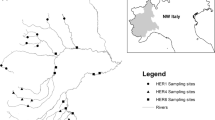
Abstract
Understanding aquatic insect diversity is fundamental for river monitoring, conservation, and restoration. In contrast to the existence of general patterns for aquatic insects at large scales, weak or non-significant patterns are common at small scales. Numerical resolution and statistical approaches are considered key technical factors influencing the revealed patterns. In the present study, we examined the taxonomic composition and diversity of aquatic insects in a disturbed (sub)tropical river during wet and dry seasons and demonstrated seasonal patterns using linear and nonlinear approaches with both occurrence and abundance data. Collector-gatherers were more abundant and scrapers were less abundant in the wet season than in the dry season. Alpha diversity did not change significantly between the seasons but was affected seasonally by different environmental variables. However, beta diversity measured by both Sorensen and Bray–Curtis dissimilarity varied seasonally. Beta diversity was predicted to vary nonlinearly by environmental distance, more strongly in the wet season, and Bray–Curtis dissimilarity was predicted better than Sorensen dissimilarity index. Our study supports the role of environmental selection in structuring the community composition and diversity of aquatic insects in (sub)tropical rivers and emphasises that quantitative data and nonlinear approaches are more sensitive to community analyses at small scales.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this article.
References
Akaike, H., 1973. Information Theory and an Extension of the Maximum Likelihood Principle. In Petrov, B. N. & F. Csaki (eds), Proceedings of the 2nd International Symposium on Information Theory. Akadémiai Kiadó Press, Budapest, Hungary.
Anderson, M. J., T. O. Crist, J. M. Chase, M. Vellend, B. D. Inouye, A. L. Freestone, N. J. Sanders, H. V. Cornell, L. S. Comita, K. F. Davies, S. P. Harrison, N. J. B. Kraft, J. C. Stegen & N. G. Swenson, 2011. Navigating the multiple meanings of β diversity: a roadmap for the practicing ecologist. Ecology Letters 14: 19–28. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2010.01552.x.
Armitage, P. D., D. Moss, J. F. Wright & M. T. Furse, 1983. The performance of a new biological water quality score system based on macroinvertebrates over a wide range of unpolluted running-water sites. Water Research 17: 333–347. https://doi.org/10.1016/0043-1354(83)90188-4.
Bailey, R. C., R. H. Norris & T. B. Reynoldson, 2001. Taxonomic resolution of benthic macroinvertebrate communities in bioassessments. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 20: 280–286. https://doi.org/10.2307/1468322.
Barbour, M. T., J. Gerritsen, B. D. Snyder & J. B. Stribling, 1999. Rapid Bioassessment for Use in Streams and Wadeable Rivers: Periphyton, Benthic Macroinvertebrates and Fish, 2nd ed. US Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Water, Washington, D.C:
Baselga, A., D. Orme, S. Villeger, J. De Bortoli, F. Leprieur, M. Logez, R. Henriques-Silva, S. Mart, R. Mart, C. Gmez-Rodrguez & R. Crujeiras, 2022. Betapart: Partitioning Beta Diversity into Turnover and Nestedness Components. Package ‘betapart’. R package version 1.5.6. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=betapart.
Beisel, J. N., P. Usseglio-polatera, S. Thomas & J. S. Moreteau, 1998. Stream community structure in relation to spatial variation: the influence of microhabitat characteristics. Hydrobiologia 389: 73–88. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003519429979.
Bini, L. M., V. L. Landeiro, A. A. Padial, T. Siqueira & J. Heino, 2014. Nutrient enrichment is related to two facets of beta diversity from stream invertebrates across the United States. Ecology 95: 1569–1578. https://doi.org/10.1890/13-0656.1.
Bonada, N., N. Prat, V. H. Resh & B. Statzner, 2006. Developments in aquatic insect biomonitoring: a comparative analysis of recent approaches. Annual Review of Entomology 51: 495–523. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ento.51.110104.151124.
Bowman, M. F. & R. C. Bailey, 1997. Does taxonomic resolution affect the multivariate description of the structure of freshwater benthic macroinvertebrate communities. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 54: 1802–1807. https://doi.org/10.1139/f97-085.
Brown, B. L. & C. M. Swan, 2010. Dendritic network structure constrains metacommunity properties in riverine ecosystems. Journal of Animal Ecology 79: 571–580. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2656.2010.01668.x.
Carvalho, P. C. & G. K. Davoren, 2020. Niche dynamics of sympatric non-breeding shearwaters under varying prey availability. Ibis 162: 701–712. https://doi.org/10.1111/ibi.12783.
