Abstract
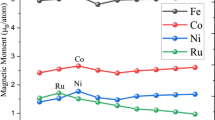
3d-metal antimonides: Fe1+x Sb, N+x Sb, Co+x Sb and the (Ni1−y Fe y )Sb solid solution have been studied by the Mössbauer effect method at 57Fe and 119Sn. It was found that the quadrupole interactions at the Fe and Sn nucleus in 3d-metal antimonides are very sensitive to the filling of different crystallographic sites with metal atoms. The metal atoms in trigonal-bipyramidal sites have a strong effect on the quadrupole splitting of 119Sn. They are nearest to anions (Sb or Sn) with the typical axial ratio of c/a = 1.25. The QS(x) dependence of 119 Sn in 3d-metal antimonides in the 0 ≤ x ≤ 0.1 concentration range can be used to determine x – the concentration of transition metal excess relative to the stoichiometric composition.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sirota, N.N.: Physical–Chemical Nature of the Variable Composition Phases, p. 68. Nauka i technika, Minsk (1970)
Teramoto, I., van Run, A.M.J.G.: J. Phys. Chem. Solids 29, 347 (1968)
Vasilev, E.A., Tkachenka T.M.: Cryst. Res. Technol. 32, 931 (1997)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tkachenka, T.M., Virchenko, V.A. Quadrupole interactions at 57Fe and 119Sn in 3d-metal antimonides. Hyperfine Interact 168, 1047–1050 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10751-006-9392-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10751-006-9392-4