Abstract
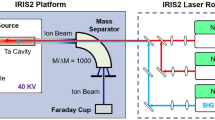
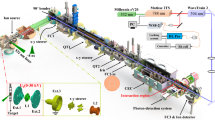
On account of its high efficiency, speed and unmatched selectivity, the Resonance Ionization Laser Ion Source (RILIS) is the preferred method for ionizing the nuclear reaction products at the ISOLDE on-line isotope separator facility. By exploiting the unique electronic energy level ‘fingerprint’ of a chosen element, the RILIS process of laser step-wise resonance ionization enables an ion beam of high chemical purity to be sent through the mass selective separator magnet. The isobaric purity of a beam of a chosen isotope is therefore greatly increased. The RILIS, comprising of up to three frequency tunable pulsed dye lasers has been upgraded with the installation of a Nd:YAG pump laser as a replacement for the old Copper Vapor Laser (CVL) system. A summary of the current Nd:YAG pumped RILIS performance is given. To accompany the RILIS pump laser upgrade, a new ionization scheme for manganese has been developed at the newly constructed LAser Resonance Ionization Spectroscopy (LARIS) laboratory and successfully applied for on-line RILIS operation. An overview of the LARIS facility is given along with details of the ionization scheme development work for manganese.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mishin, V., Fedoseyev, V., Kluge, H.-J., Letokhov, V., Ravn, H., Scheerer, V., Shirakabe, Y., Sundell, S, Tengblad, O.: Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., B 73, 550 (1993)
Fedoseyev, V., Huber, G., Köster, U., Lettry, J., Mishin, V., Ravn, H., Sebastian, V.: Hyperfine Interact. 127, 409 (2000)
Lindroos, M., Butler, P., Huyse, M., Riisager, K.: Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., B 266(19–20), 4687 (2008)
Fedosseev, V., Berg, L., Lebas, N., Launila, O., Lindroos, M., Losito, R., Marsh, B., Osterdahl, F., Pauchard, T., Transtromer, G.: Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., B 266(19–20), 4378 (2008)
Du, K., Wu, N., Xu, J., Giesekus, J., Loosen, P., Poprawe, R.: Opt. Lett. 23(5), 370 (1998)
Marsh, B.A., Fedosseev, V.N., Kosuri, P.: Hyperfine Interact. 171, 109 (2007)
Smalley, R.E.: Laser Chem. 2(3–4), 167 (1983)
Doverstal, M., Lindgren, B., Sassenberg, U., Yu, H.: Phys. Scr. 43, 572 (1991)
Gangrsky, Yu. P., Zemlyanoi, S.G., Izosimov, I.N., Markov, B.N., Tam, T.K.: Instrum. Exp. Tech. 33, 168 (1990)
Batzner, K., Fedoseyev, V.N., Catherall, R., Evensen, A.H.M., Forkel-Wirth, D., Jonsson, O.C., Kugler, E., Lettry, J., Mishin, V.I., Ravn, H.L., Weyer, G.: Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., B 126(1–4), 88 (1997)
Kurucz, R.: Transactions of the International Astronomical Union, vol. XXB, pp. 168–172 (edited by M. McNally). Kluwer, Dordrecht (1988)
Ralchenko, Y., Kramida, A.E., Reader, J., and NIST ASD Team: NIST Atomic Spectra Database 3.1.5 (2008)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
F. K. Österdahl, deceased.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marsh, B.A., Berg, LE., Fedorov, D.V. et al. The ISOLDE RILIS pump laser upgrade and the LARIS Laboratory. Hyperfine Interact 196, 129–141 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10751-010-0168-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10751-010-0168-5