Chambers, J. M. & M. J. M. Chambers, 2014. Functions and Examples for ‘Software for Data Analysis’. Package ‘SoDA’. R package version 1.0-6. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=SoDA.
Covich, A. P., M. A. Palmer & T. A. Crowl, 1999. The role of benthic invertebrate species in freshwater ecosystems. BioScience 49: 119–127. https://doi.org/10.2307/1313537.
Cummins, K. W., 1962. An evaluation of some techniques for the collection and analysis of benthic samples with special emphasis on lotic waters. American Midland Naturalist 67: 477–504. https://doi.org/10.2307/2422722.
Cummins, K. W., 1974. Structure and function of stream ecosystems. BioScience 24: 631–641. https://doi.org/10.2307/1296676.
Debastiani, V. J., 2020. Package ‘SYNCSA’. Analysis of Functional and Phylogenetic Patterns in Metacommunities. R package version 1.3.4. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=SYNCSA.
Dobson, M., A. Magana, J. M. Mathooko & F. K. Ndegwa, 2002. Detritivores in Kenyan highland streams: more evidence for the paucity of shredders in the tropics? Freshwater Biology 47: 909–919. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2427.2002.00818.x.
Dong, R., Y. Wang, C. Lu, G. Lei & L. Wen, 2021. The seasonality of macroinvertebrate β diversity along the gradient of hydrological connectivity in a dynamic river-floodplain system. Ecological Indicators 121: 107112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.107112.
Duan, X. H., Z. Y. Wang & M. Z. Xu, 2010. Benthic macroinvertebrate and application in the assessment of stream ecology, TsingHua University Press, Beijing, China:
Dudgeon, D., 2006. The impacts of human disturbance on stream benthic invertebrates and their drift in North Sulawesi, Indonesia. Freshwater Biology 51: 1710–1729. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2427.2006.01596.x.
EPBC, 2002. Standard Methods for the Monitoring and Analysis on Water and Wastewater, 4th ed. Chinese Environmental Science Press, Beijing, China:
Ferrier, S., G. Manion, J. Elith & K. Richardson, 2007. Using generalized dissimilarity modelling to analyse and predict patterns of beta diversity in regional biodiversity assessment. Diversity and Distributions 13: 252–264. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1472-4642.2007.00341.x.
Fitzpatrick, M. C., K. Mokany, G. Manion, D. Nieto-Lugilde & S. Ferrier, 2022. gdm: generalized dissimilarity modeling. R package version 1.5.0-1. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=gdm.
Fu, L., Y. Jiang, J. Ding, Q. Liu, Q.-Z. Peng & M.-Y. Kang, 2016. Impacts of land use and environmental factors on macroinvertebrate functional feeding groups in the Dongjiang River basin, southeast China. Journal of Freshwater Ecology 31: 21–35. https://doi.org/10.1080/02705060.2015.1017847.
Fugère, V., A. Kasangaki & L. J. Chapman, 2016. Land use changes in an afrotropical biodiversity hotspot affect stream alpha and beta diversity. Ecosphere 7: e0135. https://doi.org/10.1002/ecs2.1355.
Hawkins, C. P., H. Mykrä, J. Oksanen & J. J. Vander Laan, 2015. Environmental disturbance can increase beta diversity of stream macroinvertebrate assemblages. Global Ecology and Biogeography 24: 483–494. https://doi.org/10.1111/geb.12254.
Heino, J., 2008. Influence of taxonomic resolution and data transformation on biotic matrix concordance and assemblage-environment relationships in stream macroinvertebrates. Boreal Environment Research 13: 359–369. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008WR006866.
Heino, J., 2011. A marcoecological perspective of diversity patterns in the freshwater realm. Freshwater Biology 201: 1703–1722. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2427.2011.02610.x.
Heino, J., 2014. Taxonomic surrogacy, numerical resolution and responses of stream macroinvertebrate communities to ecological gradients: are the inferences transferable among regions? Ecological Indicators 36: 186–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2013.07.022.
Heino, J. & J. Soininen, 2007. Are higher taxa adequate surrogates for species-level assemblage patterns and species richness in stream organisms? Biological Conservation 137: 78–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocon.2007.01.017.
Heino, J. & H. Mykrä, 2008. Control of stream insect assemblages: roles of spatial configuration and local environmental factors. Ecological Entomology 33: 614–622. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2311.2008.01012.x.
Heino, J. & B. L. Peckarsky, 2014. Integrating behavioral, population and large-scale approaches for understanding stream insect communities. Current Opinion in Insect Science 2: 7–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cois.2014.06.002.
