Abstract
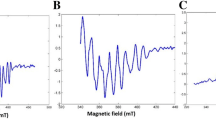
Understanding the structure of oxygen evolving complex (OEC) fully still remains a challenge. Lately computational chemistry with the data from more detailed X-ray diffraction (XRD) OEC structure, has been used extensively in exploring the mechanisms of water oxidation in the OEC (Gatt et al., J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 104(1–2), 80–93 2011). Knowledge of the oxidation states is very crucial for understanding the core principles of catalysis by photosystem II (PSII) and catalytic mechanism of OEC. The present study involves simulation studies of the X-band continuous wave electron-magnetic resonance (CW-EPR) generated S 2 state signals, to investigate whether the data is in agreement with the four manganese ions in the OEC, being organised as a ‘3 + 1’ (trimer plus one) model (Gatt et al., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 51, 12025–12028 2012; Petrie et al., Chem. A Eur. J. 21, 6780–6792 2015; Terrett et al., Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 50, 8–11 2014) or ‘dimer of dimers’ model (Terrett et al. 2016). The question that still remains is how much does each Mn ion contribute to the “ g2multiline” signal through its hyperfine interactions in OEC also to differentiate between the ‘high oxidation state (HOS)’ and ‘low oxidation state (LOS)’ paradigms? This is revealed in part by the structure of multiline (ML) signal studied in this project. Two possibilities have been proposed for the redox levels of the Mn ions within the catalytic cluster, the so called ‘HOS’ and ‘LOS’ paradigms (Gatt et al., J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 104(1–2), 80–93 2011). The method of data analysis involves numerical simulations of the experimental spectra on relevant models of the OEC cluster. The simulations of the X-band CW-EPR multiline spectra, revealed three manganese ions having hyperfine couplings with large anisotropy. These are most likely Mn III centres and these clearly support the ‘LOS’ OEC paradigm model, with a mean oxidation of 3.25 in the S2 state. This is consistent with the earlier data by Jin et al. (Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. (PCCP) 16(17), 7799–812 2014), but the present results clearly indicate that heterogeneity in hyperfine couplings exist in samples as typically prepared.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gatt, P., Stranger, R., Pace, R.: Application of computational chemistry to understanding the structure and mechanism of the Mn catalytic site in photosystem II–a review. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 104(1–2), 80–93 (2011). Available at, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21396828
Jin, L., et al.: Electronic structure of the oxygen evolving complex in photosystem II, as revealed by (55)Mn Davies ENDOR studies at 2.5 K. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. (PCCP) 16(17), 7799–812 (2014). Available at, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24643307
Dismukes, G.C., Siderer, Y.: Intermediates of a polynuclear manganese center involved in photosynthetic oxidation of water. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 78(1), 274–278 (1981)
Gatt, P., Petrie, S., Stranger, R., Pace, R.J.: Rationalizing the 1.9 Å crystal structure of photosystem II-A remarkable Jahn-Teller balancing act induced by a single proton transfer. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 51, 12025–12028 (2012)
Petrie, S., Stranger, R., Pace, R.: J. Rationalising the geometric variation between the a and b monomers in the 1.9 Å crystal structure of photosystem II. Chem. A Eur. J. 21, 6780–6792 (2015)
Terrett, R., Petrie, S., Pace, R.J., Stranger, R.: What does the Sr-substituted 2.1 Å resolution crystal structure of photosystem II reveal about the water oxidation mechanism. Chem. Commun. (Camb). 50, 8–11 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/c3cc49324e
Terrett, R., Petrie, S., Stranger, R., Pace, R.J.: What computational chemistry and magnetic resonance reveal concerning the oxygen evolving centre in Photosystem II. J. Inorg. Biochem. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2016.04.009 (2016)
