Abstract
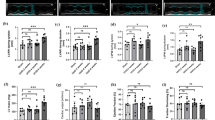
To observe the influence of Baicalin and Octreotide on liver and kidney of rats with severe acute pancreatitis (SAP) and discuss the related mechanism. SAP rats were randomly divided into model control, Baicalin treated and Octreotide treated group (n = 45). The same number of normal rats were included in sham-operated group (n = 45). In all groups, the mortality rate, pathological changes as well as expression levels of NF-κB p65 and P-selectin protein in liver and kidney were observed at 3, 6 and 12 h after operation. The survival rate of treated group was 100% at 12 h significantly higher than that of model control group (P < 0.05). The pathological changes of liver and kidney in treated groups were alleviated to different degrees, the NF-κB protein expression levels and pathological severity scores in liver and kidney of treated groups were significantly lower than those of model control group (P < 0.05 or P < 0.001). The hepatic P-selectin protein expression level in Baicalin treated group was significantly lower than that of model control group at 3 h (P < 0.01), and renal P-selectin expression level in Baicalin treated group at 3 and 6 h were significantly lower than those of model control group and Octreotide treated group (P < 0.01). (1) Early treatment with Baicalin or Octreotide have obvious protecting effects on liver and kidney injuries in SAP with their mechanisms associated to inhibiting NF-κB and P-selectin expression of liver and kidney. (2) Comparing the pharmacologic effects of Octreotide and Baicalin, we believe Baicalin as a new drug with its protecting effects on liver and kidney of SAP rats similar to Octreotide is worth further studying. (3) The advantages of tissue microarrays in pathological examination include time and energy saving and highly efficient. But the restriction of small diameter weakens the representation of tissues to various extents, which may lead to the deviation of analysis.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mofidi, R., M. D. Duff, S. J. Wigmore, K. K. Madhavan, O. J. Garden, and R. W. Parks. 2006. Association between early systemic inflammatory response, severity of multiorgan dysfunction and death in acute pancreatitis. Br. J. Surg. 93(6):738–44 PMID: 16671062. . doi:10.1002/bjs.5290.
Hirota, M., H. Sugita, K. Maeda, A. Ichibara, and M. Ogawa. 2004. Concept of SIRS and severe acute pancreatitis. Nippon Rinsho. 62:2128–2136 PMID: 155528993.
Bumbasirevic, V., D. Radenkovic, Z. Jankovic, A. Karamarkovic, B. Jovanovic, N. Milic, I. Palibrk, and N. Ivancevic. 2008. Severe acute pancreatitis: overall and early versus late mortality in intensive care units. Pancreas. 37(3):e74–82 Sep 12. PMID: 18815542
Kucuktulu, U., E. Alhan, C. Ercin, A. Cinel, and A. Calik. 1999. Effects of Octreotide on acute pancreatitis of varying severity in rats. Eur. J. Surg. 165(9):891–896 PMID: 10533767. doi:10.1080/11024159950189410.
Czakó, L., P. Hegyi, T. Takács, C. Gǒg, A. Farkas, and Y. Mándy. 2004. Effects of Octreotide on acute necrotizing pancreatitis in rabbits. World J. Gastroenterol. 10(14):2082–2086 PMID: 15237439.
Paran, H., A. Mayo, D. Paran, D. Neufeld, I. Shwartz, R. Zissin, P. Singer, O. Kaplan, Y. Skornik, and U. Freund. 2000. Octreotide treatment in patients with severe acute pancreatitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 45(11):2247–2251 PMID: 11215748. doi:10.1023/A:1026679106463.
Riazanov, D. I. 2005. Application of octrestatin in the treatment of patients with acute pancreatitis. Klin. Khir. 9:15–17 Ukrainian.
Shor, N. A., V. P. Levina, I. V. Ioffe, I. V. Andreeva, I. F. Chumak, V. I. Zhadanov, and I. I. Zelenyĭ. 2004. Application of octreotide in patients with acute pancreatitis. Klin. Khir. 2:15–7 Russian.
Cheng, R. C., J. Z. Wang, W. L. Ma, C. Diao, and H. Y. Luo. 2005. Protective effects of Octreotide on hepatocytes apoptosis induced by pancreatitis associated ascitic fluid in rats. Chin. J. Exp. Surg. 22(8):947–949 in Chinese.
Tang, C. L., L. Zhang, and S. D. Zhang. 1996. Experimental study of using Octreotide in treatment of acute pancreatitis. Journal of Hepatopancreatobiliary Surgery. 8(3):99–100 09.15 (in Chinese).
Zhang, X. P., H. Tian, and Q. H. Cheng. 2003. The current situation in pharmacological study on Baicalin. Chinesr. Pharmacol. Bull. 19(11):1212–1215 in Chinese.
Liu, I. X., D. G. Durham, and R. M. Richards. 2000. Baicalin synergy with beta-lactam antibiotics against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and other beta-lactam-resistant strains of Saureus. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 52(3):361–366 PMID: 10757427. doi:10.1211/0022357001773922.