Heino, J., T. Muotka & R. Paavola, 2003. Determinants of macroinvertebrate diversity in headwater streams: regional and local influences. Journal of Animal Ecology 72: 425–434. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2656.2003.00711.x.
Heino, J., A. S. Melo & L. M. Bini, 2015a. Reconceptualising the beta diversity-environmental heterogeneity relationship in running water systems. Freshwater Biology 60: 223–235. https://doi.org/10.1111/fwb.12502.
Heino, J., A. S. Melo, L. M. Bini, F. Altermatt, S. A. Al-Shami, D. G. Angeler, N. Bonada, C. Brand, M. Callisto, K. Cottenie, O. Dangles, D. Dudgeon, A. Encalada, E. Göthe, M. Grönroos, N. Hamada, D. Jacobsen, V. L. Landeiro, R. Ligeiro, R. T. Martins, M. L. Miserendino, C. S. Md Rawi, M. E. Rodrigues, F. O. Roque, L. Sandin, D. Schmera, L. F. Sgarbi, J. P. Simaika, T. Siqueira, R. M. Thompson & C. R. Townsend, 2015b. A comparative analysis reveals weak relationships between ecological factors and beta diversity of stream insect metacommunities at two spatial levels. Evolution and Ecology 5: 1235–1248. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.1439.
Heino, J., A. S. Melo, J. Jyrkänkallio-Mikkola, K. D. Petsch, S. V. Saito, K. T. Tolonen, L. M. Bini, V. L. Landeiro, T. S. F. Silva, V. Pajunen, J. Soininen & T. Siqueira, 2018. Subtropical streams harbour higher genus richness and lower abun-dance of insects compared to boreal streams, but scale matters. Journal of Biogeography 45: 1983–1993. https://doi.org/10.1111/jbi.13400.
Hilsenhoff, W. L., 1987. An improved biotic index of organic stream pollution. The Great Lakes Entomologist 20: 31–39.
Irons, J. G., M. W. Oswood, R. J. Stout & C. M. Pringle, 1994. Latitudinal patterns in leaf litter breakdown: is temperature really important? Freshwater Biology 32: 401–411. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2427.1994.tb01135.x.
Jiang, X., Z. Song, J. Xiong, H. Proctor & Z. Xie, 2017. Different surrogacy approaches for stream macroinvertebrates in discriminating human disturbances in Central China. Ecological Indicators 75: 182–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2016.12.039.
Johanssona, F., L. M. Bini, C. R. Svanbäck, J. Westera & J. Heino, 2019. Environmental variables drive differences in the beta diversity of dragonfly assemblages among urban stormwater ponds. Ecological Indicators 106: 10552. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.105529.
Jones, F. C., 2008. Taxonomic sufficiency: the influence of taxonomic resolution on freshwater bioassessments using benthic macroinvertebrates. Environmental Reviews 16: 45–69. https://doi.org/10.1139/A07-010.
Junk, W. J., P. B. Bayley & R. E. Sparks, 1989. The flood pulse concept in river-floodplain systems. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 106: 110–121.
Krynak, E. M., Z. Lindo & A. G. Yates, 2019. Patterns and drivers of stream benthic macroinvertebrate beta diversity in an agricultural landscape. Hydrobiologia 837: 61–75. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-019-3961-4.
Lenat, D. R. & V. H. Resh, 2001. Taxonomy and stream ecology: the benefits of genus- and species-level identifications. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 20: 287–298. https://doi.org/10.2307/1468323.
Levins, R., 1968. Evolution in changing environments, Princeton University Press, Princeton, New Jersey:
Li, A. O. & D. Dudgeon, 2009. Shredders: species richness, abundance, and role in litter breakdown in tropical Hong Kong streams. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 28: 167–180. https://doi.org/10.1899/08-043.1.
Li, F., F. Altermatt, J. Yang, S. An, A. Li & X. Zhang, 2019. Human activities’ fingerprint on multitrophic biodiversity and ecosystem functions across a major river catchment in China. Global Change Biology 26: 6867–6879. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.15357.
Li, Z., J. Heino, Z. Liu, X. Meng, X. Chen, Y. Ge & Z. Xie, 2021. The drivers of multiple dimensions of stream macroinvertebrate beta diversity across a large montane landscape. Limnology and Oceanography 66: 226–236. https://doi.org/10.1002/lno.11599.
Marshall, J. C., A. L. Steward & B. D. Harch, 2006. Taxonomic resolution and quantification of freshwater macroinvertebrate samples from an Australian dryland river: the benefits and costs using species abundance data. Hydrobiologia 572: 171–194. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-005-9007-0.