Ahrling, K., Pace, R., Evans, M.: The Catalytic Manganese Cluster:Implications from Spectroscopy. In: Wydrzynski, T.J., Satoh, K. (eds.) Photosystem II The Light Driven Water:Plastoquinone Oxidoreductase, pp 285–305. Springer, The Netherlands (2005)
Blondin, G., et al.: Electron paramagnetic resonance study of the S = 1/2 ground state of a radiolysis-generated manganese(III)-trimanganese(IV) form of [Mn-IV;O-4(6)(bipy)(6)](4 +) (bipy = 2,2’-bipyridine). Comparison with the photosynthetic Oxygen Evolving Complex, vol. 28 (1997)
Bricker, T.M., Pakrasi, H.B., Sherman, L.A.: Characterization of a spinach photosystem II core preparation isolated by a simplified method. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 237(1), 170–176 (1985)
Smith, P.J., Ahrling, K.A., Pace, R.J.: Nature of the S2 state electron paramagnetic resonance signals from the oxygen-evolving complex of photosystem II: Q-band and oriented X-band studies. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 89, 2863–2868 (1993)
Smith, P.J., Masters, V.M., Peterson, S., Wydrzynski, T., Styring, S., Pace, R.J., Krausz, E.: Magneto-optical measurements of the pigments in fully active photosystem II core complexes from plants. Biochemistry 41, 1981–1989 (2002)
Stoll, S., Schweiger, A.: EasySpin, a comprehensive software package for spectral simulation and analysis in EPR. J. Magn. Reson. 178(1), 42–55 (2006)
Teutloff, C., et al.: High-field EPR investigations of MnIIIMnIV and MnIIMnIII states of dimanganese catalase and related model systems. Magn. Reson. Chem., 43(PEC. ISS.) (2005)
Schäfer, K.O., et al.: Multifrequency EPR investigation of dimanganese catalase and related Mn(III)Mn(IV) complexes. J. Phys. Chem. B 107(5), 1242–1250 (2003)
Kurashige, Y., Chan, G.K.-L., Yanai, T.: Entangled quantum electronic wavefunctions of the Mn4CaO5 cluster in photosystem II. Nat. Chem. 5(8), 660–6 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/nchem.1677
Porra, R.J., Thompson, W.A., Kriedemann, P.E.: 320.pdf. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 975, 384–394 (1989)
Satoh, K., Wyrdzynski, T.J., Govindjee: Introduction to photosystem II, in Photosystem II: The Light-Driven Water. Plastoquinone Oxidoreductase 22, 11–22 (2005)
Koulougliotis, D., Hirsh, D.J., Brudvig, G.W.: JACS 114, 8322–8323 (1992)
Pace, R.J., Stranger, R., Petrie, S.: Why nature chose Mn for the water oxidase in Photosystem II. Dalt. Trans. 41(24), 7179 (2012)
Umena, Y., Kawakami, K., Shen, J.-R., Kamiya, N.: Crystal structure of oxygen-evolving photosystem II at a resolution of 1.9 Å. Nature 473, 55–60 (2011)
Koua, F.H.M., Umena, Y., Kawakami, K., Shen, J.-R.: Structure of Sr-substituted photosystem II at 2.1 A resolution and its implications in the mechanism of water oxidation. Proc. Natl. Acad Sci 110, 3889–3894 (2013)
Suga, M., Akita, F., Hirata, K., Ueno, G., Murakami, H., Nakajima, Y., Shimizu, T., Yamashita, K., Yamamoto, M., Ago, H., Shen, J.-R.: Nature (2014)
Jaszewski, A.R., Petrie, S., Pace, R.J., Stranger, R.: Toward the assignment of the manganese oxidation pattern in the water-oxidizing complex of photosystem II: A time-dependent DFT study of XANES energies. Chem. Eur. J. 17(20), 5699–5713 (2011)
Yachandra, V.K., Sauer, K., Klein, M.P.: Manganese cluster in photosynthesis: Where plants oxidize water to dioxygen. Chem. Rev. 96, 2927–2950 (1996)
a Pantazis, D., Ames, W., Cox, N., Lubitz, W., Neese, F.: Two interconvertible structures that explain the spectroscopic properties of the oxygen-evolving complex of photosystem II in the S2 state. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 51(39), 9935–40 (2012)
Campbell, K.A., et al.: The 23 and 17 kDa extrinsic proteins of Photosystem II modulate the magnetic properties of the S1-state manganese cluster. Biochemistry 37, 5039–5045 (1998)
Kok, B., Forbush, B., McGloin, M.: Cooperation of charges in photosynthetic O2 evolution-1. A linear four step mechanism. Photochem. Photobiol. 11, 457 (1970)
