Abstract
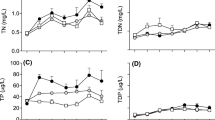
Shallow lakes are dominated by small omnivorous fish, but the roles of these small fish in aquatic ecosystems are not well-known. A small omnivorous bitterling (Acheilognathus macropterus) has been found to be dominant after lake restoration in shallow lakes. We conducted a mesocosm experiment to examine the effects of bitterling on water quality and plankton communities. Bitterling significantly increased the concentrations of nutrients, chlorophyll a (Chla) and suspended solids (TSS), and decreased the light intensity. The abundance and biomass of phytoplankton in the fish-present treatment were significantly higher than the controls, with Microcystis spp. and Dolichospermum spp. dominating the phytoplankton community. However, bitterling did not significantly affect the abundance and biomass of zooplankton, although the presence of bitterling shifted the community structure to dominance by small-sized species. Density-dependent effects of bitterling were observed on the concentrations of nutrient, TSS, organic suspended solids and Chla and on light intensity, but were not found for plankton and ratio of zooplankton to phytoplankton biomass. Our study indicates that A. macropterus can negatively affect water quality and facilitate the dominance of cyanobacteria. Therefore, monitoring and control of these small omnivorous species should be emphasized when restoring or managing shallow lakes.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Attayde, J. L. & L.-A. Hansson, 2001. The relative importance of fish predation and excretion effects on planktonic communities. Limnology and Oceanography 46: 1001–1012.
Azim, M. E., M. C. J. Verdegem, M. Singh, A. A. V. Dam & M. C. M. Beveridge, 2003. The effects of periphyton substrate and fish stocking density on water quality, phytoplankton, periphyton and fish growth. Aquaculture Research 34: 685–695.
Breukelaar, A. W., E. H. R. R. Lammens, J. G. P. K. Breteler & I. Tátrai, 1994. Effects of benthivorous bream (Abramis brama) and carp (Cyprinus carpio) on sediment resuspension and concentrations of nutrients and chlorophyll a. Freshwater Biology 32: 113–121.
Brooks, J. L. & S. I. Dodson, 1965. Predation, body size, and composition of plankton. Science 150: 28–35.
Cai, X., S. Ye, W. Li, H. Fan, Z. Li, T. Zhang & J. Liu, 2019. Spatio-temporal variability of small fishes related with environmental factors in a typical domestic tap water lake, Eastern China. Journal of Oceanology and Limnology 37: 278–289.
Carpenter, S. R. & D. M. Lodge, 1986. Effects of submersed macrophytes on ecosystem processes. Aquatic Botany 26: 341–370.
Chen, J., H. Su, G. Zhou, Y. Dai, J. Hu, Y. Zhao, Z. Liu, T. Cao, L. Ni, M. Zhang & P. Xie, 2020. Effects of benthivorous fish disturbance and snail herbivory on water quality and two submersed macrophytes. Science of the Total Environment 713: 136734.
Chiang, S. C. & N. S. Du, 1979. Fauna Sinica, Crustacea. Science Press, Beijing, Freshwater Cladocera.
DeMott, W. R., R. D. Gulati & E. Van Donk, 2001. Daphnia food limitation in three hypereutrophic Dutch lakes: evidence for exclusion of large-bodied species by interfering filaments of cyanobacteria. Limnology and oceanography 46: 2054–2060.
Dumont, H. J., I. Van de Velde & S. Dumont, 1975. The dry weight estimate of biomass in a selection of Cladocera, Copepoda and Rotifera from the plankton, periphyton and benthos of continental waters. Oecologia 19: 75–97.
González-Bergonzoni, I., M. Meerhoff, T. A. Davidson, F. Teixeira-de Mello, A. Baattrup-Pedersen & E. Jeppesen, 2012. Meta-analysis shows a consistent and strong latitudinal pattern in fish omnivory across ecosystems. Ecosystems 15: 492–503.
Gu, J., H. Jin, H. He, X. Ning, J. Yu, B. Tan, E. Jeppesen & K. Li, 2016. Effects of small-sized crucian carp (Carassius carassius) on the growth of submerged macrophytes: implications for shallow lake restoration. Ecological engineering 95: 567–573.
Gu, J., H. He, H. Jin, J. Yu, E. Jeppesen, R. W. Nairn & K. Li, 2018. Synergistic negative effects of small-sized benthivorous fish and nitrogen loading on the growth of submerged macrophytes–relevance for shallow lake restoration. Science of the Total Environment 610: 1572–1580.
