuals in a Randomized Controlled Trial. Inflammation 36, 625–632 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-012-9584-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-012-9584-9