Zhang, X. P., L. Zhang, J. X. He, R. P. Zhang, Q. H. Cheng, Y. F. Zhou, and B. Lu. 2007. Experimental study of therapeutic efficacy of Baicalin in rats with severe acute pancreatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 13(5):717–724 PMID: 17278194.
Zhang, X. P., L. Zhang, P. Yang, R. P. Zhang, and Q. H. Cheng. 2008. Protective effects of Baicalin and Octreotide on multiple organ injury in severe acute pancreatitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 53(2):581–591 PMID: 17549629. doi:10.1007/s10620-007-9868-3.
Zhang, X. P., H. Tian, Y. H. Lai, L. Chen, L. Zhang, Q. H. Cheng, W. Yan, Y. Li, Q. Y. Li, Q. He, and F. Wang. 2007. Protective effects and mechanisms of Baicalin and octreotide on renal injury of rats with severe acute pancreatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 13(38):5079–5089 PMID: 17876873.
Xiping, Z., T. Hua, C. Hanqing, C. Li, W. Zhiwei, W. Keyi, Y. Wei, L. Yun, L. Qingyu, H. Qing, and W. Fei. 2007. The protecting effects and mechanisms of Baicalin and Octreotide on heart injury in rats with SAP. Mediators Inflamm. 2007:19469 PMID: 18274634.
Aho, H. J. 1980. Experimental pancreatitis in the rats: sodium taurocholate-induced acute hemorrhagic pancreatitis. Scand J. Gastroenterol. 15(4):411–416.
Zhang, X. P., Q. Ye, X. G. Jiang, M. L. Ma, F. B. Zhu, R. P. Zhang, and Q. H. Cheng. 2007. Preparation method of an ideal model of multiple organ injury of rat with severe acute pancreatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 13(34):4566–4573 PMID: 17729407.
Zhang, X. P., L. Zhang, L. J. Chen, Q. H. Cheng, J. M. Wang, W. Cai, H. P. Shen, and J. Cai. 2007. Influence of dexamethasone on inflammatory mediators and NF-kappaB expression in multiple organs of rats with severe acute pancreatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 13(4):548–556 PMID: 17278220. doi:10.3748/wjg.13.6385.
Zhang, X., L. Chen, L. Luo, H. Tian, G. Feng, Y. Cai, R. Xu, K. Wang, and Z. Wang. 2008. Study of the protective effects of dexamethasone on ileum mucosa injury in rats with severe acute pancreatitis. Pancreas. 37(3):e74–e82. doi:10.1097/MPA.0b013e3181800d11.
Zhang, X. P., L. Zhang, Y. Wang, Q. H. Cheng, J. M. Wang, W. Cai, H. P. Shen, and J. Cai. 2007. Study of the protective effects of dexamethasone on multiple organ injury in rats with severe acute pancreatitis. JOP. 8(4):400–412 PMID: 17625291.
Bhatia, M., F. L. Wong, Y. Cao, H. Y. Lau, J. Huang, P. Puneet, and L. Chevali. 2005. Pathophysiology of acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology. 5(2–3):132–144 PMID: 15849484. doi:10.1159/000085265.
Zhang, X. P., Q. Lin, and Y. F. Zhou. 2007. Progress of study on the relationship between mediators of inflammation and apoptosis in acute pancreatitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 52(5):1199–1205 Review. PMID: 17372825. doi:10.1007/s10620-006-9388-6.
Liu, R. L., M. L. Liu, L. L. Ma, and W. Wu. 2005. Effect of ulinastatin on nuclear factor-κB expression in acute necrotic pancreatitis in rats. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi. 13(22):2700–2703 in Chinese.
Telek, G., R. Ducroc, J. Y. Scoazec, C. Pasquier, G. Feldmann, and C. Roze. 2001. Differential upregulation of cellular adhesion molecules at the sites of oxidative stress in experimental acute pancreatitis. J. Surg. Res. 96(1):56–67 PMID: 11180997. doi:10.1006/jsre.2000.6052.
Norman, J. 1998. The role of cytokines in the pathogenesis of acute pancreatitis. Am. J. Surg. 175:76–83 PMID: 9445247. doi:10.1016/S0002-9610(97)00240-7.
Vaquero, E., I. Gukovsky, V. Zaninovic, A. S. Gukovskaya, and S. J. Pandol. 2001. Localized pancreatic NF-kappaB activation and inflammatory response in taurocholate-induced pancreatitis. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 280:G1197–G1208 PMID: 11352813.
Gray, K. D., M. O. Simovic, T. S. Blackwell, J. W. Christman, A. K. May, K. S. Parman, W. C. Chapman, and S. C. Stain. 2006. Activation of nuclear factor kappa B and severe hepatic necrosis may mediate systemic inflammation in choline-deficient/ethionine-supplemented diet-induced pancreatitis. Pancreas. 33(3):260–267 PMID: 17003648. doi:10.1097/01.mpa.0000240599.95817.34.
Su, J. R. , Z. C. Zhao, W. L. Chen, and X. Wang. 2003. The effect of activated nuclear factor-kappaB in pathogenesis of acute pancreatitis. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 17:1497–500 PMID: 14521729.