Guiry, M. D. & G. M. Guiry, 2020. AlgaeBase. World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway. 2017. http://www.algaebase.org
Han, Y., J. Gu, Q. Li, Y. Zhang, H. He, R. Shen & K. Li, 2019. Effects of juvenile crucian carp (Carassius carassius) removal on submerged macrophyte growth—implications for subtropical shallow lake restoration. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07217-0.
He, H., E. Hu, J. Yu, X. Luo, K. Li, E. Jeppesen & Z. Liu, 2017. Does turbidity induced by Carassius carassius limit phytoplankton growth? A mesocosm study. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 24: 5012–5018.
He, H., H. Jin, E. Jeppesen, K. Li, Z. Liu & Y. Zhang, 2018. Fish-mediated plankton responses to increased temperature in subtropical aquatic mesocosm ecosystems: implications for lake management. Water Research 144: 304–311.
He, H., Y. Han, Q. Li, E. Jeppesen, K. Li, J. Yu & Z. Liu, 2019. Crucian carp (Carassius carassius) strongly affect C/N/P stoichiometry of suspended particulate matter in shallow warm water eutrophic lakes. Water 11: 524.
Holopainen, I. J., W. M. Tonn & C. A. Paszkowski, 1992. Effects of fish density on planktonic communities and water quality in a manipulated forest pond. Hydrobiologia 243(244): 311–321.
Hu, H., 2006. The Freshwater Algae of China: Systematics. Science Press, Beijing, Taxonomy and Ecology.
Huang, X. F., 1999. Survey Observation and Analysis of Lake Ecology. Standards Press of China, Beijing.
Jeppesen, E., T. L. Lauridsen, T. Kairesalo & M. R. Perrow, 1998. Impact of submerged macrophytes on fish-zooplankton interactions in lakes. In Jeppesen, E., M. Søndergaard, M. Søndergaard & K. Christoffersen (eds), The Structuring Role of Submerged Macrophytes in Lakes. Springer, New York: 91–114.
Jeppesen, E., J. P. Jensen, C. Jensen, B. Faafeng, D. O. Hessen, M. Søndergaard, T. Lauridsen, P. Brettum & K. Christoffersen, 2003. The impact of nutrient state and lake depth on top-down control in the pelagic zone of lakes: a study of 466 lakes from the temperate zone to the arctic. Ecosystems 6: 313–325.
Jeppesen, E., P. Nõges, T. A. Davidson, J. Haberman, T. Nõges, K. Blank, T. L. Lauridsen, M. Søndergaard, C. Sayer, R. Laugaste, L. S. Johansson, R. Bjerring & S. L. Amsinck, 2011. Zooplankton as indicators in lakes: a scientific-based plea for including zooplankton in the ecological quality assessment of lakes according to the European Water Framework Directive (WFD). Hydrobiologia 676: 279.
Jeppesen, E., M. Søndergaard, T. L. Lauridsen, T. A. Davidson, Z. Liu, N. Mazzeo, C. Trochine, K. Özkan, H. S. Jensen, D. Trolle, F. Starling, X. Lazzaro, L. S. Johansson, R. Bjerring, L. Liboriussen, S. E. Larsen, F. Landkildehus, S. Egemose & M. Meerhoff, 2012. Biomanipulation as a restoration tool to combat eutrophication: recent advances and future challenges. Advances in Ecological Research 47: 411–488.
Jin, X. & Q. Tu, 1990. The standard methods for observation and analysis in lake eutrophication. Environmental Science, Beijing.
Koutrakis, E. T., A. K. Kokkinakis, A. C. Tsikliras & E. A. Eleftheriadis, 2003. Characteristics of the European bitterling Rhodeus amarus (Cyprinidae) in the Rihios river, Greece. Journal of Freshwater Ecology 18: 615–624.
Liu, Z., J. Hu, P. Zhong, X. Zhang, J. Ning, S. E. Larsen, D. Chen, Y. Gao, H. He & E. Jeppesen, 2018. Successful restoration of a tropical shallow eutrophic lake: strong bottom-up but weak top-down effects recorded. Water Research 146: 88–97.
Qiu, X., X. Mei, V. Razlutskij, L. G. Rudstam, Z. Liu, C. Tong, & X. Zhang, 2019. Effects of common carp (Cyprinus carpio) on water quality in aquatic ecosystems dominated by submerged plants: a mesocosm study. Knowledge & Management of Aquatic Ecosystems 28.