Melo, A. S., 2005. Effects of taxonomic and numeric resolution on the ability to detect ecological patterns at a local scale using stream macroinvertebrates. Archiv Fur Hydrobiologie 164: 309–323. https://doi.org/10.1127/0003-9136/2005/0164-0309.
Melo, A. S. & C. G. Froehlich, 2022. An attractor domain model of seasonal and inter-annual β diversity of stream macroinvertebrate communities. Freshwater Biology 67: 1370–1379. https://doi.org/10.1111/fwb.13923.
Melo, A. S., F. Schneck, L. U. Hepp, N. R. Simões, T. Siqueira & L. M. Bini, 2011. Focusing on variation: methods and applications of the concept of beta diversity in aquatic ecosystems. Acta Limnologica Brasiliensia 23: 318–331. https://doi.org/10.1590/S2179-975X2012005000010.
McCreadie, J. W., N. Hamada, M. E. Grillet & P. H. Adler, 2021. A stream by any other name: does β-diversity differ between Nearctic and Neotropical streams? Hydrobiologia 848: 811–823. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-020-04484-8.
Mokany, K., C. Ware, S. N. C. Woolley, S. Ferrier & M. C. Fitzpatrick, 2022. A working guide to harnessing generalized dissimilarity modelling for biodiversity analysis and conservation assessment. Global Ecollogy and Biogeography 31: 802–821. https://doi.org/10.1111/geb.13459.
Morse, J. C., L. Yang & L. Tian, 1994. Aquatic Insects of China Useful for Monitoring Water Quality, Hohai University Press, Nanjing, China:
Mykrä, H., J. Heino & Y. Muotka, 2007. Scale-related pattern in the spatial and environmental components of stream macroinvertebrate assemblage variation. Global Ecology and Biogeography 16: 149–159. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1466-8238.2006.00272.x.
Oksanen, J., F. G. Blanchet, M. Friendly, R. Kindt, P. Legendre, D. McGlinn, P. R. Minchin, R. B. O’Hara, G. L. Simpson, P. Solymos, M. H. H. Stevens, E. Szoecs & H. Wagner, 2019. vegan: Community Ecology Package. R package version 2.5-6. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan.
Paller, M. H., S. A. Blas & R. W. Kelley, 2020. Macroinvertebrate taxonomic richness in minimally disturbed streams on the southeastern USA coastal plain. Diversity 12: 459. https://doi.org/10.3390/d12120459.
Pandit, S., J. Kolasa & K. Cottenie, 2009. Contrasts between habitat generalists and specialists: an empirical extension to the basic metacommunity framework. Ecology 90: 2253–2262. https://doi.org/10.1890/08-0851.1.
Pearson, R. G., F. Christidis, N. M. Connolly, J. A. Nolen, R. M. St Clair, A. Cairns & L. Davis, 2017. Stream macroinvertebrate assemblage uniformity and drivers in a tropical bioregion. Freshwater Biology 62: 544–558. https://doi.org/10.1111/fwb.12884.
Pires, M. M., M. G. Grech, C. Stenert, L. Maltchik, L. B. Epele, K. I. McLean, J. Kneitel, D. A. Bell, H. S. Greig, C. R. Gagne & D. P. Batzer, 2021. Does taxonomic and numerical resolution affect the assessment of invertebrate community structure in New World freshwater wetlands? Ecological Indicators 125: 107437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.107437.
Poff, N. L., 1997. Landscape filters and species traits: towards mechanistic understanding and prediction in stream ecology. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 16: 391–409. https://doi.org/10.2307/1468026.
Poff, N. L., J. D. Olden, N. K. Vieira, D. S. Finn, M. P. Simmons & B. C. Kondratieff, 2006. Functional trait niches of North American lotic insects: traits-based ecological applications in light of phylogenetic relationships. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 25: 730–755. https://doi.org/10.1899/0887-3593(2006)025[0730:FTNONA]2.0.CO;2.
Resh, V. H., A. V. Brown, A. P. Covich, M. E. Gurtz, H. W. Li, G. W. Minshall, S. R. Reice, A. L. Sheldon, J. B. Wallace & R. C. Wissmar, 1988. The role of disturbance in stream ecology. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 7: 433–455. https://doi.org/10.2307/1467300.
Santos, J. I., T. Vidal, F. J. Gonçalves, B. B. Castro & J. L. Pereira, 2021. Challenges to water quality assessment in Europe–Is there scope for improvement of the current water framework directive bioassessment scheme in rivers? Ecological Indicators 121: 107030. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.107030.
Schmera, D., J. Heino, J. Podani, T. Eros & S. Dolédec, 2017. Functional diversity: a review of methodology and current knowledge in freshwater macroinvertebrate research. Hydrobiologia 787: 27–44. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-016-2974-5.