Satoh, A., T. Shimosegawa, M. Fujita, K. Kimura, A. Masamune, M. Koizumi, and T. Toyota. 1999. Inhibition of nuclear factor-kappaB activation improves the survival rate of rats with taurocholate pancreatitis. Gut. 44(2):253–258 PMID: 9895386.
Zhang, X. P., and Q. Xie. 2005. Study progress of Somatostain and its analog to treat acute pancreatitis. Zhongguo Zhongxiyi Jiehe Waike Zazhi. 11(4):365–367 in Chinese.
Lundberg, A. H., D. N. Granger, J. Russell, O. Sabek, J. Henry, L. Gaber, M. Kotb, and A. O. Gaber. 2000. Quantitative measurement of P- and E-selectin adhesion molecules in acute pancreatitis: correlation with distant organ injury. Ann. Surg. 231(2):213–222 [PMID:10674613].
Kameda, H., I. Morita, M. Handa, J. Kaburaki, T. Yoshida, T. Mimori, S. Murota, and Y. Ikeda. 1997. Re-expression of functional P-selectin molecules on the endothelial cell surface by repeated stimulation with thrombin. Br. J. Haematol. 97(2):348–355 PMID: 9163601.
Ushiyama, S., T. M. Laue, K. L. Moore, H. P. Erickson, and R. P. McEver. 1993. Structural and functional characterization of monomeric soluble P-selectin and comparison with membrane P-selectin. J. Biol. Chem. 268(20):15229–37 PMID: 7686912.
Martinez-Mier, G., L. H. Toledo-Pereyra, J. E. McDuffie, R. L. Warner, and P. A. Ward. 2000. P-selectin and chemokine response after liver ischemia and reperfusion. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 191(4):395–402 PMID: 11030245. doi:10.1016/S1072-7515(00)00360-4.
Singbartl, K., S. A. Green, and K. Ley. 2000. Blocking P-selectin protects from ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute renal failure. FASEB J. 14(1):48–54 PMID: 10627279.
Kononen, J., L. Bubendorf, A. Kallioniemi, M. Barlund, P. Schraml, S. Leighton, J. Torhorst, M. J. Mihatsch, G. Sauter, and O. P. Kallioniemi. 1998. Tissue microarrays for high-throughput molecular profiling of tumor specimens. Nat. Med. 4(7):844–847 PMID: 9662379. doi:10.1038/nm0798-844.
Bentzen, S. M., F. M. Buffa, and G. D. Wilson. 2008. Multiple biomarker tissue microarrays: bioinformatics and practical approaches. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 27(3):481–494 Review. PMID: 18437294. doi:10.1007/s10555-008-9145-8.
Pick, E., M. M. McCarthy, and H. M. Kluger. 2008. Assessing expression of apoptotic markers using large cohort tissue microarrays. Methods Mol. Biol. 414:83–93 Review. PMID: 18175814.
Zellweger, T., C. Ninck, M. Mirlacher, M. Annefeld, A. G. Glass, T. C. Gasser, M. J. Mihatsch, E. P. Gelmann, and L. Bubendorf. 2003. Tissue microarray anaysis reveals prognostic significance of syndecan·1 expression in prostate cancer. Prostate. 55(1):20–29 PMID: 12640657. doi:10.1002/pros.10209.
Wulfing, P., R. Diallo, C. Muller, C. Wulfing, C. Poremba, A. Heinecke, A. Rody, R. R. Greb, W. Bocker, and L. Kiesel. 2003. Analysis of cyclooxygenase 2 expression in human breast cancer: high throughput tissue microarray analysis. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 129(7):375–382 PMID: 12884024. doi:10.1007/s00432-003-0459-1.
Parker, R. L., D. G. Huntsman, D. W. Lesack, J. B. Cupples, D. R. Grant, M. Akbari, and C. B Gilks. 2002. Assessment of interlaboratory variation in the immunohistochemical determination of estrogen receptor status using a breast cancer tissue microaray. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 117(5):723–728 PMID: 12090420. doi:10.1309/PEF8-GL6F-YWMC-AG56.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by Technological Foundation Project of Traditional Chinese Medicine Science of Zhejiang Province, NO. 2003C130 and NO. 2004C142; Foundation Project for Medical Science and Technology of Zhejiang province, NO. 2003B134; Grave Foundation Project for Technological and Development of Hangzhou, NO. 2003123B19; Intensive Foundation Project for Technology of Hangzhou, NO. 2004Z006; Foundation Project for Medical Science and Technology of Hangzhou, NO.2003A004; and Foundation Project for Technology of Hangzhou, NO. 2005224
Note: We claimed that this paper was original and would not have any financial interest in a company or its competitor, and that all authors meet criteria for authorship. We abided the ethics in this animal experiment study. The ethics committee approval of our hospital was secured for the animal study reported, and all rats have not been abused and executive mercifully killing when the observing time in this study was over.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiping, Z., Jie, Z., Qin, X. et al. Influence of Baicalin and Octreotide on NF-κB and P-Selectin Expression in Liver and Kidney of Rats with Severe Acute Pancreatitis. Inflammation 32, 1–11 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-008-9096-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-008-9096-9