Reynolds, R. S., 1984. The Ecology of Freshwater Phytoplankton. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Roozen, F. C. J. M., M. Lürling, H. Vlek, E. A. J. Van Der Pouw Kraan, B. W. Ibelings & M. Scheffer, 2007. Resuspension of algal cells by benthivorous fish boosts phytoplankton biomass and alters community structure in shallow lakes. Freshwater Biology 52: 977–987.
Schaus, M. H. & M. J. Vanni, 2000. Effects of gizzard shad on phytoplankton and nutrient dynamics: role of sediment feeding and fish size. Ecology 81: 1701–1719.
SEPA, 2002. Analytical methods for water and wastewater monitor. Chinese Environmental Science Press, Beijing.
Shen, J. R. & N. S. Du, 1979. Fauna Sinica, Crustacea. Science Press, Beijing, Freshwater Copepoda.
Shormann, D. E. & J. B. Cotner, 1997. The effects of benthivorous smallmouth buffalo (Ictiobus bubalus) on water quality and nutrient cycling in a shallow floodplain lake. Lake and Reservoir Management 13: 270–278.
Usui, S., K. Kanou & M. Sano, 2018. Food habits of fishes in a freshwater reed belt in Lake Kitaura, eastern Japan, in summer. Fisheries Science 84: 469–476.
Vanni, M. J., A. M. Bowling, E. M. Dickman, R. S. Hale, K. A. Higgins, M. J. Horgan, L. B. Knoll, W. H. Renwick & R. A. Stein, 2006. Nutrient cycling by fish supports relatively more primary production as lake productivity increases. Ecology 87: 1696–1709.
Ye, S., Z. Li, S. Lek-Ang, G. Feng, S. Lek & W. Cao, 2006. Community structure of small fishes in a shallow macrophytic lake (Niushan Lake) along the middle reach of the Yangtze River, China. Aquatic Living Resources 19: 349–359.
Yu, J., Z. Liu, H. He, W. Zhen, B. Guan, F. Chen, K. Li, P. Zhong, F. Teixeira-de Mello & E. Jeppesen, 2016a. Submerged macrophytes facilitate dominance of omnivorous fish in a subtropical shallow lake: implications for lake restoration. Hydrobiologia 775: 97–107.
Yu, J., Z. Liu, K. Li, F. Chen, B. Guan, Y. Hu, P. Zhong, Y. Tang, X. Zhao, H. He, H. Zeng & E. Jeppesen, 2016b. Restoration of shallow lakes in subtropical and tropical China: response of nutrients and water clarity to biomanipulation by fish removal and submerged plant transplantation. Water 8: 438.
Yuan, D., Y. Yi, A. Yakupitiyage, K. Fitzimmons & J. S. Diana, 2010. Effects of addition of red tilapia (Oreochromis spp.) at different densities and sizes on production, water quality and nutrient recovery of intensive culture of white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) in cement tanks. Aquaculture 298: 226–238.
Zhang, Z. S. & X. F. Huang, 1991. Methods in Freshwater Plankton Study (Book in Chinese). Science Press, Beijing.
Zhang, X., Z. Liu, E. Jeppesen, W. D. Taylor & L. G. Rudstam, 2016. Effects of benthic-feeding common carp and filter-feeding silver carp on benthic-pelagic coupling: implications for shallow lake management. Ecological Engineering 88: 256–264.
Zhu, Y. & H. Liu, 2007. Genetic diversity and the biogeographical process of Acheilognathus macropterus revealed by sequence variations of mitochondrial cytochrome b gene. Frontiers of Biology in China 2: 450–455.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Xiaoxia Chen and Xiumei Zhang for their help in the field and laboratory assistance. The paper was improved by suggestions from 2 anonymous reviewers. This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41877415), National Key Research and Development Project (2017YFA0605201), and the NIGLAS 135 Project (NIGLAS2018GH01). JY was supported by the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) Scholarship for a one-year research visit at the Flathead Lake Biological Station, University of Montana, United States of America.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: Pauliina Louhi
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, J., Xia, M., Zhen, W. et al. Density-dependent effects of omnivorous bitterling (Acheilognathus macropterus) on nutrient and plankton communities: implications for lake management and restoration. Hydrobiologia 847, 3309–3319 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-020-04335-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-020-04335-6