Liang, W., Roelofs, T.A., Cinco, R.M., Rompel, A., Latimer, M.J., Yu, M.O., Sauer, K., Klein, M.P., Yachandra, Y.K.: Structural change of the Mn cluster during the S-2 – > S-3 state transition of the oxygen-evolving complex of photosystem II. Does it reflect the onset of water/substrate oxidation? Determination by Mn X-ray absorption spectroscopy. JACS 122, 3399–3412 (2000)
Robblee, J.H., Messinger, J., Cinco, R.M., et al.: The Mn Cluster in the S 0 State of the Oxygen-Evolving Complex of Photosystem II Studied by EXAFS Spectroscopy: Are There Three Di- μ-oxo-bridged Mn 2 Moieties in the Tetranuclear Mn Complex. J. American Chem. Soc. 124(25), 7459–7471 (2002)
Glöckner, C., Kern, J., Broser, M., Zouni, A., Yachandra, V., Yano, J.: Structural changes of the oxygen-evolving complex in photosystem II during the catalytic cycle. J. Biol. Chem. 288(31), 22607–22620 (2013)
Haumann, M., et al.: Structural and oxidation state changes of the photosystem II manganese complex in four transitions of the water oxidation cycle (S0 – > S1, S1 – > S2, S2 – > S3, and S3,4 – > S0) characterized by X-ray absorption spectroscopy at 20 K and room temperature. Biochemistry 44, 1894–1908 (2005)
Yano, J., Yachandra, V.: Mn4Ca cluster in photosynthesis: Where and how water is oxidized to dioxygen. Chem. Rev. 114, 4175–4205 (2014)
Seigbahn, P.E.M.: Mechanisms for proton release during water oxidation in the S2 to S3 and S3 to S4 transitions in photosystem II. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys 14, 4849–4856 (2012)
Saito, T., et al.: Possible mechanisms of water splitting reaction based on proton and electron release pathways revealed for CaMn4O5 cluster of PSII refined to 1.9? X-ray resolution. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 112(1), 253–276 (2012)
Yamanaka, S., et al.: Structure and reactivity of the mixed-valence CaMn4O 5(H2O)4 and CaMn4O 4(OH)(H2O)4 clusters at oxygen evolution complex of photosystem II. Hybrid DFT (UB3LYP and UBHandHLYP) calculations. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 112(1), 321–343 (2012)
Kusunoki, M.: S1-state Mn4Ca complex of Photosystem II exists in equilibrium between the two most-stable isomeric substates: XRD and EXAFS evidence. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 104, 100–110 (2011)
Krewald, V., et al.: Metal oxidation states in biological water splitting. Chem. Sci. 6(3), 1676–1695 (2015)
Yano, J., et al.: X-ray damage to the Mn4Ca complex in single crystals of photosystem II: A case study for metalloprotein crystallography. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci 102, 12047–12052 (2005)
Liang, W., et al.: Correlation between structure and magnetic spin state of the manganese cluster in the oxygen-evolving complex of photosystem II in the S2 state: Determination by X-ray absorption spectroscopy. Biochemistry 33, 4923–4932 (1994)
Peloquin, J.M., Campbell, K.A., Randall, D.W., Evanchik, M.A., Pecoraro, V.L., Amstrong, W.H., Britt, R.D.: 55Mn ENDOR of the S2-state multiline EPR signal of photosystem II: Implications on the structure of the tetranuclear Mn cluster. JACS 122, 10926 (2000)
Acknowledgments
The author gratefully acknowledge financial support from the Australian Research Council. Bernard Baituti also acknowledges the generous scholarships provided by the Botswana International University of Science and Technology (BIUST) and ANU.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Dr Bernard Baituti-prepared the PSII samples and performed EPR measurements, performed the simulations, prepared the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Proceedings of the 3rd Mediterranean Conference on the Applications of the Mössbauer Effect (MECAME 2017), Jerusalem, Israel, 5-7 June 2017
Edited by Mira Ristic, Stjepko Krehula, Israel Nowik and Israel Felner
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baituti, B. What the multiline signal (MLS) simulation data with average of weighted computations reveal about the Mn hyperfine interactions and oxidation states of the manganese cluster in OEC?. Hyperfine Interact 238, 68 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10751-017-1440-8
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10751-017-1440-8