Sexton, J. P., J. Montiel, J. E. Shay, M. R. Stephens & R. A. Slatyer, 2017. Evolution of ecological niche breadth. Annual Review of Ecology Evolution and Systematics 48: 183–206. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-ecolsys-110316-023003.
Socolar, J. B., J. J. Gilroy, W. E. Kunin & D. P. Edwards, 2016. How should beta-diversity inform biodiversity conservation? Trends in Ecology & Evolution 31: 67–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2015.11.005.
Sundar, S., J. Heino, F. O. Roque, P. J. Simaika, A. S. Melo, J. D. Tonkin, D. G. Nogueira & D. P. Silva, 2020. Conservation of freshwater macroinvertebrate biodiversity in tropical regions. Aquatic Conservation 30: 1238–1250. https://doi.org/10.1002/aqc.3326.
Siepielski, A. M. & M. A. Mcpeek, 2013. Niche versus neutrality in structuring the beta diversity of damselfly assemblages. Freshwater Biology 58: 758–768. https://doi.org/10.1111/fwb.12082.
Thorp, J. P. & M. P. Covich, 2001. Ecology and Classification of North American Freshwater Invertebrates, 2nd ed. Academic Press, San Diego, California:
Townsend, C. R. & A. G. Hildrew, 1994. Species traits in relation to a habitat templet for river systems. Freshwater Biology 31: 265–275. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2427.1994.tb01740.x.
Vannote, R. L., G. W. Minshall, K. W. Cummins, J. R. Sedell & C. E. Cushing, 1980. The river continuum concept. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 37: 130–137. https://doi.org/10.1080/00288330.1982.9515966.
Verdonschot, P. F. M., 2006. Data composition and taxonomic resolution in macroinvertebrate stream typology. Hydrobiologia 566: 59–74. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-006-0070-y.
Wang, L., X. Lv, J. Li, L. Tan, E. Z. Rizo & B.-P. Han, 2022. Species diversity and community composition of macroinvertebrates in headwater streams of two subtropical neighboring lowland basins. Diversity 14: 402. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14050402.
Wang, L., J. Li, L. Tan & B.-P. Han, 2023. Seasonal patterns of functional alpha and beta redundancies of macroinvertebrates in a disturbed (sub) tropical river. Ecological Indicators 146: 109777. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.109777.
Whittaker, R. H., 1960. Vegetation of the Siskiyou mountains, Oregon and California. Ecological Monography 30: 279–338. https://doi.org/10.2307/1943563.
Wiggins, G. B., 1996. Larvae of the North American Caddisfly Genera (Trichoptera), 2nd ed. University of Toronto Press, Toronto, Canada:
Willig, M. R., D. M. Kaufman & R. D. Stevens, 2003. Latitudinal gradients of biodiversity: pattern, process, scale, and synthesis. Annual Review of Ecology Evolution and Systematics 34: 273–309. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.34.012103.144032.
Wolda, W., 1988. Insect seasonality: why? Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics 19: 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.es.19.110188.000245.
Xu, Y., Z. Xiang, E. Z. Rizo, L. Naselli-Flores & B. P. Han, 2022. Combination of linear and nonlinear multivariate approaches effectively uncover responses of phytoplankton communities to environmental changes at regional scale. Journal of Environmental Management 305: 114399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.114399.
Yule, C. M., 1996. Trophic relationships and food webs of the benthic invertebrate fauna of two seasonal tropical streams on Bougainville Island, Papua New Guinea. Journal of Tropical Ecology 12: 517–534. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0266467400009755.
Yule, C. M., M. Y. Leong, L. Ratnarajah, K. Schmidt, H. M. Wong, R. G. Pearson & L. Boyero, 2009. Shredders in Malaysia: abundance and richness are greater in cool highland tropical streams. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 28: 404–415. https://doi.org/10.1899/07-161.1.
Zhang, J., 2013. spaa: SPecies Association Analysis. R package version 0.2.2. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=spaa.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants from The NSF of China (32171538).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LW and BH: conceptualization, LW, YL, JL, and LT: methodology, data collection, LW and BPH: writing—original draft preparation, EZR, YK and BPH: writing—review and editing, and BH: funding acquisition. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest relevant to the content of this article to declare.
Additional information
Handling editor: Marcelo S. Moretti
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Li, Y., Li, J. et al. The seasonal patterns of aquatic insect composition and diversity in a disturbed (sub)tropical river revealed by linear and nonlinear approaches with occurrence and abundance data. Hydrobiologia 850, 3949–3963 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-023-05278-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-023-05278-4